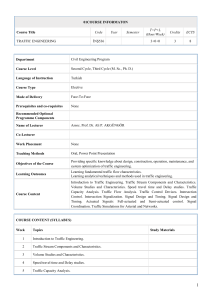
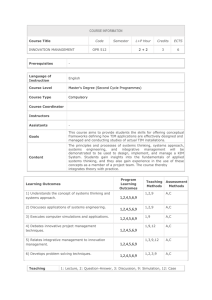
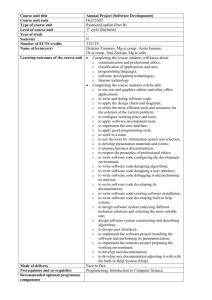
COURSE INFORMATON Course Title Code Year Semester T+P+L
advertisement
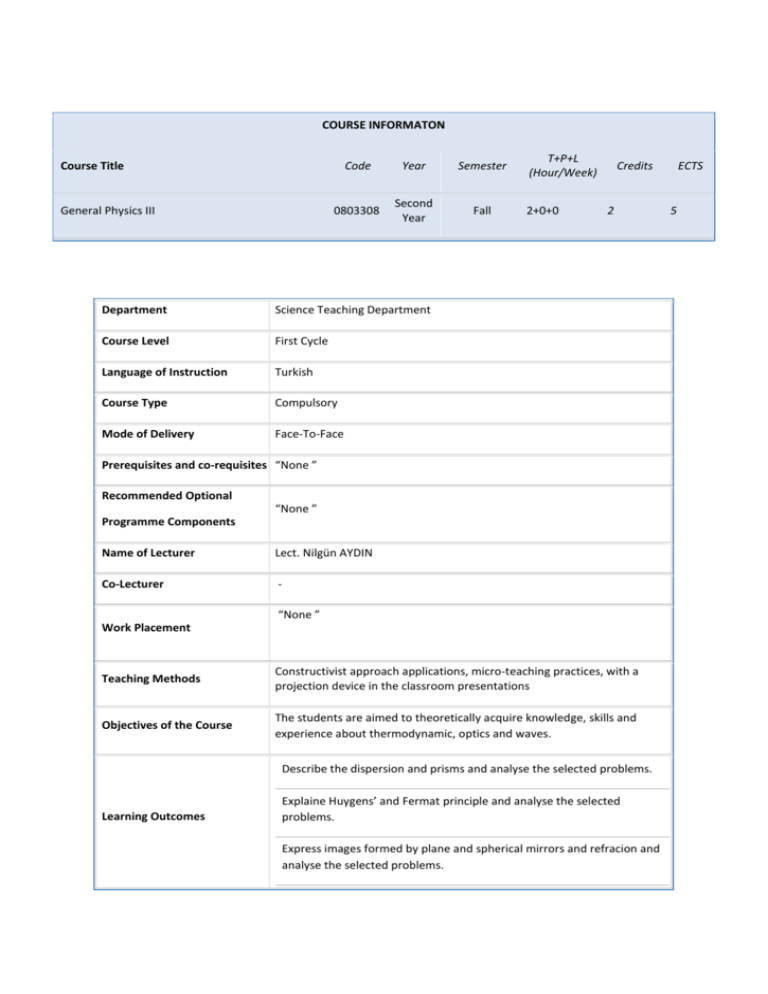
COURSE INFORMATON Course Title General Physics III Code Year Semester 0803308 Second Year Fall Department Science Teaching Department Course Level First Cycle Language of Instruction Turkish Course Type Compulsory Mode of Delivery Face-To-Face T+P+L (Hour/Week) 2+0+0 Credits 2 Prerequisites and co-requisites “None ” Recommended Optional “None ” Programme Components Name of Lecturer Lect. Nilgün AYDIN Co-Lecturer “None ” Work Placement Teaching Methods Constructivist approach applications, micro-teaching practices, with a projection device in the classroom presentations Objectives of the Course The students are aimed to theoretically acquire knowledge, skills and experience about thermodynamic, optics and waves. Describe the dispersion and prisms and analyse the selected problems. Learning Outcomes Explaine Huygens’ and Fermat principle and analyse the selected problems. Express images formed by plane and spherical mirrors and refracion and analyse the selected problems. ECTS 5 Express the interference in thin films and analyse the selected problems. Course Content Thermodynamic, heat and temperature, thermal properties of matter (specific heat, thermal conductivity, thermal expansion) , thermodynamics? laws, reversible and irreversible phenomena, output and entropy, geometrical optic, structure, velocity and supplies of the light, reflection and mirrors, breaking and lens, wave optic, interference, thin films, refractory, solubility, polarity, optical apparatus, magnifying glass, glass, microscope, OHP, projection, field glasses, telescope, photograph machine, wave motion, kinematics, dynamics, energy, reflection, refractory and interference, sound wave, resonance, sound intensity, Doppler effect, AC circuit, resistance in RL, RC and RLC circuits, current, phase difference, resonance state, electro magnetic wave, nucleus physics, radio activity, nucleus reactions (fusion and fission) and energy, reactors, COURSE CONTENT (SYLLABUS) Week Topics 1 The kinematics, dynamic and energy of waves, 2 Reflection, refraction and interference of waves, 3 Sound waves, standing waves, resonance, intensity of sound, Doppler event. 4 Electric and magnetic vibration, radiation from an antenna, electromagnetic spectrum, energy and momentum of electromagnetic waves. 5 The nature, speed and source of light, reflection and mirrors 6 Plane mirrors 7 General assessment 8 Spherical mirrors 9 Refraction and lenses 10 Interference and diffraction, dispersion, polarization 11 AC Circuits: The circuit of RL, RC ve RLC, resistance, current, resonance, radio transmitter and receiver 12 Introduction of the lesson. and thermodynamic, the zero and first laws of thermodynamic Study Materials 13 Heat and temperature, thermal properties of mass (spesific heat, thermal conductivity, thermal expansion 14 Nuclear physics: The energy of nuclei, natural and artificial radioactivity, nuclear reactors. RECOMMENDED SOURCES Textbook Physics for Science and Engineer. Serway V.I Palme pub. Additional Resources Fundamental Physic-I ,Halliday&Resnick Savaş-Teori pub. MATERIAL SHARING Documents Assignments Exams ASSESSMENT EXAMS QUANTITY PERCENTAGE Contribution of Mid -Term Examination to Overall Grade 1 40 Contribution of Final Examination to Overall Grade 1 60 TOTAL 2 100 COURSE'S CONTRIBUTION TO PROGRAMME Contribution Nr. Programme Learning Outcomes 1 2 3 4 5 1 The student who takes this lesson applies physic, chemistry and biology knowledge into science education. 2 Knows measurement and evaluation methods using in comprehensive process of active learning activities. 3 Identifies, models and solves the problems in science education field. 4 Makes teaching practices which can support individuals in international competition within the framework of active learning environment. 5 Designs and analyses a process according to defined targets in science education field. 6 Realizes the importance of technology within the framework of marketing and creating knowledge; gains the ability of inquiry in applications. 7 Adopts computer based learning; creates original instructional designs; develops and applies simulations. 8 Analyses and designs experiments; interprets the results considering the scientific process skills in science education field. 9 Shares activities with his environment by organizing accordance to science education field. 10 Uses web sites, portals and data bases for researching, accessing and sharing information. 11 Creates projects both individual and together with students in science education field. 12 Applies the methods and techniques of science research in to all kind of problems which faced by lifelong and into all kind of studies. 13 Benefits from the views of parents, students, colleagues and administrators when he determines his professional competences 14 Attends science teaching conferences, open sessions, scientific meetings and seminars as a listener. 15 Organizes classroom activities that suitable for practicing-experiencing; organizes out of classroom activities that suitable for nature of science. 16 Organizes the learning environment considering individual differences, students’ ability, requirements and skills. ECTS ALLOCATED BASED ON STUDENT WORKLOAD BY THE COURSE DESCRIPTION Duration Activities Quantity (Hour) Total Workload (Hour) Course Duration (Including the exam week: 16x Total course hours) 16 2 32 Hours for off-the-classroom study (Pre-study, practice) 16 3 48 Assignments 2 10 20 Presentation / Preparing Seminar 2 10 20 Mid-term 1 10 10 Final examination 1 20 20 Total Work Load Total Work Load / 30 (h) ECTS Credit of the Course 150 150/30 5 COURSE INFORMATON Course Title General Physics III Lab. Code Year Semester 0803309 Second Year Fall Department Science Teaching Department Course Level First Cycle Language of Instruction Turkish Course Type Compulsory Mode of Delivery Face-To-Face T+P+L (Hour/Week) 0+0+2 Credits 1 Prerequisites and co-requisites “None ” Recommended Optional “None ” Programme Components Name of Lecturer Lect. Nilgün AYDIN Co-Lecturer “None ” Work Placement Teaching Methods Constructivist approach applications, micro-teaching practices, with a projection device in the classroom presentations Objectives of the Course To help students while they make experiments related to physics II concepts Apply the experiment of the refraction of light and report the results. Apply the experiments of prism and colour filters and report the results. Learning Outcomes Apply the experiments of images formed by plane and spherical mirrors and report the results. Apply the experiments of convex and concave lenses, determine their ECTS 4 focal lengths and report the results. Course Content Mechanical equivalent of the calorie, determination of the elongation number and heat conduction of the solids, reflection laws and the properties of the images on smooth, cavity, bump mirror, the formation of the images on thin- and thick layer lens, the way of the light, interference in double cleavage, resonance, interference of water wave and Doppler event, dispersion of sound, formation of the sound waves, reflection of the sound and formation of echo. COURSE CONTENT (SYLLABUS) Week Topics 1 The mechanical equivalent of calories Longitudinal expansion coefficient determination and thermal conductivity of solids 2 The mechanical equivalent of calories, Longitudinal expansion coefficient Determination. and thermal conductivity of solids 3 Laws of reflection in the mirror and the plane of the image features 4 Laws of reflection in the mirror and the plane of the image features 5 Pit and mound in the mirror beam drawings and image features 6 In the thin and thick-edged lenses light drawing and image formation 7 In the thin and thick-edged lenses light drawing and image formation 8 Mid-term exam 9 The roads follow the changing light environment and light prism double-slit interference in 10 Resonance, interference of water waves and the Doppler incident 11 Resonance, interference of water waves and the Doppler incident 12 Sound propagation, sound waves formation and proliferation 13 Sound absorption, sound reflection and echo formation 14 Sound absorption, sound reflection and echo formation Study Materials RECOMMENDED SOURCES Textbook Physics for Science and Engineer. Serway V.I Palme pub. Additional Resources Fundamental Physic-I ,Halliday&Resnick Savaş-Teori pub. MATERIAL SHARING Documents Assignments Exams ASSESSMENT EXAMS QUANTITY PERCENTAGE Contribution of Mid -Term Examination to Overall Grade 1 40 Contribution of Final Examination to Overall Grade 1 60 TOTAL 2 100 COURSE'S CONTRIBUTION TO PROGRAMME Contribution Nr. Programme Learning Outcomes 1 2 3 4 5 1 The student who takes this lesson applies physic, chemistry and biology knowledge into science education. 2 Knows measurement and evaluation methods using in comprehensive process of active learning activities. 3 Identifies, models and solves the problems in science education field. 4 Makes teaching practices which can support individuals in international competition within the framework of active learning environment. 5 Designs and analyses a process according to defined targets in science education field. 6 Realizes the importance of technology within the framework of marketing and creating knowledge; gains the ability of inquiry in applications. 7 Adopts computer based learning; creates original instructional designs; develops and applies simulations. 8 Analyses and designs experiments; interprets the results considering the scientific process skills in science education field. 9 Shares activities with his environment by organizing accordance to science education field. 10 Uses web sites, portals and data bases for researching, accessing and sharing information. 11 Creates projects both individual and together with students in science education field. 12 Applies the methods and techniques of science research in to all kind of problems which faced by lifelong and into all kind of studies. 13 Benefits from the views of parents, students, colleagues and administrators when he determines his professional competences 14 Attends science teaching conferences, open sessions, scientific meetings and seminars as a listener. 15 Organizes classroom activities that suitable for practicing-experiencing; organizes out of classroom activities that suitable for nature of science. 16 Organizes the learning environment considering individual differences, students’ ability, requirements and skills. ECTS ALLOCATED BASED ON STUDENT WORKLOAD BY THE COURSE DESCRIPTION Duration Activities Quantity (Hour) Total Workload (Hour) Course Duration (Including the exam week: 16x Total course hours) 16 2 32 Hours for off-the-classroom study (Pre-study, practice) 16 2 32 Assignments 16 1 16 Presentation / Preparing Seminar 2 5 10 Mid-term 1 10 10 Final examination 1 20 20 Total Work Load Total Work Load / 30 (h) ECTS Credit of the Course 120 120/30 4 COURSE INFORMATON Course Title Turkish Education History Code Year Semester 0803512 Third Year Fall Department Science Teaching Department Course Level First Cycle Language of Instruction Turkish Course Type Compulsory Mode of Delivery Face-To-Face T+P+L (Hour/Week) 2+0+0 Credits 2 Prerequisites and co-requisites “None ” Recommended Optional “None ” Programme Components Name of Lecturer Lect. Nilgün AYDIN Co-Lecturer “None ” Work Placement Teaching Methods Constructivist approach applications, micro-teaching practices, with a projection device in the classroom presentations Objectives of the Course To comprehend the importance of history of Turkish EducationTo comprehend the general properties of pre-İslamic age Turkish EducationTo comprehend the properties of İslamic age Turkish EducationTo comprehend the developing and changes in Turkish Education in Republican ageTo comprehend the developing and changes in Turkish Education nowadays Define the historical development of Turkish educational system. Learning Outcomes Analyze the new trends and developments in education. ECTS 2 Estimate about Village Institutes, Education Institutes and Higher Teacher. Recognize universities and teacher training systems. Course Content The importance of the history of Turkish Education, educational status before the Republic and teachers institutions, Turkish Education Revaluation 1: philosophy, mental and political background of the revaluation, Turkish Education Revaluation 2: Tevhid-İ Tedrisat Law, historical background, contents, applying and importance, secularism in Turkish Education System, Turkish Education Revaluation 3: education of girls, society schools, basic principles of Republican Education System, village institutes, education institute and high teacher schools, universities and preparing teachers, new development in teacher education COURSE CONTENT (SYLLABUS) Week Topics 1 The importance of Turkish Educational History 2 Aspect of educational phenomena, Education circumstances before the republic and teacher training institutions 3 Turkish Educational Revolution 1: historical background of revolution, philosophical and political foundations of revolution. 4 Unity in Education, foundations and applications of it. 5 Atatürk’s perspectives to Education and suggestions 6 Laicism in Turkish Education system and Girls in education. 7 Coeducation 8 Scripture Revolution, public houses 9 Basic principles of Turkish Republic Education System 10 Village institutions and Higher Teacher School. 11 Universities and teacher training Institutions 12 Universities 13 Teacher training Institutions and applications Study Materials 14 Developments of Turkish education system in recent period. RECOMMENDED SOURCES Textbook AKYÜZ, Yahya. Türk Eğitim Tarihi. Pegem A Yay. Ankara, 2010. Additional Resources ERGIN, Osman. Türkiye Maarif Tarihi. İstanbul, 1977. MATERIAL SHARING Documents Assignments Exams ASSESSMENT EXAMS QUANTITY PERCENTAGE Contribution of Mid -Term Examination to Overall Grade 1 40 Contribution of Final Examination to Overall Grade 1 60 TOTAL 2 100 COURSE'S CONTRIBUTION TO PROGRAMME Contribution Nr. Programme Learning Outcomes 1 2 3 4 5 1 The student who takes this lesson applies physic, chemistry and biology knowledge into science education. 2 Knows measurement and evaluation methods using in comprehensive process of active learning activities. 3 Identifies, models and solves the problems in science education field. 4 Makes teaching practices which can support individuals in international competition within the framework of active learning environment. 5 Designs and analyses a process according to defined targets in science education field. 6 Realizes the importance of technology within the framework of marketing and creating knowledge; gains the ability of inquiry in applications. 7 Adopts computer based learning; creates original instructional designs; develops and applies simulations. 8 Analyses and designs experiments; interprets the results considering the scientific process skills in science education field. 9 Shares activities with his environment by organizing accordance to science education field. 10 Uses web sites, portals and data bases for researching, accessing and sharing information. 11 Creates projects both individual and together with students in science education field. 12 Applies the methods and techniques of science research in to all kind of problems which faced by lifelong and into all kind of studies. 13 Benefits from the views of parents, students, colleagues and administrators when he determines his professional competences 14 Attends science teaching conferences, open sessions, scientific meetings and seminars as a listener. 15 Organizes classroom activities that suitable for practicing-experiencing; organizes out of classroom activities that suitable for nature of science. 16 Organizes the learning environment considering individual differences, students’ ability, requirements and skills. ECTS ALLOCATED BASED ON STUDENT WORKLOAD BY THE COURSE DESCRIPTION Duration Activities Total Workload (Hour) Quantity (Hour) Course Duration (Including the exam week: 16x Total course hours) 16 2 32 Hours for off-the-classroom study (Pre-study, practice) 16 1 16 Assignments - - - Presentation / Preparing Seminar - - - Mid-term 1 6 6 Final examination Total Work Load Total Work Load / 30 (h) ECTS Credit of the Course 1 6 6 60 60/30 2 COURSE INFORMATON Course Title The Nature of Science and History of Science Code Year Semester 0803609 Third Year Spring Department Science Teaching Department Course Level First Cycle Language of Instruction Turkish Course Type Compulsory Mode of Delivery Face-To-Face T+P+L (Hour/Week) 3+0+0 Credits 3 Prerequisites and co-requisites “None ” Recommended Optional “None ” Programme Components Name of Lecturer Assoc. Prof.Dr/ Asst. Prof. Dr. Co-Lecturer “None ” Work Placement Teaching Methods Constructivist approach applications, micro-teaching practices, with a projection device in the classroom presentations Objectives of the Course Development of the science from past to future, to inform students related to famous and important science resear Recognize scientific discoveries. Explain the advantages of scientific studies in society. Learning Outcomes Define the necessity of continuity of scientific studies. Describe the definition, goals, characteristics and development of science. ECTS 5 Definition, aims, properties and developments of the science, history of science, philosophy of science, philosophical approaches and their effect on the development of science, history of innovations, epistemology, ontology, nature scientific concepts, scientific knowledge and its properties, scientific method, scientific thinking, scientific inquiry, science and society, sociology and anthropology of science, scientific ethic Course Content COURSE CONTENT (SYLLABUS) Week Topics Study Materials 1 The definition of science, objectives, characteristics, development and stages 2 The history of science, philosophy of science, philosophical currents and its effect On the development of science, the history of inventions 3 Epistemology, ontology, the nature of scientific concepts 4 How is access to information, scientific information and features 5 The concept of presence 6 Scientific method, scientific thinking, scientific inquiry 7 Science and society, science, sociology and anthropology, science ethics 8 The First time science, Mesopotamia science 9 Former Indian science 10 Ancient science in China 11 Former science in Europe 12 Ancient Greek science 13 Science in ancient egypt 14 20th century science RECOMMENDED SOURCES Textbook TOPDEMIR, H. G., UNAT, Y. 2008; Bilim Tarihi, Pegema Yayıncılık, Ankara Additional Resources ÇEPNI, S., AYVACI, H. Ş., BACANAK, A. 1999; Fen Teknoloji ve Toplum, Celepler Matbaacılık, Trabzon MATERIAL SHARING Documents Assignments Exams ASSESSMENT EXAMS QUANTITY PERCENTAGE Contribution of Mid -Term Examination to Overall Grade 1 40 Contribution of Final Examination to Overall Grade 1 60 TOTAL 2 100 COURSE'S CONTRIBUTION TO PROGRAMME Contribution Nr. Programme Learning Outcomes 1 2 3 4 5 1 The student who takes this lesson applies physic, chemistry and biology knowledge into science education. 2 Knows measurement and evaluation methods using in comprehensive process of active learning activities. 3 Identifies, models and solves the problems in science education field. 4 Makes teaching practices which can support individuals in international competition within the framework of active learning environment. 5 Designs and analyses a process according to defined targets in science education field. 6 Realizes the importance of technology within the framework of marketing and creating knowledge; gains the ability of inquiry in applications. 7 Adopts computer based learning; creates original instructional designs; develops and applies simulations. 8 Analyses and designs experiments; interprets the results considering the scientific process skills in science education field. 9 Shares activities with his environment by organizing accordance to science education field. 10 Uses web sites, portals and data bases for researching, accessing and sharing information. 11 Creates projects both individual and together with students in science education field. 12 Applies the methods and techniques of science research in to all kind of problems which faced by lifelong and into all kind of studies. 13 Benefits from the views of parents, students, colleagues and administrators when he determines his professional competences 14 Attends science teaching conferences, open sessions, scientific meetings and seminars as a listener. 15 Organizes classroom activities that suitable for practicing-experiencing; organizes out of classroom activities that suitable for nature of science. 16 Organizes the learning environment considering individual differences, students’ ability, requirements and skills. ECTS ALLOCATED BASED ON STUDENT WORKLOAD BY THE COURSE DESCRIPTION Duration Activities Quantity (Hour) Total Workload (Hour) Course Duration (Including the exam week: 16x Total course hours) 16 3 48 Hours for off-the-classroom study (Pre-study, practice) 16 2 32 Assignments 5 4 20 Presentation / Preparing Seminar 5 4 20 Mid-term 1 10 10 Final examination 1 20 20 Total Work Load Total Work Load / 30 (h) 150 150/30 ECTS Credit of the Course 5 COURSE INFORMATON Course Title Code Year Semester T+P+L (Hour/Week) Earth Science 0803611 Third Year Spring 2+0+0 Department Science Teaching Department Course Level First Cycle Language of Instruction Turkish Course Type Compulsory Mode of Delivery Face-To-Face Credits 2 Prerequisites and co-requisites “None ” Recommended Optional “None ” Programme Components Name of Lecturer Assoc. Prof.Dr/ Asst. Prof. Dr. Co-Lecturer “None ” Work Placement Teaching Methods Constructivist approach applications, micro-teaching practices, with a projection device in the classroom presentations Objectives of the Course Formation of the earth, big-bang theory, formation of the solid earth, hydrosphere, atmosphere, formation of the rocks, formation of the earth movement, earthquake and volcanoes, soil formation from the rocks Define earth crust materials. Define processes in the earth. Learning Outcomes Define origin and properties of minerals. Define origin and properties of rocks. ECTS 4 Course Content Definition and scope of the geology, basic information about the earth, the shape and dimensions of the earth, motions of the earth, geo-sphere of the earth, gravity, the age of earth, the components of the earth, minerals, definition and properties, rocks from minerals, rocks, definition and general information, magmatic rocks, metamorphism and metamorphic rocks, sediment rocks, dissolution and soil, kind of dissolution, formation of the oil, tectonic motions, orogenic motions, ephirogenic motion, fault, volcanoes, earthquakes, geological times COURSE CONTENT (SYLLABUS) Week Topics 1 Description and content of Earth Science. 2 General principles and subbranches of Earth Science. 3 The earth as a planet: shape, movements and dimentions of Earth. 4 The structure of Earth: Atmosphere, hydrosphere, mantle, core and their physical characteristics. 5 The structure of lithospher: Characteristics and varieties of minerals. 6 The structure of lithospher: Characteristics and varieties of rocks. 7 Temperature and gravity of Earth, and isostasy. 8 Plate techtonics: orogenic and epirogenic movements. 9 Plate techtonics: earthquakes and volcanic activities 10 Erosion: process of abrasion, transfering and accumulation activities on Earth. 11 Erosion factors: wind, rivers and glacial aktivities 12 Forming conditions and vareties of soils. 13 General principles of stratigraphy. 14 Geological times: Fosills and determinations of age of rocks. RECOMMENDED SOURCES Study Materials Textbook Bahceci Z. 2007; Yer Bilimi, Göktuğ Yayınları, Amasya. Additional Resources MATERIAL SHARING Documents Assignments Exams ASSESSMENT EXAMS QUANTITY PERCENTAGE Contribution of Mid -Term Examination to Overall Grade 1 40 Contribution of Final Examination to Overall Grade 1 60 TOTAL 2 100 COURSE'S CONTRIBUTION TO PROGRAMME Contribution Nr. Programme Learning Outcomes 1 2 3 4 5 1 The student who takes this lesson applies physic, chemistry and biology knowledge into science education. 2 Knows measurement and evaluation methods using in comprehensive process of active learning activities. 3 Identifies, models and solves the problems in science education field. 4 Makes teaching practices which can support individuals in international competition within the framework of active learning environment. 5 Designs and analyses a process according to defined targets in science education field. 6 Realizes the importance of technology within the framework of marketing and creating knowledge; gains the ability of inquiry in applications. 7 Adopts computer based learning; creates original instructional designs; develops and applies simulations. 8 Analyses and designs experiments; interprets the results considering the scientific process skills in science education field. 9 Shares activities with his environment by organizing accordance to science education field. 10 Uses web sites, portals and data bases for researching, accessing and sharing information. 11 Creates projects both individual and together with students in science education field. 12 Applies the methods and techniques of science research in to all kind of problems which faced by lifelong and into all kind of studies. 13 Benefits from the views of parents, students, colleagues and administrators when he determines his professional competences 14 Attends science teaching conferences, open sessions, scientific meetings and seminars as a listener. 15 Organizes classroom activities that suitable for practicing-experiencing; organizes out of classroom activities that suitable for nature of science. 16 Organizes the learning environment considering individual differences, students’ ability, requirements and skills. ECTS ALLOCATED BASED ON STUDENT WORKLOAD BY THE COURSE DESCRIPTION Duration Activities Quantity (Hour) Total Workload (Hour) Course Duration (Including the exam week: 16x Total course hours) 16 16 16 Hours for off-the-classroom study (Pre-study, practice) 16 16 16 Assignments 16 16 16 Presentation / Preparing Seminar 2 2 2 Mid-term 1 1 1 Final examination 1 1 1 Total Work Load Total Work Load / 30 (h) 120 120/30 ECTS Credit of the Course 4 COURSE INFORMATON Course Title Code Astronomy 0803805 Year Semester T+P+L (Hour/Week) Fourth Year Spring 2+0+0 Department Science Teaching Department Course Level First Cycle Language of Instruction Turkish Course Type Compulsory Mode of Delivery Face-To-Face Credits 2 Prerequisites and co-requisites “None” Recommended Optional “None” Programme Components Name of Lecturer Assoc. Prof.Dr/ Asst. Prof. Dr. Co-Lecturer - Work Placement “None” Teaching Methods Constructivist approach applications, micro-teaching practices, with a projection device in the classroom presentations Objectives of the Course To know space, to understand the formation of the space and scientific principles found by the researchers during the history Express the artificial satellites for communaciations, telescopes and dedectors. Learning Outcomes Explain the science of stars, energy production and transport in stars. Define the black body radiation, and the star spectrum. Express the formation and evolution of stars, and classification in detail. Course Content Kepplers law and the structure of the solar system, planets and their properties, satellates, general structure of the universe, galaxies, formation of the stars, red monster, neutron stars, white manikins, ECTS 6 blackholes COURSE CONTENT (SYLLABUS) Week Topics Study Materials 1 Introduction 2 Universe and Univers Models 3 Star concept and star’s life process 4 Galaxys 5 First phase Galaxy : Quasars 6 Solar system and other system 7 Midterm Exams 8 Observation with Telescope 9 Blackholes 10 Lunar phases 11 Observation with telescope 12 The other object in the solar system 13 Communucation satellites and working principle 14 Observation (without telescope) RECOMMENDED SOURCES Textbook Additional Resources MATERIAL SHARING Documents Atkinson, Stuart. 2003; Tübitak Popüler Bilim Yayınları, Ankara Assignments Exams ASSESSMENT EXAMS QUANTITY PERCENTAGE Contribution of Mid -Term Examination to Overall Grade 1 40 Contribution of Final Examination to Overall Grade 1 60 TOTAL 100 COURSE'S CONTRIBUTION TO PROGRAMME Contribution Nr. Programme Learning Outcomes 1 2 3 4 5 1 The student who takes this lesson applies physic, chemistry and biology knowledge into science education. 2 Knows measurement and evaluation methods using in comprehensive process of active learning activities. 3 Identifies, models and solves the problems in science education field. 4 Makes teaching practices which can support individuals in international competition within the framework of active learning environment. 5 Designs and analyses a process according to defined targets in science education field. 6 Realizes the importance of technology within the framework of marketing and creating knowledge; gains the ability of inquiry in applications. 7 Adopts computer based learning; creates original instructional designs; develops and applies simulations. 8 Analyses and designs experiments; interprets the results considering the scientific process skills in science education field. 9 Shares activities with his environment by organizing accordance to science education field. 10 Uses web sites, portals and data bases for researching, accessing and sharing information. 11 Creates projects both individual and together with students in science education field. 12 Applies the methods and techniques of science research in to all kind of problems which faced by lifelong and into all kind of studies. 13 Benefits from the views of parents, students, colleagues and administrators when he determines his professional competences 14 Attends science teaching conferences, open sessions, scientific meetings and seminars as a listener. 15 Organizes classroom activities that suitable for practicing-experiencing; organizes out of classroom activities that suitable for nature of science. 16 Organizes the learning environment considering individual differences, students’ ability, requirements and skills. ECTS ALLOCATED BASED ON STUDENT WORKLOAD BY THE COURSE DESCRIPTION Duration Activities Quantity (Hour) Total Workload (Hour) Course Duration (Including the exam week: 16x Total course hours) 16 2 32 Hours for off-the-classroom study (Pre-study, practice) 16 3 48 Assignments 4 10 40 Presentation / Preparing Seminar 3 10 30 Mid-term 1 10 10 Final examination 1 20 20 Total Work Load Total Work Load / 30 (h) ECTS Credit of the Course 180 180/30 6