document
advertisement

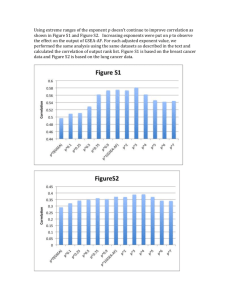
SOC101Y Introduction to Sociology Professor Robert Brym Lecture #3 Social Interaction 29 Sep 10 A status is a recognized position in a social interaction. How We Get Emotional external stimulus For example, a grizzly bear attacks. physiological response and initial emotion Your pulse rate increases etc.; you experience fear. cultural script You have learned that lying still and playing dead increases the chance the grizzly bear will lose interest in you. modified emotional response Still fearful, you act according to the cultural script, which gives you hope. Emotion management involves people obeying “feeling rules” and responding appropriately to the situations in which they find themselves. Emotion labour is emotion management that one does as part of one’s job and for which one is paid. The crude death rate is the annual number of deaths per 1,000 people in a population. A rate is the frequency with which an event occurs in a given time span per population unit. Calculating a Rate Population A Population B N=4,782 M=12 N=613 M=3 3 / 613 = .0048939 .0048939 * 1,000 = 4.8 12 / 4,782 = .0025094 .0025094 * 1,000 = 2.5 N = number of people in a population at a given time. M = number of marriages in the population over a given period. The marriage rate = (M/N) * 1,000. That is, you divide the frequency of an event (how often it occurs in a given time span, such as a year) by the size of the population and multiply by 1,000 to find the rate of the event per 1,000 people. Multiply by 100 to find the rate per 100 people. Higher Education, Top 12 Countries ABSOLUTE SCORE* * Absolute score = number of universities in a country ranked in the top 200 universities in the world by the Times Higher Education Supplement (2010-11) RELATIVE SCORE* * Relative score = (a/b)*100, where a = number of universities in a country ranked in the top 200 universities in the world by the Times Higher Education Supplement (2010-11) and b = country’s population in 2010 How would you calculate the rate of top universities in each country? A Competitive Conversation Draws attention to himself John: “I’m feeling really starved.” Begins to compete by refocusing attention on herself Mary: “Oh, I just ate.” Engages in the competition by trying to draw attention back to himself John: “Well, I’m feeling really starved.” Mary: “When was the last time you ate?” Concedes the competition by allowing the conversation to focus on John Norms are standards of behavior or generally accepted ways of doing things. Values are shared ideas about what is right and wrong. Why We Interact we gain valued resources from interaction and we compete to maximize our gains we learn norms and values (some of them altruistic) that require interaction Where Do Norms and Values Come From? from culture from creative negotiation: we manipulate the impressions we make on others we communicate verbally and nonverbally Impression management is the manipulation of how we present ourselves to others so as to appear in the best possible light. Important Types of Nonverbal Communication facial expressions, gestures and body language status cues (visual indicators of other people’s social positions) stereotypes (rigid views of how members of various groups act, regardless of whether individual group members really behave that way) (Lower case indicates sample; upper case indicates population.) Probability of Being Stopped by the Police, Toronto, by Race, Sex, and Age (n=1,257) Probability Which category has the highest probability of being stopped? For white and Asian males and females, what is the relationship between age/education and the probability of being stopped? For black males and females, what is the relationship between age/education and the probability of being stopped? Correlation A variable is a concept that can have more than one value. A correlation is the relationship or association between two variables. The correlation coefficient (r) measures the strength of the association between two variables. Its value ranges from -1 to +1, with -1 indicating a perfect negative linear association, +1 indicating a perfect positive linear association, and 0 indicating no association. Correlation Variable y 60 Variable y Variable y 60 60 r = .85 40 40 20 20 r=0 r = -.92 40 20 0 0 0 2 4 6 8 Variable x 0 0 2 4 6 8 Variable x 0 2 4 6 8 Variable x 1. Positive Correlation 2. Negative Correlation 3. No Correlation