here - WordPress.com
advertisement

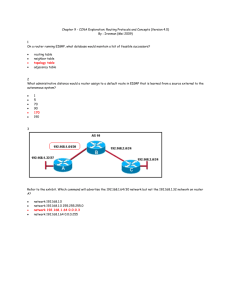
Maria Coffey Ch 2 EIGRP Review Questions 1. What are some features of EIGRP? a. Fast convergence - uses DUAL to achieve. A router running EIGRP stores its neighbors' routing tables to quickly adapt to changes in the network. EIGRP will query its neighbors if no route exists in the local routing table or topology table. The queries are propagated until an alternative route is found or it is determined no route exists. b. Partial updates - sends when triggered rather than periodically. They are triggered when a route or metric changes, and only sends information about the change. The updates are automatically bounded so only routers that need the information receive it. This mean EIGRP uses much less bandwidth for routing updates. c. Multiple network layer support - supports IPv4, IPv6, AppleTalk, and IPX using protocoldependent modules (see question 3 for more info). Offers superior performance/stability when implemented in IP, IPv6, AppleTalk and IPX networks. d. Use of multicast and unicast - because broadcast is not used, end stations are not affected by routing updates or queries. The multicast address used in EIGRP is 224.0.0.10 e. VSLM and discontinuous network support - classless routing protocol, advertises the subnet mask in updates. f. Sophisticated metrics - support for unequal metric load balancing to allow admins to better distribute traffic in the network g. Seamless connectivity across all data link layer protocols/topologies - does not require special configuration to work across any layer 2 protocols. Designed to operate efficiently on either LAN or WAN networks. 2. Is EIGRP operational traffic multicast or broadcast? a. Multicast. 3. What are the four key technologies used by EIGRP? a. Neighbor discovery/recovery mechanism - enables routers to dynamically learn about other routers on their directly connected networks. It also lets them discover if their neighbors become unreachable or inoperative. (HELLO packets) b. Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP) - responsible for guaranteed, ordered delivery of EIGRP packets to all neighbors. RTP supports the mixed transmission of multicast or unicast packets. Only certain EIGRP packets are transmitted using RTP for efficiency. c. DUAL finite-state machine - DUAL tracks all routes that are advertised by neighbors and uses distance information (composite metric or cost) to select efficient and loop-free routes to all destinations d. Protocol-dependent modules - responsible for network layer protocol-specific requirements. Each protocol (IP, IPv6, AppleTalk, IPX) has its own module and operates independently of the others. 4. What best describes the EIGRP topology table? a. It contains all learned routes to a destination. 5. Describe the 5 types of EIGRP packets. a. HELLO - used for neighbor discovery. Sent as a multicast and don't require acknowledgements. Carry an acknowledgement number of 0. b. UPDATE - contain route change information. Sent to communicate routes that the router has used to converge, and sent only to affected routers via multicast when a new route is discovered and when it becomes passive. During EIGRP start up, update packets are sent to neighbors by unicast to synchronize topology tables. Update packets are sent via RTP. c. QUERY - sent to neighbors when a router is performing route computation (DUAL) and does not have a feasible successor (FS) to see if they have a successor to the destination. Usually multicast, but can be retransmitted as a unicast for certain situations. Sent via RTP. d. REPLY - sent in response to a query. Unicast and sent back to the originator of the query packet via RTP. All routers must reply to queries. e. ACK - used to acknowledge updates, queries, and replies. They are unicast hello packets and contain a nonzero acknowledgement number. Does not require an acknowledgement back. 6. How often are HELLO packets sent on a LAN link (or serial interface)? a. 5 seconds by default b. As a note, hello intervals by default are 60 seconds on a T1 or slower NBMA interface. This only applies to low speed, NBMA media (T1 or lower). 7. What is the difference between hold time and the hello interval? a. The hold time is by default three times the hello interval. b. For example, if the hello interval is 5 seconds, the hold time is 15 seconds. c. Hold time is the amount of time that a router considers a neighbor up without receiving a hello packet from them. d. Hold times must be updated manually if the hello interval is changed, it will not automatically update when the hello interval is changed. The command used to do this is ip hold-time eigrp <as-number seconds> in interface configuration 8. What statements are true about EIGRP? a. A route is considered passive when the router is not performing recomputation on that route. b. A route is considered active when it is undergoing recomputation. c. Passive is the operational state for a route. 9. What is the command used to see the RTO and hold time? a. show ip eigrp neighbors b. RTO - the amount of time (in milliseconds) that a router will wait for an acknowledgement before retransmitting a reliable packet from the retransmission queue to a neighbor 10. Why are EIGRP routing updates described as reliable? a. Because they are sent using RTP. The packets have a sequence number assigned to them, and must receive an acknowledgement from the destination router. 11. What are two true statements about advertised distance (AD) and feasible distance (FD)? a. The FD is the EIGRP metric for this router to reach a particular network. b. The AD is the EIGRP metric for a neighboring router to reach a particular network. 12. What does it mean when a route is marked with an FS? a. It means that the route is a feasible successor - a loop-free backup route. When a route goes down, the router will first check its topology table for a FS. If there is one, it is installed in the routing table and the route does not go into active state. A topology table can hold more than one FS for a particular destination. b. To be a FS, the next-hop router much have an AD less than the FD of the current successor route. 13. Describe the following terms: a. Successor - A neighbor router that has the best path to a destination. b. Feasible successor - A neighbor router that has a loop-free alternative path to a destination. c. Hello - A multicast packet used to discover neighbors d. Topology table - A table that contains FS information e. IP - A network protocol that EIGRP supports f. Update - A packet sent by EIGRP routers when a new neighbor is discovered and when a change occurs. g. IPv6 - A network protocol that EIGRP supports h. Routing table - The AD determines routing information that is included in this table. i. DUAL - An algorithm used by EIGRP that ensures fast convergence j. IPX - A network protocol that EIGRP supports 14. The following is part of the output of the show ip eigrp topology command, what do the numbers in parentheses mean? P 10.1.3.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 10514432 via 10.1.2.2 (10514432/28160), Serial0/0/0 a. The first is the FD for the network through the next-hop router, and the second is the advertised distance from the next-hop router to the destination network 15. True or False? a. EIGRP performs autosummarizaion. - True b. EIGRP autosummarizaion cannot be turned off. - False c. EIGRP supports VLSM. - True d. EIGRP can maintain independent routing tables. - True e. The EIGRP hello interval is an unchangeable, fixed value. - False 16. How do IGRP and EIGRP differ in their metric calculation? a. They use the same metric formula, but IGRP used 24-bit representation while EIGRP uses 32-bit representation. This allows for a more gradual decision to be made when determining successor and feasible successor. 17. What units are the bandwidth and delay parameters in the EIGRP metric calculation? a. The default formula is metric = bandwidth + delay. b. Delay is the sum of the delays in the path in tens of microseconds, multiplied by 256 (show interfaces command displays delay in microseconds). c. Bandwidth is determined by the minimum bandwidth link along a path (in kbps) and dividing 107 by this value, then multiplying the result by 256. 18. What are some of the tasks that should be listed in the implementation plan for EIGRP? a. enabling EIGRP b. configuring proper network statements c. configuring the metric to proper interfaces (optional) 19. Router A has 3 interfaces with IP addresses 172.16.1.1/24, 172.16.2.3/24, and 172.16.5.1/24. What commands would be used to configure EIGRP to run in autonomous system 100 on only interfaces with the addresses 172.16.2.3/24 and 172.16.5.1/24? RouterA(config)#router eigrp 100 RouterA(config-router)#network 172.16.2.0 0.0.0.255 RouterA(config-router)#network 172.16.5.0 0.0.0.255 20. What does the passive-interface command do when configured with EIGRP? a. It prevents routing updates from being sent through the specified router interface. 21. Router R1 is configured with the ip default-network 172.17.0.0 command, and the network 17.17.0.0 command under the EIGRP process. Router R2 is an EIGRP neighbor to R1 and learns about the 172.17.0.0 network from R1. How are the routing tables on both routers affected by the ip default-network 172.17.0.0 command? a. R2 will flag the 172.17.0.0 network as a candidate default route, and will set its gateway of last resort to R1's IP address. b. R1 will have 172.17.0.0 flagged as the default route, and also have it as its gateway of last resort. 22. Routers A and B are connected and running EIGRP on all their interfaces. Router A has 4 interfaces, with IP addresses: 172.16.1.1 /24 172.16.2.3 /24 172.16.5.1 /24 10.1.1.1 /24 Router B has 2 interfaces, with IP addresses: 172.16.1.2 /24 192.168.1.1 /24 There are other routers on the network that are connected on each of the interfaces of these two routers that are also running EIGRP. What summary addresses will Router A generate automatically (assuming autosummarization is enabled)? a. 172.16.0.0 /16 b. 10.0.0.0 /8 23. What are some true statements about EIGRP and Layer 2 WAN protocols? a. For Frame Relay point-to-point interfaces, set the bandwidth to the CIR. b. For Frame Relay multipoint connections, set the bandwidth to the sum of all CIRs. c. For generic serial interfaces such as PPP and HDLC, set the bandwidth to match the line speed. d. CIR = Committed Information Rate - specified amount of guaranteed bandwidth (measured in bits per second) on a Frame Relay service 24. Router R1 with IP address 172.16.1.1 can reach Router R2 with IP address 172.16.1.2 over a Frame Relay connection. The DLCI of the connection on R1 is 100 and the DLCI of the connection on R2 is 200. What is the command that configures a static map on Router R1 so that R1 can send EIGRP updates to R2? a. frame-relay map ip 172.16.1.2 100 broadcast b. Router R2's IP address with R1's DLCI 25. On what type of interfaces is split horizons either enabled or disabled by default? a. Split horizons is disabled on Frame Relay physical interfaces. b. Split horizons is enabled on Frame Relay multipoint subinterfaces. 26. What does the EIGRP neighbor command do? a. EIGRP neighbor command defines a neighboring router with which to exchange EIGRP routing information. The information is exchanged via unicast rather than multicast. The router will not process incoming multicast EIGRP packets on that interface, and will no longer send multicast EIGRP packets. 27. What are the differences between a Layer 2 MPLS VPN and a Layer 3 MPLS VPN? a. A layer 2 MPLS VPN provides layer 2 service to the backbone where routes connected together are on the same subnet. It is just like switching. b. A layer 3 MPLS VPN provides layer 3 service to the backbone, where routers are connected to edge ISP routers and separate subnets are used on either end. It is just like routing. c. MPLS = multiprotocol label switching 28. You are deploying EIGRP over EoMPLS (Ethernet over MPLS). Your main office has R1 connected to a provider edge router PE1. A branch office has R2, connected to a provider edge router PE2. Between which routers is and EIGRP neighbor relationship formed? a. Between the main office's R1 and the branch office's R2. To EIGRP, routers PE1 and PE2 as well as the MPLS backbone are nonexistent. 29. Router A has 4 EIGRP paths to a destination. Path 1 has a metric of 1100. Path 2 has a metric of 1200, path 3 has a metric of 2000, and path 4 has a metric of 4000. Assuming no potential routing loops exist and the command variance 3 is configured on Router A, which paths would be included for load balancing? a. Paths 1, 2, and 3. b. For load balancing, the routing table will only use feasible paths. This means the path must be loop-free, and the metric of the path must be lower than the variance multiplied by the best path's feasible distance (metric). So the best path above is Path 1 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. at 1100. 1100 x 3 = 3300 - the router will only add paths with a metric below that number. Router A has the following configuration: interface s0 ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 100 40 bandwidth 256 router eigrp 100 network 10.0.0.0 What is the maximum bandwidth (in kbps) that EIGRP uses on the s0 interface? a. 102 kbps b. The command ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 100 40 means that the EIGRP AS 100 will only use 40% of the available bandwidth on an interface. What is the default EIGRP authentication? a. None When configuring EIGRP authentication on a link, does each router have a unique password? a. No, they must be using the same password. What does the accept-lifetime command do for EIGRP authentication? a. It specifies a time period where a key will be accepted for use on received packets. This is optional. What command is used to troubleshoot EIGRP authentication? a. debug ip eigrp packets What is the default EIGRP stuck-in-active timer? a. 3 minutes. With the EIGRP active process enhancement, when does the SIA-Query get sent? a. At the midway point of the stuck-in-active timer. This is 1.5 minutes by default. b. This validates the status of a neighboring router so it will not terminate neighbor relationship. How does EIGRP summarization limit the query range? a. A remote router will only extend a query about a network when it has an exact match to the network in its routing table. How does the EIGRP stub feature limit the query range? a. EIGRP queries are not sent to stub neighbors. What does the eigrp stub receive-only command do? a. It configures a router as a stub and will not allow it to share it routes (connected, static, or summary). In which EIGRP packet type are goodbye messages sent? a. Hello packets