What Is the Role of Pigments in Photosynthesis?
advertisement

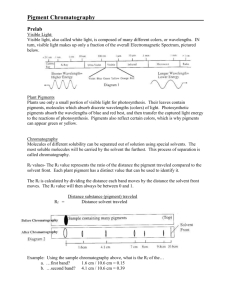
What Is the Role of Pigments in Photosynthesis? Light and Pigments Role of Pigments Pigments are light-absorbing colored molecules. Different pigments absorb different wavelengths of light. Chlorophylls are the major lightabsorbing pigments in plants. They absorb energy from violet-blue light and reflect green light, giving plants their green color. Chloroplast Accessory Pigments Role of Accessory Pigments: Accessory pigments help plants absorb additional light. Plants need to make these accessory pigments to maximize the amount of photosynthesis they can do. More pigments = More glucose or food for the plant! Types of Accessory Pigments Carotenoids: reflect yellow, orange, and red light. Carotenoids give carrots and sweet potatoes their orange color and are very common in our area. Anthocyans: reflect red, blue, violet light. Xanthophylls: reflect yellow light. Accessory Pigments Accessory pigments are the reason leaves change colors in autumn. In green leaves, there is so much chlorophyll that it masks the other pigments. In autumn, as trees prepare to lose their leaves, the chlorophyll molecules break down, revealing the colors of other pigments. The colors red, yellow, and orange can be seen. Chlorophyll a and b http://file.scirp.org/Html/4-1190315%5C8cdaa9b5-1607-4e22bf41-2766e06060c9.jpg Absorption Spectrum http://www.emeraldecocity.com/clip_image002_0009.jpg Differences in chlorophyll Chlorophyll a will absorb light at 665 and 465 nm Chlorophyll b will absorb light at 640 and 450 nm Chlorophyll a has a CH3 group Chlorophyll b has a C=OH group (wider range of light absorbed=many plants are green) Uses for Chromatography • Chromatography is used by scientists to: Analyze – examine a mixture, its components, and their relations to one another • Identify – determine the identity of a mixture or components based on known components • Purify – separate components in order to isolate one of interest for further study • Quantify – determine the amount of the a mixture and/or the components present in the sample How does chromatography work? Solubility of molecule in solvent used (better solubility further it will move) Size of molecule (bigger, slower) Attraction to the paper Longer time, better separation Purpose: Do green leaves contain other pigments? 1.Obtain a strip of chromatography paper. 2. Use a ruler to measure and draw a light pencil line 2-cm above the bottom of the paper strip. 3. Place the edge of the spinach leaf over the pencil line and using the edge of a coin gently press on the spinach leaf to create a single green line over the pencil line. You want this line to be thin and concentrated with the pigment from the spinach leaf. Therefore, repeat this edging process carefully about 3-4 times. Be sure not to press too hard or you will poke a hole through the paper. 4. Carefully add isopropyl alcohol to the beaker until it reaches a depth of 1-cm in the beaker. 5.Fold the top of the paper strip so that the end of the strip with the green line hangs down. The paper should be folded over the top of the beaker with the bottom of the paper strip just touching the alcohol. DO NOT have alcohol touch spinach line 6. Record observations in data table. Results: Each pigment has an Rf value, the speed at which it moves over the paper compared with the speed of the solvent. Rf = Distance moved by the pigment Distance moved by the solvent Measure the distance in cm from the starting point (pencil line) to the center of each pigment band. Then measure the entire distance traveled by the solvent. Remember, the starting point for the solvent is also the pencil line and the ending point for the solvent is the top edge of the paper. Do the required divisions and record your Rf values in the DATA TABLE of your report sheet. Images: http://www.chs.helena.k12.mt.us/faculty/hbosch/biologytopics_file s/webnotes/ch%208%20and%209/Ch8and9review_files/image002. jpg http://mrhalverson.com/2010B_chromatogram.png Rf results: Carotene: 1 Xanthophyll: 0.615 chlorophyll a:0.340 Chlorophyll b: 0.231