File
advertisement

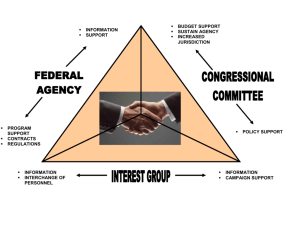
The Key to the Door of American Politcs Interest Groups Question • Does it matter if some sections of society are poorly represented? • What is a lobbyist? • How does a Lobbyist differ from a Interest Group? Definitions • Lobby – Groups who seek to influence public policy, generally employees of associations who try to influence the Executive and legislative functions. An example is the Ford Motor Company • Interest Group – Associations of People who come together on the basis of shared attitudes to try and influence public policy An Interest Group, wanting a limit on cheese in Cheeseburger www.theonion.com Research Task • Find out about the Legislative Reorganisation Act (1946) and how the number of groups has increased • Produce a Case Study on the National Rifle Association and the different reasons for membership The NRA Question • How do Interest Groups differ from political parties? Types of American Interest Group • Institutional or Protective Groups – i.e. American Medical Association • Self interested and seek to defend the position of their members. They possess substantial economic power • Membership or Promotional Groups – i.e. the American Civil Liberties Union • Primarily concerned with propaganda and are offering a benefit to society Institutional Groups • Seek to represent other organisations and groups • American Business Conference, National Association of Manufacturers • US Chamber of Commerce represents hundreds of groups across America • The American Federation of LaborCongress of Industrial Organisations (AFL-CIO) is the US equivalent of the TUC Membership Groups • Represent individual Americans rather than organisations and groups • Americans are more likely to join social, charitable, civic, political and religious groups than EU counterparts, but less likely to join T.U.’S • Single issue groups – Mothers Against Drink Driving (MADD), American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) • Common gender or race issues (National Organisation for Women (NOW) or the National Association of advancement for Colored People (NAACP) Types of Pressure Group Business Groups Agricultural Groups Ideological and Single Issue Groups Public Interest Groups Labour Groups Professional Groups Task • Using a Sheet of A3 • Take one of these types of Pressure Group • Produce • a) a Presentation to the class on your type of group, including an information sheet • b) Similar to last years task produce a poster advertising an example of a Pressure Group within your type Task • What are the functions of an Interest Group? • What is their raison d’etre? Functions of an Interest Group Representative Programme Monitoring Participation Education Agenda building Task • What are the methods a Pressure Group may use? Methods used by Pressure Group Electioneering Litigation in the courts Ideological and Single Issue Groups Lobbying Publicity Organising grassroots activities Political Action Committee • A PAC is an organisation whose purpose is to raise funds on behalf of candidates • Incumbent house members receive the most money ($176m in 2002 midterm, compared to $29m for challengers) • National Assoc. of Realtors gave $3.8m, American Federation of Teachers $4m Research task • How effective are PAC’s? • Is lobbying a more effective method? Lobbyists • Lobbyists are integral to the US system • Provide accurate, detailed information to those who need it • PG information helps Legislators take a stance on a range of bewildering issues • PGs often have offices in Washington DC to make access easier – ‘The K Street Corridor’ How effective are Lobbyists • Some PGs publish a list of how often an individual has voted for their policy • Being ranked as ‘Very Liberal’ or ‘Very Conservative’ could also have the opposite effect on voters • Every 2 years the League of Conservation Voters (LCV) publish a list of the top 12 worst Senators or Congressmen’s voting record on environmental issues (The dirty dozen)…..in 2000 out of 9 Congressmen, 6 were defeated at the next election. Publicity • Publicity is aimed to educate people • TV advertising is called ‘Issue advertising’ i.e. insurance companies launching a campaign to kill off Clintons Healthcare reforms • US Term Limits Group – Attempt to defeat long serving members in Congress, accounted for Tom Foley, the then speaker of the house More issues • The Food and Drink Administration tried to ban saccharin due to possible links with cancer – The Calorie Control Council (linked with Coca-Cola) ran a campaign denouncing the claims www.caloriecontrol.org Task • Can you think of other methods of Publicity? • Public Policy Journals – circulated to Congress, Senior White House Staff, executive agencies and departments What about these? Promo Videos • A campaign for Congress To tighten laws on production of Veal meat Grassroots Activities • What are they? • Postal blitz on Congress • Marches and Demonstrations • Supreme Court lobbying – partic. On big issues - abortion, School Prayers I’m in there somewhere!! Litigation in the Courts • The Courts interpret the law AND the Constitution • Therefore the court is an ideal place for an Interest Group • Brown Vs Board of Education was brought by the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) More examples • The ACLU brought – Allegheny County Vs American Civil Liberties (1989) – banned religious Christmas displays in publicly owned shopping malls • Reny Vs ACLU (1997) – Declared the 1996 Common Indecency Act was unconstitutional therefore Congress could not ban pornography on the internet. Research task • Look at the impact of Interest Groups on the following:- Try and find a case study • Civil Rights for African Americans • Environmental Protection • Women’s Rights • Abortion Rights • Gun Control • Health Impact on Congress • Direct contact with Congressman and senior members of their staff • Contact with Congressional Committees • Organise Direct mailshots, phone or email blitzes – Most likely to oocur just before an important vote • Publication of voting records • Fundraising for candidates and media advertising Impact on the Executive • Maintenance of strong ties with relevant executive agencies • Interested in business, transport, communications and the environment • Also links with ‘producer groups’ seeking protection, funding, subsidies or price guarantee mechanisms (Monopolies) Impact on Judiciary • Remember amicus curiae? • Briefings on particular cases, presenting ideas in briefings, before the oral discussion. • Been effective in civil rights cases, abortion and 1st amendment rights Regulation on Pressure Groups • Read amendment One – What does it say? • What about the Federal Regulation of Lobbying Act (1946)? • Requires lobbyists to register with the Clerk of the House of Representatives if they were spending money to help or hinder the passage of a bill Abscam • The Congressional Scandal as Arab Interests attempted to bribe leading Congressmen – made more groups register • Congress in the 1990s expanded the definition of an Interest Group, therefore making more register • Also banning gifts to members • Completely useless legislation as has not controlled Interest Gp activity with the Executive. Task • Can you think of any arguments for and against Interest Groups? Arguments for IG’s Arguments against IG’s Provide useful info Revolving Door syndrome Order to policy debate Iron Triangle syndrome Make Govt. Inequality of Groups accountable Special Interest vs Public Interest Buying influence Direct Action Revolving Door Syndrome • Interest Groups and Companies employ people specifically to lobby Congress • Problem is the majority of these people are former Congressmen or Congressional staff members • People walk out of the political door and walk back in as a Washington lobbyist – although must wait 1 year! • Unfair as they exploit knowledge and contacts – making a pot of cash in the mean-time • Plus Congressmen may favour a particular IG whilst in office, hoping for a job when they leave Facts • In 1998 there were 128 former members of congress now working as lobbyists • This is 12% of all people who had left Congress since 1970 • President of the World Federalist Association – John Anderson represented Illinois for 20 years, before an unsuccessful Presidential bid in 1980 (3rd party candidate) The Iron Triangle Interest Groups Congressional Commitees Relevant Government Department or agency The Iron Triangle cont…. • Or the Cosy triangle as some call it • Guarantees policy outcomes which benefits all 3 parties involved • Par example, The ‘Veterans iron Triangle’ • On one side the IG’s – Disabled American Veterans, American Legion • On another side Veterans affairs committees of House and Senate • On the 3rd side Department of Veterans Affairs • In areas such as Defence and agriculture the Iron Triangle is sooo strong it forms a subGovernment Inequality of groups • Power of big Business far outweigh power of environmentalists • Battle between NRA and Handgun Control inc. is unequal • The tobacco industry spent $64 million on lobbying in 1998 Buying influence • In 1999 $1.45bn spent on lobbying and continues to grow at 7.3% / year • 2002 – Mid-termsm PACs donated $215m to House candidates and $60m to Senators • On average a quarter of a billion is spent in just one mid-term election Direct Action • On a slightly different level to us Brits • Includes Shootings, Bombings and murders conducted around abortion clinics by pro-life groups in the 1990s • Bombing of the Federal Government building in Oklahoma in 1995, by Tim McVeigh (subsequently executed) Oklahoma 1995 Winning photo of 1995 Pulitzer Prize Revision Questions • Describe the different types of Interest Group found in the US • Explain the main functions of an Interest Group • What methods do Interest Groups use to further their aims? • Explain the impact Interest Groups have had in 4 policy areas • Explain how Interest Groups are regulated Key Terms • Revolving Door Syndrome • Iron Triangles • Pluralism • Competing Elites • Atomisation • Direct Action Exam Questions • Examine the claim that Interest Groups are undemocratic and work for narrow goals in the US system • Are Interest Groups too powerful? • Have Interest Groups become more important than political parties in US politics?