Study of the Incidence Hyperglycemia and
advertisement

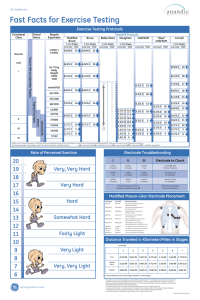
Research Symposium Study of the incidence hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia before and after introduction of glycemic control protocol at Catholic Health System hospitals. Presenter: Marat Gitman, PGY3 Mentor: Howard Lippes, MD 6/9/11 Background • Hospitalized patients are subjected to direct complications of high BG levels. • High BG levels cause indirect harm. • There is evidence of importance of glycemic control in recovery from many serious illnesses. • Hyperglycemia is found to be associated with increased length of hospitalization and healthcare costs. Irl B. Hirsch, MD, Insulin in the Hospital Setting, ISBN/0-9701451-8-7, Adelphi Inc, 2002 Background • ADVANCE - 11,140 patients. • ACCORD -10,251 patients- high risk CV patients. • NICE-SUGAR trial - 6,104 adults admitted to ICU. • 4T study. R. Hollman, Addition of Biphasic, Parandial and Basal Insulin to oral therapy in type 2 DM., NEJM Background Currently fasting BG below 140 mg/dL and random BG below 180 mg/dL are the targets for BG control in non-critically-ill patients. • In order to avoid hypoglycemia, reassessment of insulin regiment is recommended if BG level is below 100 mg/dL and reassessment is warranted if BG level is below 70 mg/dL. • All the decisions need to include considerations about clinical conditions leading to the event. • Updated guidelines are being developed. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists And American Diabetes Association CONSENSUS STATEMENT ON INPATIENT GLYCEMIC CONTROL. Endocrine Practice Vol 15 No. 4 May/June 2009 Background ACE/ADA Inpatient Diabetes and Glycemic Control Consensus Conference. 2006 • Jack L. Leahy, MD. Insulin management of diabetic patients on general medical and surgical floors. (University of Vermont) • Mary Korytkowski, MD. Evolution of a diabetes inpatient committee. (University of Pittsburgh) Based on this research, glycemic control protocol was developed and implemented at CHS hospitals Background • Basal-bolus approach - 0.5 U/kg basal insulin. • 0.1 U/kg rapid analog with meals for average pt. • Dose of basal is lowered by 0.2 U/kg for medical conditions with a high sensitivity to insulin or that have an added risk for hypoglycemia. • Renal or hepatic impairment, thin or normal weight, elderly, frail, hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency,… • Extra 0.2 U/kg basal is given for states of presumed high insulin resistance. • Marked obesity with metabolic syndrome, open wounds, infections, … Jack L. Leahy, MD. Insulin management of diabetic patients on general medical and surgical floors. Glycemic Control Protocol at CHS The initial rollout of the glycemic protocols was in October 2008. Phase 2 Rollout was in May 2009. Phase 3 Rollout was in November 2010 Phase 4 education began in April of 2011 with a pilot at SOCH. RALS-TGCM RALS-TGCM system was implemented at CHS hospitals in prior years was used in current project . • POC glucometers linked wirelessly to a database. • Advantages: reliable, unbiased data collection (no human decision involved in sampling), ease-ofaccess, tools available for ad-hock trend analysis. • Disadvantages: Although basic analysis is readily available, advanced analysis is rather limited, limited data presentation parameters causing possibility for ascertainment bias and standardization problems. Sample RALS output for one month of critical values Methods This study is retrospective database review. CHS patients with Point-of-Care blood glucose measurements. Admitted to Medical-Surgical floors. During May of 2006 through February of 2011 (57 months). Compares monthly averages during 29 months before the introduction of protocol to monthly averages during 28 months post introduction. Methods During this time period, following data was reviewed. 426,563 BGTs at SOCH 840,787 BGTs at SBMH 240,849 BGTs at SJ 281,622 BGTs at KMH Total of 1,789,821 BGTs reviewed. No individual patient information was collected. Data Analysis Data was analyzed in multiple categories. • Critical Hypoglycemia (BG < 40) - % of total # BGTs • Critical l Hypoglycemia (BG < 40) - Mean Values. • Pre- & postmeal Hypoglycemia - % of total # BGTs • Pre- & postmeal Hypoglycemia -Mean Values. • Pre- & postmeal Hyperglycemia - % of total # BGTs • Pre- & postmeal Hyperglycemia - Mean Values. SPSS software was used to find two tailed t-test for independent (unmatched) samples. 11-Jan 10-Sep SJ <= 39 10-Jan 0.009 0.008 0.007 0.006 0.005 0.004 0.003 0.002 0.001 0.000 10-May SJ Critical Lows % 9-Sep 0.000 9-May 0.001 9-Jan 0.002 8-Sep SOCH <= 39 8-Jan 0.004 8-May 0.005 7-Sep SOCH Critical Lows % 7-May 0.006 7-Jan 0.003 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan 0.007 6-Sep 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan 0.008 6-May 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb Hypoglycemia Critical Values-Percent SBMH Critical Lows % 0.010 0.009 0.008 0.007 0.006 0.005 0.004 0.003 0.002 0.001 0.000 SBMH <= 39 KMH Critical Lows % 0.007 0.006 0.005 0.004 0.003 0.002 KMH <= 39 0.001 0.000 Hypoglycemia Critical Values-Percent SOCH_Below39_Percent SBMH_Below39_Percent SJ_Below39_Percent KMH_Below39_Percent Group N Mean SD SE Mean P-Value pre 29 0.0042 0.0011 0.0002 0.017 post 28 0.0033 0.0016 0.0003 pre 29 0.0048 0.0015 0.0003 post 28 0.0032 0.0009 0.0002 pre 29 0.0037 0.0018 0.0003 post 28 0.0025 0.0013 0.0002 pre 29 0.0033 0.0014 0.0003 post 28 0.0024 0.0011 0.0002 < 0.001 0.003 0.016 15 15 10 5 0 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb SOCH Critical Lows (Mean) 40 40 35 35 30 30 25 25 20 20 SOCH <= 39 10 10 5 5 0 0 SJ Critical Lows (Mean) 40 35 30 25 20 SJ <= 39 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb Hypoglycemia Critical Values-Means SBMH Critical Lows (Mean) 15 SBMH <= 39 KMH Critical Lows (Mean) 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 KMH <= 39 Hypoglycemia Critical Values-Mean SOCH_Below39_Mean SBMH_Below39_Mean SJ_Below39_Mean KMH_Below39_Mean Group N Mean SD SE Mean P-Value pre 29 30.8159 2.1017 0.3903 0.580 post 28 30.4864 2.3543 0.4449 pre 29 30.7724 0.9132 0.1696 post 28 30.6368 1.5105 0.2855 pre 29 31.1910 2.0801 0.3863 post 28 29.6596 2.8887 0.5459 pre 29 29.7921 2.2884 0.4249 post 28 30.9871 2.6485 0.5005 0.685 0.026 0.074 11-Jan 10-Sep 10-May 10-Jan SJ <= 69 9-Sep 0.045 0.040 0.035 0.030 0.025 0.020 0.015 0.010 0.005 0.000 9-May SJ Hypo (%)-Postmeal 9-Jan 0.000 8-Sep 0.010 8-May SOCH <= 69 8-Jan 0.030 7-Sep 0.040 7-May SOCH Hypo (%)-Postmeal 7-Jan 0.050 6-Sep 0.020 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan 0.060 6-May 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb Postmeal Hypoglycemia-Percent SBMH Hypo (%)-Postmeal 0.045 0.040 0.035 0.030 0.025 0.020 0.015 0.010 0.005 0.000 SBMH <= 69 KMH Hypo (%)-Postmeal 0.045 0.040 0.035 0.030 0.025 0.020 0.015 0.010 0.005 0.000 KMH <= 69 Postmeal Hypoglycemia - Percent Group N Mean SD SE Mean SOCH_PostMeal_Below_69 pre _Percent post 29 0.0328 0.0056 0.0010 28 0.0279 0.0084 0.0016 SBMH_PostMeal_Below_69 pre _Percent post 29 0.0332 0.0043 0.0008 28 0.0234 0.0033 0.0006 SJ_PostMeal_Below_69 _Percent pre 29 0.0266 0.0065 0.0012 post 28 0.0199 0.0049 0.0009 KMH_PostMeal_Below_69 _Percent pre 29 0.0246 0.0056 0.0010 post 28 0.0201 0.0052 0.0010 P-Value 0.013 <0.001 <0.001 0.003 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 30 20 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb SOCH Hypo (Mean)-Postmeal SOCH <= 69 SJ Hypo (Mean)-Postmeal 70 60 60 58 50 40 SJ <= 69 10 50 0 48 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb Postmeal-Hypoglyecemia-Mean SBMH Hypo (Mean)-Postmeal 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 SBMH <= 69 KMH Hypo (Mean)-Postmeal 56 54 52 KMH <= 69 Postmeal-Hypoglyecemia-Mean group N Mean SD SE Mean P-Value SOCH_PostMeal _Below_69_Mean pre post 29 28 54.5876 55.1496 0.9527 1.1566 0.1769 0.2186 0.051 SBMH_PostMeal _Below_69_Mean pre post 29 28 54.3472 54.8304 1.0436 1.1116 0.1938 0.2101 0.097 SJ_PostMeal _Below_69_Mean pre post 29 28 54.5090 54.9950 2.0987 2.0941 0.3897 0.3957 0.385 KMH_PostMeal _Below_69_Mean pre post 29 28 54.6324 55.7504 1.5301 1.3474 0.2841 0.2546 0.005 0.010 0.010 0.000 0.000 SJ Premeal Hypo % 0.060 0.070 0.050 0.060 0.040 0.030 0.020 SJ <= 79 0.010 0.010 0.000 0.000 11-Jan 0.020 10-Sep 0.020 10-May SOCH <= 79 10-Jan 0.040 9-Sep 0.040 9-May 0.050 9-Jan 0.050 8-Sep 0.060 8-May 0.060 8-Jan 0.070 7-Sep 0.070 7-May SOCH Premeal Hypo % 7-Jan 0.080 6-Sep 0.030 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan 0.080 6-May 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb Premeal Hypoglycemia-Percent SBMH Premeal Hypo % 0.030 SBMH <= 79 KMH Premeal Hypo % 0.050 0.040 0.030 0.020 KMH <= 79 Premeal Hypoglyecemia-Percent group SOCH_PreMeal pre _Below_79_Percent post N 29 28 Mean 0.0534 0.0463 SD 0.0080 0.0121 SE Mean 0.0015 0.0023 P-Value 0.013 SBMH_PreMeal pre _Below_79_Percent post 29 28 0.0551 0.0404 0.0060 0.0046 0.0011 0.0009 <0.001 SJ_PreMeal pre _Below_79_Percent post 29 28 0.0423 0.0331 0.0079 0.0066 0.0015 0.0012 <0.001 KMH_PreMeal pre _Below_79_Percent post 29 28 0.0414 0.0350 0.0079 0.0082 0.0015 0.0016 0.004 67 66 65 64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 58 56 54 52 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb SOCH-Premeal-Hypo-Mean SOCH <= 79 SJ-Premeal-Hypo-Mean 68 66 64 62 60 SJ <= 79 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb 6-May 6-Aug 6-Nov 7-Feb 7-May 7-Aug 7-Nov 8-Feb 8-May 8-Aug 8-Nov 9-Feb 9-May 9-Aug 9-Nov 10-Feb 10-May 10-Aug 10-Nov 11-Feb Premeal Hypoglycemia - Mean SBMH-Premeal-Hypo-Mean 66 65 64 63 62 61 SBMH <= 79 60 59 58 KMH-Premeal-Hypo-Mean 67 66 65 64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 KMH <= 79 Premeal Hypoglycemia - Mean N 29 Mean 62.4017 SD SE Mean 0.1949 1.0493 post 28 63.1436 1.2853 0.2429 SBMH_PreMeal _Below_79_Mean pre post 29 28 62.5352 63.2525 0.8381 0.9839 0.1556 0.1859 0.005 SJ_PreMeal _Below_79_Mean pre post 29 28 62.2197 62.9118 2.1032 2.0707 0.3906 0.3913 0.216 KMH_PreMeal _Below_79_Mean pre 29 62.9769 1.3766 0.2556 0.009 post 28 63.9618 1.3866 0.2621 SOCH_PreMeal _Below_79_Mean Group pre P-Value 0.021 SBMH_PostMeal_181_230 _Percent SBMH_PostMeal_231_300 _Percent SBMH_PostMeal_Above_301 _Percent SJ_PostMeal_181_230 _Percent SJ_PostMeal_231_300 _Percent SJ_PostMeal_Above_301 _Percent KMH_PostMeal_181_230 _Percent KMH_PostMeal_231_300 _Percent KMH_PostMeal_Above_301 _Percent 0.1702 0.1692 0.1183 0.1151 0.0821 0.0838 0.1468 0.1651 0.0838 0.1069 0.0446 0.0645 0.1901 0.1992 0.1358 0.1482 0.0875 0.0998 0.1720 0.1679 0.1178 0.1119 0.0841 0.0681 SOCH Hyper (%)-Postmeal 0.689 0.200 0.150 0.100 0.050 0.000 0.201 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 P-Value 0.546 <0.001 0.250 0.200 0.150 0.100 0.050 0.000 <0.001 <0.001 SJ Hyper (%)-Postmeal 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan SOCH_PostMeal_Above_301 _Percent pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post Mean 0.026 0.200 0.150 0.100 0.050 0.000 0.002 0.004 SBMH Hyper (%)-Postmeal 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan SOCH_PostMeal_231_300 _Percent N 0.270 0.095 <0.001 181-230 231-300 > 301 0.250 0.200 0.150 0.100 0.050 0.000 KMH Hyper (%)-Postmeal 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan SOCH_PostMeal_181_230 _Percent Group SOCH - Hyper-(Mean) Postmeal P-Value 390 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 203.1603 202.9543 260.5900 260.3157 372.0231 374.6471 202.3269 202.9314 259.2638 259.9486 366.0331 368.3818 203.4759 203.5961 260.5597 260.7350 368.3514 369.6021 202.9483 202.6629 260.5945 259.9736 372.0886 366.5211 0.139 340 290 240 0.161 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan 190 0.055 SBMH - Hyper- (Mean) Postmeal 390 340 290 240 190 <0.001 0.001 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan pre post SOCH_PostMeal_231_300 pre _Mean post SOCH_PostMeal_Above_301 pre _Mean post SBMH_PostMeal_181_230 pre _Mean post SBMH_PostMeal_231_300 pre _Mean post SBMH_PostMeal_Above_301 pre _Mean post SJ_PostMeal_181_230 pre _Mean post SJ_PostMeal_231_300 pre _Mean post SJ_PostMeal_Above_301 pre _Mean post KMH_PostMeal_181_230 pre _Mean post KMH_PostMeal_231_300 pre _Mean post KMH_PostMeal_Above_301 pre _Mean post Mean 0.036 SJ - Hyper- (Mean) Postmeal 390 340 290 240 190 0.510 0.519 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan SOCH_PostMeal_181_230 _Mean N 0.405 KMH - Hyper- (Mean) Postmeal 0.064 390 340 0.012 290 240 0.004 181-230 231-300 > 301 190 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan Group SOCH Premeal Hyper (%) SBMH_PreMeal_131_150 _Percent SBMH_PreMeal_151_180 _Percent SBMH_PreMeal_Above_181 _Percent SJ_PreMeal_131_150 _Percent SJ_PreMeal_151_180 _Percent SJ_PreMeal_Above_181 _Percent KMH_PreMeal_131_150 _Percent KMH_PreMeal_151_180 _Percent KMH_PreMeal_Above_181 _Percent P-Value pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post pre post 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 0.1264 0.1310 0.1550 0.1611 0.3706 0.3680 0.1502 0.1434 0.1628 0.1632 0.2750 0.3361 0.1282 0.1237 0.1670 0.1619 0.4134 0.4470 0.1359 0.1446 0.1629 0.1674 0.3738 0.3478 0.034 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan 0.023 0.676 0.400 <0.001 SBMH Premeal Hyper (%) 0.300 0.200 0.841 0.100 0.000 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan SOCH_PreMeal_Above_181 _Percent Mean <0.001 0.095 0.600 0.500 0.400 0.300 0.200 0.100 0.000 0.085 <0.001 0.006 0.113 0.004 SJ Premeal Hyper (%) 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan SOCH_PreMeal_151_180 _Percent N 181-230 231-300 > 301 0.500 0.400 0.300 0.200 0.100 0.000 KMH Premeal Hyper (%) 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan SOCH_PreMeal_131_150 _Percent Group 0.500 0.400 0.300 0.200 0.100 0.000 ud N Mean P-Value pre post pre SOCH_PreMeal_151_180 _Mean post SOCH_PreMeal_Above_181 pre _Mean post pre SBMH_PreMeal_131_150 _Mean post pre SBMH_PreMeal_151_180 _Mean post SBMH_PreMeal_Above_181 pre _Mean post pre SJ_PreMeal_131_150 _Mean post pre SJ_PreMeal_151_180 _Mean post pre SJ_PreMeal_Above_181 _Mean post pre KMH_PreMeal_131_150 _Mean post pre KMH_PreMeal_151_180 _Mean post KMH_PreMeal_Above_181 pre _Mean post 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 29 28 140.3345 140.3293 164.7983 164.6443 258.0503 258.7389 140.0714 140.1757 164.4186 164.5729 245.4752 252.0386 140.3738 140.4454 164.9714 164.9607 256.2062 258.8514 140.2886 140.1893 164.5734 164.6321 258.3093 252.4832 0.899 0.075 SOCH Premeal Hyper (Mean) 270 220 170 120 0.477 270 SBMH Premeal Hyper (Mean) 0.005 220 0.007 170 120 0.324 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan <0.001 SJ Premeal Hyper (Mean) 320 270 0.886 220 170 120 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan 0.058 0.18 0.569 <0.001 KMH Premeal Hyper (Mean) 320 270 220 170 120 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan SOCH_PreMeal_131_150 _Mean 320 6-May 6-Sep 7-Jan 7-May 7-Sep 8-Jan 8-May 8-Sep 9-Jan 9-May 9-Sep 10-Jan 10-May 10-Sep 11-Jan Group Conclusions The adoption of glycemic control protocols for noncritically-ill patients resulted: • Statistically significant reduction in the incidence of critical hypoglycemia. • This change is consistent in all 4 hospitals. • Mixed trend in mean BG during critical hypoglycemic episodes. • Statistically significant worsening at SJ, but mixed non-statistically significant trend at SOCH, SBMH, and KMH Conclusions • Statistically significant reduction in the incidence of post-meal and pre-meal hypoglycemia. • This change is consistent in all 4 hospitals. • Trend towards improvement in mean BG during post-meal hypoglycemic episodes. • Statistically significant only achieved at KMH with SOCH being borderline at (0.05) • Statistically significant improvement in mean BG during pre-meal hypoglycemic episodes. • This change is consistent at 3 out of 4 hospitals with 4th hospital showing trend toward improvement. Conclusions • Mixed trend in the incidence and mean BG of pre-meal and post-meal hyperglycemia. • Inconsistent between the hospitals and in statistical significance. Closing Remarks • Back to 4T study • CHS hospitals mostly trend to use of basal coverage with omission of bolus coverage. With KMH and SOCH showing trend toward the optimization of these modalities . • How can this study be improved: • Chart review to identify site and time specific trends in protocol use can give better insight when aligned with findings of this study. Acknowledgements Dr. Howard Lippes Sharon Wicks Amanda Weber IRB staff and committee References 1) Irl B. Hirsch, MD, Insulin in the Hospital Setting, ISBN/0-9701451-8-7, Adelphi Inc, 2002 2) S H Golden, C Peart-Vigilance, W H Kao and F L Brancat. Perioperative glycemic control and the risk of infectious complications in a cohort of adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care, September 1999 vol. 22 no. 9 1408-1414 3.) Kathryn J. Zerr, MBA, Anthony P. Furnary, MD, Gary L. Grunkemeier, PhD, Stephen Bookin, MD, Vivek Kanhere, MD, Albert Starr, MD, Glucose Control Lowers the Risk of Wound Infection in Diabetics After Open Heart Operations, Ann Thorac Surg 1997;63:356-361 4) Castellanos MR, Szerszen A, Saifan C, Zigelboym I, Khoueiry G, Rafeh NA, Wetz RV, Kleiner M, Aoun N, Weiserbs KF, Maniatis T, Rothman J.Fasting hyperglycemia upon hospital admission is associated with higher pneumonia complication rates among the elderly. Int Arch Med. 2010 Aug 2;3:16. 5) Pulsinelli WA, Levy DE, Sigsbee B, Scherer P, Plum F: Increased damage after ischemic stroke in patients with hyperglycemia with or without established diabetes mellitus. Am J Med 74:540–544, 1983ischemic stroke in patients with hyperglycemia with or without established diabetes mellitus. Am J Med 74:540–544, 1983 6) O'sullivan JJ, Conroy RM, Robinson K, Hickey N, Mulcahy R: In-hospital prognosis of patients with fasting hyperglycemia after first myocardial infarction. Diabetes Care 14:758–760, 1991 7.) McAlister FA, Majumdar SR, Blitz S, Rowe BH, Romney J, Marrie TJ, The relation between hyperglycemia and outcomes in 2,471 patients admitted to the hospital with community-acquired pneumonia. Diabetes Care. 2005 Apr;28(4):810-5. 8) Etie S. Moghissi, MD, FACP, FACE; Mary T. Korytkowski, MD; Monica DiNardo, MSN, CRNP, CDE; Daniel Einhorn, MD, FACP, FACE; Richard Hellman, MD, FACP, FACE; Irl B. Hirsch, MD; Silvio E. Inzucchi, MD; Faramarz Ismail-Beigi, MD, PhD; M. Sue Kirkman, MD; Guillermo E. Umpierrez, MD. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists And American Diabetes Association CONSENSUS STATEMENT ON INPATIENT GLYCEMIC CONTROL. Endocrine Practice Vol 15 No. 4 May/June 2009 9) The ADVANCE Collaborative Group, Intensive Blood Glucose Control and Vascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, n engl j med 358;24 june 12, 2008 10) The Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group (ACCORD). Effects of Intensive Glucose Lowering in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008; 358:2545-2559 June 12, 2008 11.) NICE-SUGAR Study Investigators. Intensive versus conventional glucose control in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med 2009;360:1283–97 12) Jack L. Leahy, MD, Insulin management of diabetic patients on general medical and surgical floors. Endocrine Practice, Vol 12 (Suppl 3) July/August 2006 Thank you.