“Good” Vibrations
advertisement
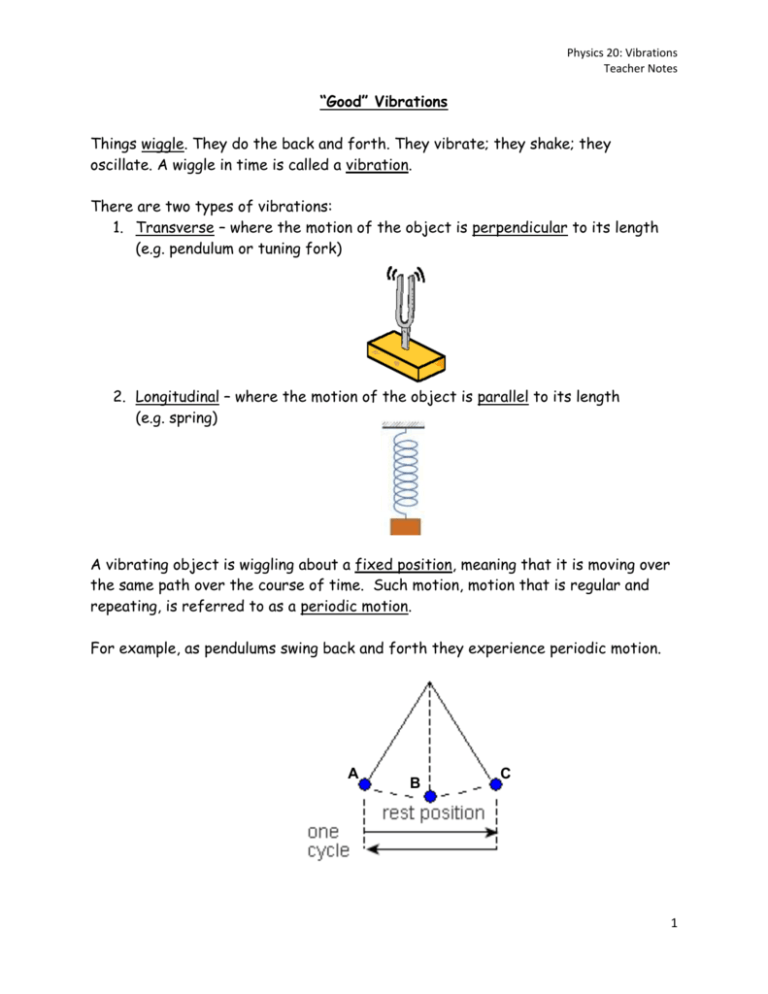
Physics 20: Vibrations Teacher Notes “Good” Vibrations Things wiggle. They do the back and forth. They vibrate; they shake; they oscillate. A wiggle in time is called a vibration. There are two types of vibrations: 1. Transverse – where the motion of the object is perpendicular to its length (e.g. pendulum or tuning fork) 2. Longitudinal – where the motion of the object is parallel to its length (e.g. spring) A vibrating object is wiggling about a fixed position, meaning that it is moving over the same path over the course of time. Such motion, motion that is regular and repeating, is referred to as a periodic motion. For example, as pendulums swing back and forth they experience periodic motion. A B C .......... 1 Physics 20: Vibrations Teacher Notes A single movement is called a pulse. One complete vibration, or oscillation, is called a cycle. In the pendulum above, one cycle is going there and back. Amplitude is the maximum displacement from rest position (e.g. distance from A to B or C to B on the pendulum). The time required to complete one cycle is called period, (T). 𝑇= where 𝛥𝑡 𝑁 T = period (in seconds, s) Δt = time elapsed (in seconds, s) N = # of vibrations The number of cycles in 1 second is called frequency, (f). 𝑓= where 𝑁 𝛥𝑡 f = frequency (in 1/seconds, 1/s, s-1) (also known as Hz – see below) N = # of vibrations Δt = time elapsed (in seconds, s) The unit used to measure frequency is the hertz, (Hz), named after Heinrich Hertz. One cycle per second is one hertz. * Note: The two quantities frequency and period are inversely related to each other. They are mathematical reciprocals of each other. *. period = the time for one full cycle to complete itself; seconds/cycle frequency = the number of cycles completed per time; cycles/second 𝑇= 1 𝑓 𝑓= 1 𝑇 2 Physics 20: Vibrations Teacher Notes Additional Vocabulary The diagram below shows both pendulums moving in the same direction. The pendulums are in phase. In phase refers to two objects that are always moving in the same direction at the same time. However, the following diagram shows the one pendulum moving right while the other moves left, so they are out of phase. Out of phase refers to two objects that are moving in opposite directions during any part of their cycles. The specific frequency at which an object naturally vibrates is referred to as its natural frequency. The setting of a body into vibration at its own natural frequency as a result of the vibrations of another nearby body that is vibrating at the same frequency is called resonance. Pendulum X and pendulum C are of the same natural frequency. Hence pendulum C is at resonance. 3 Physics 20: Vibrations Teacher Notes Frequency & Period Examples 1. A pendulum completes 32 cycles in 16 seconds. What is the frequency? What is the period? 𝒇= 𝑵 𝜟𝒕 The frequency is 2.0 hertz. The period is 0.50 seconds. 2. If 212 waves pass through a certain spot in 0.50 s, what is the period of the wave? What is the frequency? 𝑇= 𝛥𝑡 𝑁 𝑇= 0.50𝑠 212 𝑤𝑎𝑣𝑒𝑠 𝑇 = 0.0024 𝑠 𝑓= 1 𝑇 𝑓= 1 0.0024𝑠 𝑓 = 416.7 𝐻𝑧 𝑓 = 420 𝐻𝑧 4