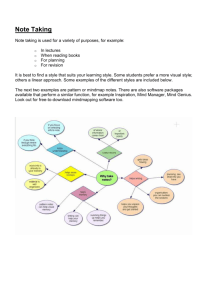
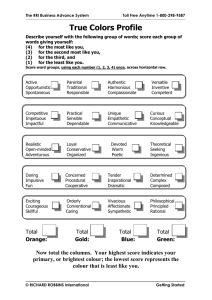
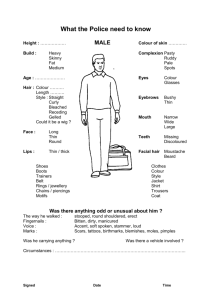
3 - McMaster University
advertisement

MM2A03 New Media Design and Social Network Strategies Robert Hamilton McMaster University New-media design vocabularies and techniques. New-media design has evolved from a diverse range of art and design practices. It’s most obvious precursors are print and motion (film and television) graphics. Print graphics combine words and static images to produce books, magazines, newspapers, posters, stationary, packaging, maps, charts, environmental signage, business cards, badges, logos, etc. Motion graphics combine words, images, sound, movement and narrative to make film titles, cinematic effects for film, music videos and animated sequences for the web, television, interactive kiosks and mobile devices. New Media graphic design New media graphic design also owes a debt to product design, sound design, fine art, and performance art. Product design explores how people touch, hold, move and touch objects. The interactive nature of new media means designers need to determine ways for people to open, close, or move objects on screen, and indeed how those screen actions can be triggered by using keyboards, smart pens or sensor networks in the environment. Fine-arts question and reflect on prevailing conventions, so are useful in pointing the way to possible new processes that open up the designer’s imagination. Terms Layout: is concerned with how words and images are organized. Invisible “grids” are normally used as the underlying framework to give a page or whole book coherence. Grids both divide and unite the page. They are used to break the page down into blocks of of text or image while arranging these blocks into a system. The graphic designer’s job is to lead the user’s eye through a layout. Tables: are are rows and columns used to constrain words, images or videos so they appear in the same place regardless of which browser is installed on the computer. CSS: offers an additional level of control over typographic elements. Navigation Diagrams, charts, graphs and maps belong to an area of graphics known as information design, which aims to make large quantities of complex information sets accessible and navigable. Images: Graphic designers use images to communicate their message in an instantaneous and evocative way. Illustration was traditionally drawn by hand using pen and paper. Illustrations still use paper but many incorporate screenbased work too – drawing and collage with the mouse or using a graphics tablet and stylus, such as a Wacom – in pursuit of their own recognizable style. They also use photography, video, film or 3d modeling. Colour Colour is an essential tool. Designers use colour to distinguish between choices – for example, subway routes; to “colour code” or categorize sets of information such as products in catalogues; and to guide people, for example through green “nothing to Declare” signs at Customs. Colour theory seeks to to analyze colour through the colour wheel, complimentary colours, colour harmonies, saturation, temperature and spatial effects. Storyboards are used to visualize an unfolding series of images for motion graphics, film or video. Details Aspects such as continuity, sound and movement can all contribute to the overall impact of a project. Narrative: stories have always been an important element of design and the new media continues this tradition. In both the old and new media, the story (content) and the telling of the story (expression) are referred to as the “narrative.” Design is the art of association: the creation of metaphors or analogies that drive the design concept. Prototyping: the first version of a design solution. Useability Useability is a term describing the ease with which the user of a product can understand how it works and how to get it to perform. Jacob Nielsen (www.useit.com) is particularly well known for his contribution on this subject. Please see page 79: Designing Effective Websites. The Design Process invariably begins with when a designer or design studio is contacted by a client to create a new product, a website, a video, etc. It’s a business arrangement, sometimes complex – please read pages 80 – 85. On page 90 there is a diagram of the typical strategies/stages and responsibilities in building a medium to large-scale commercial website. The creative process Some designers advocate creative techniques such as brainstorming associations, enjoying the range of ideas that come up; and not worrying about producing the the obvious clichés – they should be got out into the open quickly and dismissed. Many designers sketch ideas or use Wacom sketch tablets to explore ideas. These images are printed out and presented to the client on presentation boards or similar. Powerpoint presentations are also popular. The design process typically involves a lengthy negotiation with the client. Social Network: Word of Mouth Goes World of Mouth Word of Mouth helps to cut through “information indigestion” Broadcast TV: “one program to millions but can’t do the opposite of bringing millions of shows to each person, but the Internet can. Increasingly, the mass market is turning into a mass of niches.” Blog: expression as an individual but participating online with a potentially large online social set. Who cares what you’re doing? Are the life events that people report in social networks inconsequential? Does anyone care? Yes – perhaps not specifically to every entry, but the conglomeration of updates gives the opportunity for others to stay abreast of their friends activities via casual observation. The updates, the tweets become the fabric of being up-todate. There is a constant need or driving force to want the most recent news or updates. Foreign friends are not forgotten Social media can keep us globally connected. Friends are able to keep in contact much more than previously. Casually checking friend’s updates or updating one’s own can lead to new social opportunities. Search Engines: Social media cannot replace search engines. However, social media can offer associations and personal taste. For example, it is difficult to search through social network previous updates from oneself or others. Further, Facebook has allowed the option of not listing one’s page with a search engine. Social media was not invented to compete with Google. Google has been addressing semantics for some time. Social media however can address popularity of an idea, for example through ‘upvotes’ as in Reddit. We no longer search for the news – it finds us. In The USA, data from the Newspaper Association of America stated the advertising revenue from 2008 declined 18.1% Classifieds fell 30% and online advertising sales fell 3. People are increasingly turning away from newspapers. But it’s not that news was becoming less popular – people were turning to other sources. An American TV show Saturday Night Live produced skits parodying Sarah Palin – more than 50 million viewers accessed the skits online. Consequentially viewership for SNL increased dramatically. The American public are increasingly turning to online sources for their favourite TV shows. Hulu, YouTube and torrents are popular. A popular news-skewering web-based project is Auto-Tune the News. Newspapers and Magazines are diminished in power. In the social network era, small talk is somewhat more specific: people have often read each other status updates and already have a sense of what’s new. Social networks allow for quicker and more profound connections between individuals. We have shifted from a world where the information and news was held by a few and distributed to millions, to a world where the information is held by millions and distributed to a few (niche markets). This is part of the remediation of the print media. PC Magazine for example moved all publications online, PCMag and ceased the print version. Newspapers online… While it’s relatively simple to publish the same material available in print to the Internet, generating profits has proven to be challenging. In it’s news feed, Google continues to link to newspaper stories for free. In 2009 Associated Press requested Google to stop this practice but by doing so they saw their traffic significantly drop. New York Times will be implementing a subscription service – something that is being closely monitored by other newspapers. Will people pay for their news? Wikipedia Because Wikipedia has a diverse and extraordinary large contributing user base, the nature of it’s accuracy can be quite high. Wikipedia proves the value of collaboration on a global basis. The output of many minds can result in a clarity of purpose and innovation. The lesson to be learned is that if collaboration among strangers across the Internet can result in something as useful as Wikipedia, think about how collaborations among colleagues can transform business. Dancing Matt. One company that was able to leverage an overnight sensation was the chewing gum brand “Stride” (Cadbury) Matthew “Matt” Harding had a particularly unusual dance. Quitting a job as a game developer, he went on a long vacation and danced at each locale. He recorded 15 dance scenes in exotic locations. It became viral on YouTube and Stride Gum offered to sponsor his travels. All in all he traveled to 42 countries. Matt’s two most popular videos have been seen over 33 million times. Finally… The Financial Times of London reports that 92% of people say they trust word of mouth from friends, associates and colleagues when it comes to making a consumer decision. 75% say they trust collective wisdom sites like Yelp and TripAdvisor. And only 60% of people report trusting traditional image-based advertising. Global Advertising: Consumers Trust Real Friends and Virtual Strangers the Most