The Quality Improvement Model
advertisement
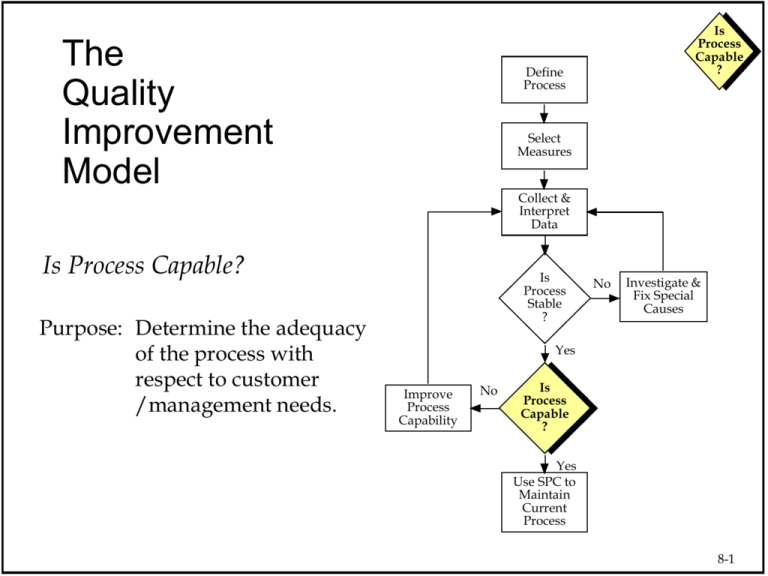
The Quality Improvement Model Define Process Select Measures Collect & Interpret Data Is Process Capable? Purpose: Determine the adequacy of the process with respect to customer /management needs. Is Process Capable ? Is Process Stable ? No Investigate & Fix Special Causes Yes Improve Process Capability No Is Process Capable ? Yes Use SPC to Maintain Current Process 8-1 Is Process Capable ? Capable Process A stable process that meets customer requirements. Histogram Control Chart UCL CL LCL 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 Run Order Lower Spec Target Upper Spec Capability assessments for unstable processes, may not be indicative of how the process is actually performing. 8-2 Assessing Process Capability Counting Measures Is Process Capable ? The average percent defectives. The average number of defects. Instrument Measures Comparing both the center of the process and the process variation 8-3 Capability Assessment for Counting Measures “Order Entry Process” Week # Errors 1 15 2 22 3 18 4 10 5 13 6 9 7 27 8 12 9 24 10 22 11 8 12 8 13 26 14 16 15 20 16 10 17 16 18 9 19 15 20 20 Total 320 Control Chart 35 30 Number of Errors Is Process Capable ? UCL=28.0 25 20 Avg=16.0 15 10 5 0 LCL=4.0 5 10 15 20 Week Is this process adequate as is? Should it be improved? 8-4 Measures of Process Capability USL - LSL Cp = Specification Range = 6sc True Process Range Is Process Capable ? Cp < 1.0 Process is not capable of meeting specs Cp = 1.0 Process is marginally capable Cp > 1.0 Process is capable of meeting specs Problem: We are assuming the process has a target that is in the center of the specification range, and that the process is in fact centered on that target. Distance from process average specification limit = min (USL - x , x - LSL) Cpk = to closest 1 True Process Range 3sc 2 Note: a negative result is possible if the process average is outside specifications Cpk < 1.0 Process is not capable of meeting specs Cpk = 1.0 Process is marginally capable Cpk > 1.0 Process is capable of meeting specs Benefits: • Optimal values are attained by running exactly between specs. • Can (must) be used for 1-sided specifications Warning: Capability assessments for unstable processes, may not be indicative of how the process is actually performing. 8-5 Is Process Capable ? Process Capability LSL USL How much material is out of spec? In the short term? In the long term? 8-6 Is Process Capable ? Process Capability Ratios LSL USL Voice of The Process Voice of The Customer 8-7 Is Process Capable ? 8-8 Process Capability - The Strategy Is Process Capable ? Centering –The Process Is On Target Spread – Reduce The Variation Defects LSL Defects USL 8-9 Process Capability Ratios Is Process Capable ? 2 Key Metrics for Measuring Capability USL LSL Cp 6sc X- LSL USL- X Cpk Min( , ) 3sc 3sc 8-10 Process Capability Ratios - Concept Is Process Capable ? USL LSL Cp 6sc Cp Total Tolerance Process Spread 8-11 CP & CPK Measure Short-term I Chart for C1 Capability 39 Is Process Capable ? Is The Process In Control ? Is It Producing Defects ? Individual Value 3.0SL=37.36 34 X=30.60 29 24 -3.0SL=23.84 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Observation Number A Short-term Capability study covers a relatively short period of time (days, weeks) generally consisting of 30 to 50 data points. The actual number depends on the subject under study. 8-12 Long Term Performance I Chart for C3 Is Process Capable ? 50 Is The Process In Control ? Is It Producing Defects ? Individual Value 3.0SL=47.12 40 Short term Capability X=33.80 30 -3.0SL=20.49 20 0 50 100 Observation Number A long-term capability study covers a relatively long period of time (weeks, months) generally consisting of 100-200 data points. Again, the actual amount depends on the subject under study. 8-13 A Further Look at Capability Is Process Capable ? Compare the estimates of the process deviations from the short-term and long-term data Descriptive Statistics Variable short term long term N 30 180 Mean 30.6 33.8 StdDev 2.23 4.44 What is the difference between the short-term and the long-term data? What implication does this have in doing capability studies? 8-14 Measures of Process Performance Pp = Specification Range = USL - LSL 6ss True Process Range Is Process Capable ? P p < 1.0 Process Performance is not meeting specs P p = 1.0 Process Performance is marginally meeting specs P p > 1.0 Process Performance is meeting specs Problem: We are assuming the process has a target that is in the center of the specification range, and that the process is in fact centered on that target. Distance from process average to closest specification limit min (USL - x , x - LSL) P pk = = 1 3ss True Process Range 2 Note: a negative result is possible if the process average is outside specifications Ppk < 1.0 Process Performance is not meeting specs Ppk = 1.0 Process Performance is marginally meeting specs Ppk > 1.0 Process Performance is meeting specs Benefits: • Optimal values are attained by running exactly between specs. • Can (must) be used for 1-sided specifications 8-15 Performance vs. Capability Is Process Capable ? Days Outstanding 55 Days CO2Sales Levels for 55 Timefor Points 14 DSO CO2-Shrt 13 12 11 10 Index 10 20 30 40 50 These data show that the process, if well controlled can perform much better than it currently is 8-16 Is Process Capable ? Capability vs. Performance Days Outstanding 55 Days CO2Sales Levels for 55 Timefor Points 14 DSO CO2-Shrt 13 12 11 10 Index 10 20 30 40 50 Capability: Only random or short term variability Process Performance: Total Variation including shifts and drifts (Cp & Cpk) (Pp & Ppk) 8-17 Process Performance Ratios P p Is Process Capable ? USL LSL 6ss X- LSL USL- X P pk Min( , ) 3ss 3ss The P-family of indices are computationally the same as the C-family of ‘capability’ indices, but use the observed long-term standard deviation. 8-18 WARNING!!! Is Process Capable ? Statistical Assumptions Made In Capability Studies 1. Data Comes From a Stable Process If not, work towards getting the process in control Don’t despair, you can still make some assumptions about your process in the mean time 8-19