Muscular System outline PPT
advertisement

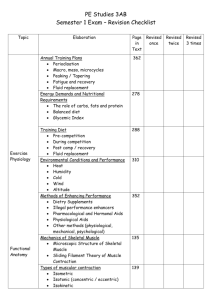
Muscular System Outline 1. Skeletal 2. Visceral 3. Cardiac 3 Types of Muscle Tissue Aid in movement Provide and maintain posture Protect internal organs Provide movement of blood, food and waste products throughout the body Open and close body openings Produces heat Functions of Muscle Contraction = movement and shortening of muscle Tonus = slight continuous contraction Flacid = soft, not contracted Vocab 1. Electrically 2. Mechanically 3. Chemically Muscle stimulation Irritability or excitability: ability to respond to a stimulus Contractility: ability to shorten Extensibility: ability to stretch and lengthen Elasticity: ability to recoil to its resting length Vocabulary Makes up 40 % of body weight Increase in size and weight with exercise Named according to: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Location Related bones Shape Action size Looks striated under microscope Tendons attach muscle to bone Skeletal Muscle Sarcomere: - Causes contraction - Made up of actin and myosin Units of Muscle Fibers 1. Origin: attached to the less movable part of bone – proximal attachment 2. Insertion: attached to the more movable part of the bone – distal attachment 3. Body: middle part of the muscle 3 parts of Skeletal muscle Flexion = decreasing joint angle Extension = increasing joint angle Abduction = movement away from midline Adduction = movement towards the midline Pronation = turning palms down Supination = turning palms up Fill in movement Definitions Lines organs Makes up walls of blood vessels In the digestive system Smooth – has no striations Contracts when stimulated Controlled by the autonomic nervous system Visceral Muscle Only in the heart Striated muscle Involuntary control Cardiac Muscle Sliding Filament Theory of muscle contraction Sliding Filament Theory of muscle contraction Types of Muscle Contraction Isotonic: muscle shortening produces movement through a full range of motion Muscle tone (Tonus) : partial contraction, maintains posture Isometric: contraction/shortening of muscle with no movement Tetanic: continued contraction of muscle Fibrillation; uncoordinated contraction of muscle fiber Convulsion; groups of muscles contract in abnormal manner Spasms: involuntary contractions