The Business Plan Section Summary
advertisement
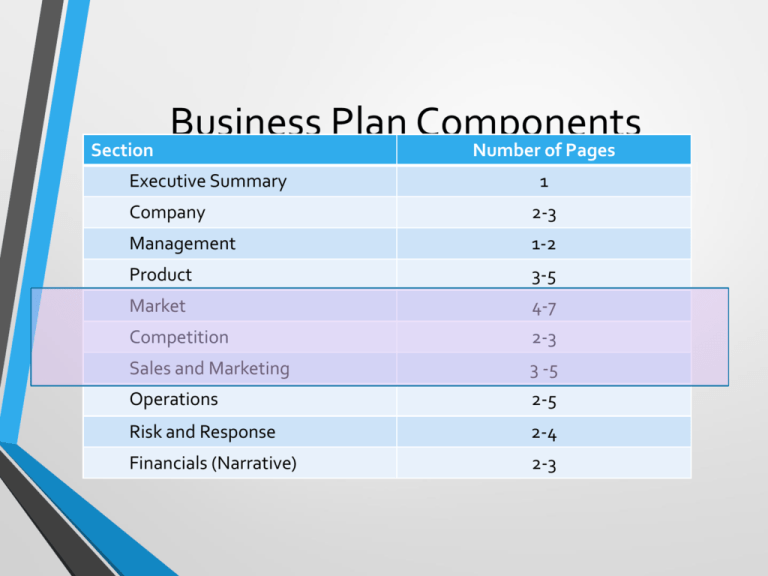
Section Business Plan Components Number of Pages Executive Summary 1 Company 2-3 Management 1-2 Product 3-5 Market 4-7 Competition 2-3 Sales and Marketing 3 -5 Operations 2-5 Risk and Response 2-4 Financials (Narrative) 2-3 Market and Marketing Strategy • Market definition • Market share projection • Positioning strategy • Pricing strategy • Distribution strategy • Promotion plan Market Section • Fundamental intent • Detailed, defensible description of the market being addressed by the business’ product or service • Market definition analysis: narrowing definitions from total market to feasible market The Narrowing Process • Starts with brief description of total general market • • • • Size Geography Growth prospects Type • • • • Niche Perfectively competitive Monopolistic General type and level of competition Narrowing Process (2) • Transitions quickly to more narrow target market • Narrows down total market through segmentation to • • total addressable market Segmentation factors can be geography, customer attributes, product orientation Solar panels for pool heating: focus would be on number of pool users in geographies with significant sun exposure • Definition of target market critical for advertising • Playskool advertises toys on Nickelodeon • Target market characterized in terms of size, structure, growth prospects and market potential Narrowing Process (3) • Next, further narrow by defining feasible market within target market • Example: • Microbrewery case: plans to brew premium lager beer • Total feasible market determined by number of drinkers of premium pilsner beers in target market • Feasible market the portion of market capturable given perfect environmental conditions and little competition Market Share • Market share projection a subjective estimate • Basis is highly targeted and competitive distribution, pricing, promotional strategies • Microbrewery case: even with large number of drinkers of premium pilsners forming total feasible market, distribution network has to reach them at a market acceptable and competitive price point • Customers have to be made aware of availability and purchase points • Share projection required in plan though • Make it defensible Market Share (2) • Factors underpinning market share • Industry growth • • Increases number of customers Conversion of users (from feasible market) • Affected by new product adoption cycle • Early pioneer users • Early users • Early majority users • Late majority users • Late users • Again, key is make it defensible • Granular detail helps Who Are Competitors? • Beware of the conclusion: We have no direct competitors; or worse: We have no competitors • Usually signifies a shallow-thinking entrepreneur • • • It validates the market It validates business models It drives value creation for customers • Competition is good • No competition is not good • • • Maybe there isn’t a market Maybe the economics are such that it’s not really a good opportunity Maybe there isn’t an effective business model Competition - Types • Direct • Easily identifiable • • • Coke - Pepsi Crispy Kreme – Dunkin Donuts Honda Motorcycle – Harley Davidson • Indirect • Less easily identifiable • • • Coke – Bottled Water Crispy Kreme – Breakfast Burrito Honda Motorcycle – Schwinn Bike • Obtuse, but still a competitor • Sometimes difficult to identify • • • Coke – Fresh Fruit Crispy Kreme - GHFC Honda Motorcycle – RTS Bus Competitive Analysis • Purpose • • • • Determine strengths & weaknesses of market segment competitors Scope out strategies that will provide distinct advantages Determine developable barriers to prevent new competitor entries Scope out exploitable weaknesses for product development cycle Competitive Analysis (2) • Process • Identify current and potential competition • Two approaches • Customer driven approach – group competitors by degree to which they contend for customers’ expenditures • Strategy driven approach – group according to various competitive strategies showcasing what motivates them • Analyze strategies to identify vulnerability areas • Examine competitors’ strengths & weaknesses Positioning Business • Positioning strategy defines how you want product perceived by customers and competitors • Kobe Bryant and OJ Simpson, for example, both lost endorsement base in close proximity to court cases • Driven by variables tied to: • Motivations and requirements of target customers • Customer need fulfilled by product • Competitor factors • • Competitor positioning Competitive advantages of product Pricing • Precepts of pricing strategy • • Prices must cover costs Prices established to assure sales • • • Resist pricing against competitive action Price to sell Prices must reflect product utility, longevity, maintenance, end use Pricing (2) • Methods of establishing pricing • Competitive • • Cost-based • • Used frequently upon entering market where product differentiation difficult Assures costs covered and gross margin attained Value-based • Establishes price reflective of value created for customer Distribution • Defines the process of moving product from factory to end • • user Distribution strategy will reflect industry norms, size of market, internal resources Types • • Direct Sales • • Positives: focused, controlled sales Negatives: fixed cost OEM • • • Your product a subsystem component of another’s, and their distribution used Positives: leverages sales capability Negatives: high customer concentration • Types (cont) Distribution (2) • Manufacturer’s reps • • • • Agency sales people that handle complementary products Positives: pay for performance Negatives: effectiveness; focus on high volume products Video broadcast example • Brokers • • • Third party distributors who deal direct with retailers and end users Positives: broad coverage and can deliver volume Negatives: expensive Distribution (3) • Types (cont) • Internet • • • • • • B-to-B; B-to-C Positives: scale Negatives: technical sell difficult; driving traffic difficult and expensive Wholesale distributors Retail distributors Direct mail Promotion Plan • Follows structuring of distribution strategy • Defines controlled distribution of communication targeted to sell product or service • Panera Bread targets restaurants as upscale, unique - artwork on walls, classical music in background – all to create sense of tranquility (and willingness of patrons to pay upscale prices for food offered Promotional Plan (2) • Elements of communication effort • Advertising • • Packaging • • • • Which media McDonald’s arches on fries FedEx wrapping on packages Public relations Sales promotion • • Coupons, special offers Think of the oil changes ads






