Cell Signaling and Tissue Engineering
advertisement

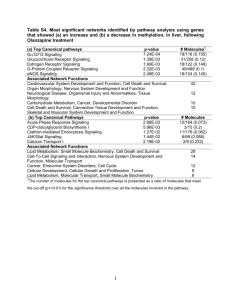
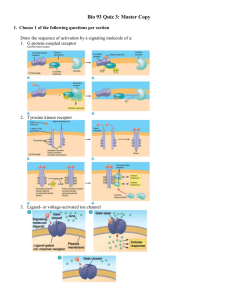
Cell Signaling and Tissue Engineering Why Cell Signaling? • Complex system of communication • Affects a cell’s ability to respond to its environment Cell signaling affects: • Development • Tissue Repair • Immunity • Movement • Diseases What Happens When Cells Miscommunicate?? Diabetes Rheumatoid Arthritis Cancer Lupus Multiple Sclerosis Asthma How Do Cells Send Signals? There are five different types of signaling pathways: 1. Contact Dependent 2. Autocrine 3. Paracrine 4. Synaptic 5. Endocrine Why does such a variety of signaling pathways exist? Three Stages to Extracellular Signaling 1. Ligand Binding – Ligand binding to receptor induces conformational change 2. Transduction – Amplification and spreading of signal down specific pathways in cell 3. Cellular Response – – Cell response to signal May result in any of the following: i. ii. iii. Gene transcription Cell proliferation/division Cell survival Extracellular Signaling in a Nutshell The signaling cell produces a particular type of signal molecule that is detected by the target cell. The target cells possess receptor proteins that recognize and respond specifically to the signal molecule. Seem Simple? Think Again How many different signaling molecules exist? • HUNDREDS How do you think this effects a signals ability to be transduced? • Each cell responds selectively to a mixture of signals – – Disregards some Reacts to others What complications can arise? • • One signal, binding to one type of receptor protein, can cause a variety of effects in the target cell Cells have an assortment of different receptors, making them sensitive to many signals Cellular Suicide? What do you think happens in the absence of signals? • In most cases, cells kill themselves. Strengthening and Maintaining a Signal Recall Synaptic Signaling Pathway How can we alter/strengthen a signal? • Neuroplasticity – ability to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences 4 Stages to Neuroplasticity 1. Induction – Neuron realizes input needs to be changed 2. Selectivity – Type of change is based on input parameters (gain or loss) 3. Expression – Synaptic efficiency is changed 4. Maintenance – Change is maintained over long period of time Wanna Make a Memory? What is learning? • The ability to acquire new knowledge/ skills through instruction or experience What is memory? • Process by which learning is maintained over time How do you think a memory forms?? CELL SIGNALING!