Civil Rights Act of 1964

Civil Liberties and Civil Rights
Unit VI
Chapters 4 & 5
Liberties v. Rights
Civil Liberties - legal, constitutional protections AGAINST government, and are listed in the Bill of Rights
Civil Rights – policies designed to protect people against arbitrary or discriminatory treatment by government officials
Fourteenth Amendment
“No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of the citizens of the United
States.”
Due process now applies to States as well as the federal government – equal protection of the law at all levels
Incorporation Doctrine – the legal concept under which the Supreme Court nationalized the Bill of Rights
Establishment Clause
“Congress shall make no law respecting the establishment of religion…”
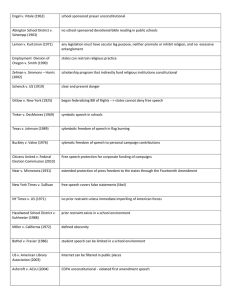
Lemon v. Kurtzman
Supreme Court ruled that aid to church-related schools must:
Have a secular (non-religious) legislative purpose (i.e., public funds may be used for buildings, textbooks, etc.)
Have a primary effect that neither advances or inhibits religion’
Not foster excessive government entanglement with religion
Establishment Clause cont.
Zelman v. Simmons-Harris
The Supreme Court upheld a program that provided families in Cleveland, Ohio, vouchers that could be used to pay tuition at religious schools
Group discussion – are school vouchers constitutional?
Freedom of Religion
Free Exercise Clause – prohibits government from interfering with the practice of religion
Prayer in school – NOT unconstitutional; student may pray silently, BUT, student-led prayer at sporting games was ruled as unconstitutional in 2000
“Moments of silence” – unconstitutional because the intent was to bring prayer back to schools
Freedom of Expression
Prior restraint – government preventing material from being published =
UNCONSTITUTIONAL
Near v. Minnesota – a newspaper editor called local politicians a slew of non-flattering names, and the State closed down his business.
However, the S.C. ordered that the newspaper be reopened because newspapers are protected by the First Amendment, just as people are
HOWEVER, prior restraint may be used during wartime, and someone may be punished for their words after something is published
Freedom of Expression cont.
Speech is limited if it presents a “clear and present danger” (i.e., encouraging people to resist the draft)
Speech cannot be used to incite anyone to imminent lawless action
Speech is generally protected in public places, but usually not on another’s private property (i.e., shopping malls, businesses)
Freedom of Expression cont.
Obscenity – although not clearly defined, obscene speech is NOT protected
Miller v. California – Supreme Court held that community standards be used to determine whether material is obscene
Obscene if it:
Showed patently offensive sexual conduct
Lacked serious literary, artistic, political, or scientific value
Freedom of Expression cont.
NOT PROTECTED
Libel – the publication of false or malicious statements that damage someone’s reputation (written)
Slander - the publication of false or malicious statements that damage someone’s reputation (spoken)
Freedom of Expression
Symbolic speech – nonverbal communication (i.e. flag burning or wearing an arm band) IS protected
Commercial speech – most restricted and regulated form of speech (Federal Trade Commission)
Right to Assemble – time, place, manner rules apply
Right to Associate – freedom to join groups without government interference
Defendants’ Rights – spelled out in Amendments 4, 5,
6, 7, 8)
Probable cause, no unreasonable search and seizure, protection against self incrimination, right to counsel and trials, no cruel or unusual punishment
Equality
Equal opportunity = same chances
Equal results – same rewards
Civil Rights Era
Plessy v. Ferguson – separate but equal accommodations are constitutional
Brown v. Board of Education – overturned
Plessy; school segregation was unconstitutional
Civil Rights Act of 1964
Made racial discrimination illegal in hotels, restaurants, and other public accommodation
Created the Equal Employment Opportunity
Commission (EEOC)
Voting
Suffrage – the right to vote
Fifteenth Amendment – allowed African
Americans to vote
Poll taxes – small taxes levied on the right to vote (later outlawed in the 24 th Amendment)
White Primary – only whites were allowed to vote in the party primaries (ended in 1944 as a result of Smith v. Allwright
Nineteenth Amendment – allowed women to vote
Affirmative Action
A policy designed to give special attention to previously disadvantaged groups (limited in Adarand Constructors v.
Pena)