Practice Problems In the general population, the prevalence of
advertisement

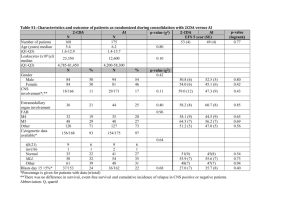
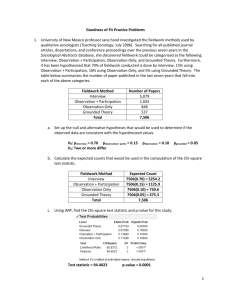
Practice Problems 1. In the general population, the prevalence of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is estimated to be about 5% in male adults. In a southwestern city, 95 male firefighters were randomly selected and surveyed, and it was found that 10 of the 95 (10.5%) had PTSD. Research Question - Does this provide evidence that the prevalence of PTSD is higher for male firefighters in this southwestern city than for males in the general population? a. Define the population of interest. All male firefighters b. Define the sample for the study. 95 firefighters selected c. Define the variable of interest for the study. PTSD Status d. Suppose you wanted to conduct a simulation study to answer the research question of interest. Using the online applet, carry out a simulation with 500 trials and sketch your plot below. You’re graphs will vary, but you should have changed the probability to 0.05 and set the number of tosses to 95 as shown below. e. Using the plot created in part d, calculate the estimated probability of observing results at least as extreme as observed. Using your plot you’ll want to find P(X ≥ 10) = # dots 10 & above 500 1 f. Using the estimated p-value found in part e, does this study provide evidence that the prevalence of PTSD is higher for male firefighters in this southwestern city than for males in the general population? Explain. If your p-value < 0.05 then there IS EVIDENCE the prevalence of PTSD is higher for firefighters than for the general population. If your p-value is > 0.05 then there is NO EVIDENCE the prevalence of PTSD is higher for firefighters than for the general population. 2. Wagenknect et al. (2002) collected data on a sample of 301 Hispanic women living in San Antonio, TX. One variable of interest was the percentage of subjects with impaired fasting glucose (IFG). IFG refers to a metabolic stage intermediate between normal glucose homeostasis and diabetes. In the study 24 women were classified in the IFG stage. The article sites population estimates for IFG among women in Texas was 6.3%. Research Question – Is there sufficient evidence to indicate that the population of Hispanic women in San Antonio has a prevalence of IFG higher than 6.3%? a. Define the population of interest. All Hispanic women living in San Antonio, TX b. Define the variable of interest for the study. IFG Status c. Describe in context how this study can be modeled using a binomial distribution. 1. 2. 3. 4. n = 301 women 2 outcomes – Have IFG, Does not have IFG P(IFG) = 0.063 for each Hispanic woman Hispanic women are independent of each other d. Assuming 6.3% of women in Texas are classified as having IFG, how many of the 301 Hispanic women living in the San Antonio area would you expect to be classified as having IFG? 301(0.063) = 18.96 2 e. Using JMP, find the probability of observing results at least as extreme as observed. P(X ≥ 24) = 0.1416 f. Using the p-value found in part e, does this study provide evidence that the population of Hispanic women in San Antonio has a prevalence of IFG higher than 6.3%? Explain. No Evidence (p-value = 0.1416) that the population of Hispanic women living in San Antonio, TX has a prevalence of IFG higher than 6.3%. 3. A Pew Research Center survey found that 1,120 of the 1,931 adult internet users interviewed said that the internet has helped them in some way with obtaining health information. a. Using JMP construct a 95% confidence interval for the true proportion of adult internet users who say the internet has helped them in some way with obtaining health information. b. Interpret the interval found in part a. 95% confident the true proportion of adult internet users who say the internet has helped them in some way with obtaining health information is between 0.06 and 0.60. 3 4. University of New Mexico professor Jane hood investigated the fieldwork methods used by qualitative sociologists (Teaching Sociology, July 2006). Searching for all published journal articles, dissertations, and conference proceedings over the previous seven years in the Sociological Abstracts database, she discovered fieldwork could be categorized as the following: Interview, Observation + Participation, Observation Only, and Grounded Theory. Furthermore, it has been hypothesized that 70% of fieldwork conducted is done by interview, 15% using Observation + Participation, 10% using Observation Only, and 5% using Grounded Theory. The table below summarizes the number of paper published in the last seven years that fall into each of the above categories. Fieldwork Method Interview Observation + Participation Observation Only Grounded Theory Total Number of Papers 5,079 1,042 848 537 7,506 a. Set up the null and alternative hypotheses that would be used to determine if the observed data are consistent with the hypothesized values. H0: pinterview = 0.70 pobs + part = 0.15 Ha: Two or more differ pobservation = 0.10 pgrounded = 0.05 b. Calculate the expected counts that would be used in the computation of the Chi-square test statistic. Interview 7506(0.70) = 5254.20 Observation + Participation 7506(0.15) = 1125.9 Observation Only 7506(0.10) = 750.6 Grounded Theory 7506(0.05) = 375.3 c. Using JMP, find the Chi-square test statistic and p-value for this study. Test Statistic = 94.4023 p-value = 0.0001 d. Using the p-value from part c, is there evidence that the observed data are consistent with the hypothesized values? Explain. Evidence (p-value = 0.0001) that the observed data is not consistent with the hypothesized values. 4