HIAT/MCPS/2007
advertisement

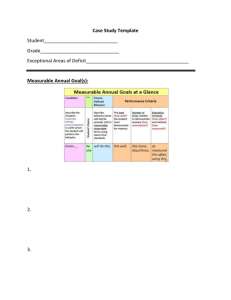
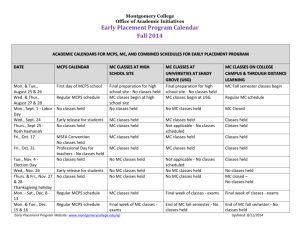
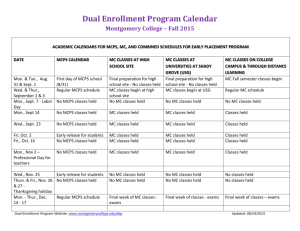
Beth Poss, Instructor 301-407-0617(h) 301-367-8763(c) Beth_J_Poss@mcpsmd.org possbeth@gmail.com Welcome! Introductions/Warm-up Syllabus Course expectations Weekly Web Crawl Assignments Universal Design for Learning Introduction UDL Scavenger Hunt Wrap Up How Do You Use Technology? With Students Personal Work/Productivity Syllabus Weekly Web Crawl Class begins at 5:00 Web Crawl for the week www.matnonline.com >MATN Wiki >Towson Sped 646 20-30 minutes to explore website and resources available Universal Design for Learning An Introduction Today’s Objectives: Define Universal Design (UD) Define Assistive Technology Differentiate AT from UD Examine principles of UD Explore federal regulations impacting UD/AT Explore ways AT can support UD Find UD in place at USGC Casey’s Story Casey is seventeen years old and is a sophomore in high school. He was a sophomore last year also, but because he is entitled to an education through age 21, his team decided he should do 2 sophomore years, 2 juniors years and 2 senior years. He spends the morning in the special education classroom learning skills he will need someday in the real world. At noon, an aide brings him his lunch in the special education room. After lunch he goes to a 9th grade art class. He sits in the back of the room with his aide and works on counting and color recognition skills. Instead of a report card, at the end of each quarter Casey gets stickers for the number of “good days” he had in school. The Art teacher gives him a pass/fail grade. Art is the only general education class he takes as his team feels he wouldn’t get anything out of any of the other high school classes. There is some discussion that perhaps he could spend a day a week at the middle school taking a music class. Casey spends his afternoons in the community—shopping, taking a bus, crossing streets, and bowling. When in the community he uses a Barney backpack that was purchased for him to hold all of his things. When at school, he keeps his things in a cubby in the special education classroom. Everyday after school Casey goes home and spends much of his afternoon watching videos of Grease, Cabaret, West Side Story, Phantom of the Opera, and Rent. He can act out many of the parts and sings most of the songs. He would love to someday be in a play. When asked about friendships, Casey reports that his best friend is Ms. White, the school nurse, and Miss Angela his teacher. Casey wants a job so he can earn some money. It was arranged that he would volunteer at the town library one day every other month. A meeting to discuss Casey’s IEP is scheduled for next month. It was scheduled in the morning so that Casey’s aide that works with him in art could attend the meeting and one of the other aides could work with Casey during that time. Last month a school-wide career fair was held at the school. Because the special education classroom was temporarily converted into the “Computer Careers Center”, Casey’s time in the community was increased to full days so that he wouldn’t miss out on opportunities to learn vocational skills. His team has agreed to support Casey to attend a school dance once he has successfully mastered (with 85% accuracy) the socialization goals on his IEP. Casey wants a girlfriend. What is wrong with this picture? Universal Design for Learning Included materials from Marsye Kaplan, Rebecca Mahoney Universal Design Definition •Concept or philosophy for designing products and services that are usable by people with the widest possible range of functional capabilities. What is the intent of UD? To simplify life for everyone by making products, communications, and the built environment more usable by as many people as possible at little or no extra cost. Universal design benefits people of all ages and abilities. From http://www.design.ncsu.edu:8120/cud/univ_design/ud.htm Work smarter not harder! How did the term originate? Architectural term--Center for Universal Design UD examples Curb Cuts Captioning Automatic Doors Ramps Universal Design For Learning—UD in the World of Education (UDL) Children with disabilities do not constitute a separate category, but fall along a continuum of learning differences. Leads us to make adjustments for learner differences for all students, not just those with disabilities. Development and use of curriculum materials varied and diverse, including digital and online resources, rather than centering instruction on a single text book. transforms the old paradigm of “fixing” students, so that they can manage a set curriculum, into a new paradigm that “ fixes” the curriculum by making it flexible and adjustable. Http://www.cast.org Universal Design vs. Assistive Technology Wide range of students AT specifically considered for an with diverse learning individual student needs Used by a student to Makes the curriculum meet the expectations accessible -students with of a given curriculum varying needs Implemented by general Under review of special educators education teachers IEP based Universal Design For Learning Tips Teachers’ technology skills must be relatively well developed and supported with ongoing opportunities for learning There must be a clearly defined, but flexible curriculum in place. The software and instructional materials must be compatible with both the curriculum and with the range of existing students needs. UD in Education Universal Design for Learning David Rose-http://cast.org Materials and curriculum Present materials in multiple ways Multiple ways for students to demonstrate learning Provide multiple ways for students to interact and make meaning out of curriculum and materials UDL in Education cont. Provide options for demonstrating knowledge and skills Offer instruction and student response through distance learning Make materials available electronically as much as possible Provide material in multiple formats This is a process, as we learn from our experiences we will continue to add to the list. • In the mid 1990’s, the concept of universal design was applied to education (www.cast.org) • UDL is a national initiative at this time in the educational world because the technology is available to make it happen. ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 • In 1975, PL 94-142 promoted “education for all.” • This was huge step forward, focusing more attention on the individualized needs of students with disabilities. • This resulted in an IEP driven curriculum that was parallel to the general education curriculum. ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 In special education classrooms, students made progress, but grew further behind compared to peers. Upon graduation, this resulted in students having fewer post secondary opportunities. IDEA focuses on access, participation AND progress in relation to peers. ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 • Special education staff can no longer work separately from general education. • General educators and special educators need to collaborate to design good instruction with a shared understanding of standards and benchmarks. • No single medium and method will work for all students. • Differentiated instructional (DI) strategies as well as flexible materials©HIAT/MCPS/2007 benefit all students (UDL). No UDL is a framework to support the range of learners that exist in typical classrooms. This would include gifted students, disengaged students, ELL students, as well as, students with documented disabilities. ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 …harnesses the power and flexibility of modern technology. Technology provides the flexibility needed to adjust to learner differences ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 Students have: Teachers provide: 1. Flexible ways of presenting lesson content 1. Options for how they learn 1. Choices which will 1. Flexible options for student engagement engage student interest 1. Flexible methods of expression, and assessment 3. Choices for how they demonstrate their learning ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 Options for how students learn ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 Traditional Text ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 E-Text: Electronic Text of Holes using Kurzweil Software ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 • Prereading chapter summaries ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 Houghton Mifflin Social Studies Online Chapter Summary ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 Giving students choices ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 Choices to express new learning: • Paper and pencil • MS Word • Portable word processors (Alphasmart/NEO) • PowerPoint • Windows Movie Maker ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 Options for how students demonstrate their learning ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 Typing instead of writing for students who need handwriting and spelling support. ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 • Both DI and UDL are frameworks for instruction, but UDL is a framework that guides instructional materials as well as methods. • UDL focuses on the flexible capacity of new media, and therefore, the use of digitized instructional materials. • AT is concerned with individuals – UDL is concerned with all students ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 Designing Lessons Hall, Strangman & Meyer, 2003 ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 Opportunities • Increase awareness of UDL principles. • Make a commitment as a school to make curriculum materials more flexible. • School collaboration to shift to a more universally designed curriculum. ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 • Learn to create flexible, digital materials. • Training on the tools available at your school. • Use the Web to locate curriculum specific digital materials. • Build an a personal and school inventory of digital materials. ©HIAT/MCPS/2007 by Alec Couros from http://franksblog.edublogs.org/2008/03/29/helpingcolleagues-get-connected-one-by-one/