Rights & Freedoms - mrs. black's website
advertisement

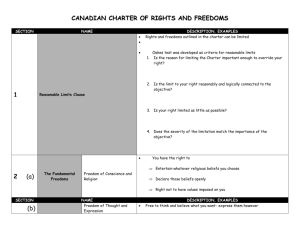
Unit #2 Would the Charter of Rights and Freedoms have any application in April’s complaint? What is the difference between a right and a privilege? Right vs Freedom RIGHT a legal, moral, or social entitlement What we can expect Ex. Right to be presumed innocent FREEDOM Ability to go about your business without interference from the government Ex. Freedom of speech Brainstorm: Rights & Freedoms With a partner, create a list of pros & cons of the Charter. Evolution of Canada’s Rights and Freedoms 1. CANADIAN BILL OF RIGHTS Drafted in response to horrendous human rights abuses in WWII Recognized many rights and freedoms It was a federal statute Problems: ○ Easily changed because it did not have authority over other statutes ○ Equality issues Evolution of Canada’s Rights and Freedoms 2. CANADIAN CHARTER OF RIGHTS AND FREEDOMS Included in Constitution Act, 1982 Entrenched our rights ○ Rights and freedoms can only be changed by an amendment to the Constitution (so very difficult) Enforced by the Supreme Court ○ Judges will strike down laws that violate the Charter Problems: ○ Written too broadly???? Lets look at some of the sections of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 1: REASONABLE LIMITS CLAUSE Rights and freedoms outlined in the Charter can be limited as long as the limits are reasonable (justified) Rights are NOT absolute Ex. R.I.D.E Program Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 33: NOTWITHSTANDING CLAUSE Allows the federal and provincial governments to pass laws that are exempt from section 2 (fundamental freedoms) and 7-15 (legal & equality rights) in the Charter Exemption lasts for 5 years, then must be renewed Ex. Quebec Exemption Clause (Sept 2013) Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 2: FUNDAMENTAL FREEDOMS (a) - Freedom of Conscience and Religion You have the right to: Entertain the religious beliefs you choose Declare those beliefs openly without fear Right not to have values imposed on us (ex. no longer say the Lord’s Prayer in school) Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 2: FUNDAMENTAL FREEDOMS (b) - Freedom of Thought and Expression to think and believe what you want – express through writing, speech, painting, photography, etc. Free Freedom of the press and other media Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 2: FUNDAMENTAL FREEDOMS (c) - Freedom of Peaceful Assembly to gather peacefully – ex: political demonstrations Freedom Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 2: FUNDAMENTAL FREEDOMS (d) – Freedom of Association Freedom to connect with other people or groups – ex: unions, political parties Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 3-5: DEMOCRATIC RIGHTS 3 – Right to Vote Right to vote in an election and run for office Subject to reasonable restrictions such as age, mental capacity, residence, and registration 4 – Election Opportunity to elect a new federal and provincial government every five years except under extraordinary circumstances – ex: war Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 3-5: DEMOCRATIC RIGHTS 5 – Parliament & Legislative Assemblies Parliament and legislative assemblies must hold at least one session a year Provides an opportunity for both elected members and the public to question government actions and policy Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 6: MOBILITY RIGHTS Concerns the rights of Canadian citizens to move in and out of the country and between provinces Ex. People are free to live here in Waterloo, then move out to BC (as Mrs. Black did) In 1991, Richard Sauve, who was serving a life sentence for first-degree murder, challenged the Canada Elections Act arguing that s.51 c, which denied the right to vote to all inmates serving sentences, violated s. 3 (the right to vote) and s. 15 (equality rights) of the Charter. The Supreme Court needed to make a decision on this matter. Prisoner’s Voting Debate Form groups of 6 Separate into two teams of 3 Side 1 – Prisoners should have the ability to vote in elections Side 2 – Prisoners should NOT have the ability to vote in elections Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 7-13: LEGAL RIGHTS 7 – Life, Liberty, & Security of the Person Life - Right to be alive, free from government torture and execution Liberty –Free to act and choose as you want Security – Protects mental state of the individual The life of abortion activist Henry Morgentaler Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 7-13: LEGAL RIGHTS 8 – Unreasonable Search & Seizure Police must have a good reason for searching the person, home, or belongings of an accused The search must be conducted fairly Police can only search for what they have permission to search for Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 7-13: LEGAL RIGHTS 9 – Arbitrary Detention or Imprisonment People cannot be held for questioning, arrested, or kept in jail by the police without good reason Arbitrary means randomly Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 7-13: LEGAL RIGHTS 10 – Rights While Under Arrest or Detention Right to be told why you are being arrested (while being arrested) Right to be told that you may get the assistance of a lawyer – legal counsel is available free of charge if the accused cannot afford a lawyer Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 7-13: LEGAL RIGHTS 11 – Rights When Charged with a Criminal Offence Outlines several rules that protect anyone who has been charged with an offence To be assumed innocent until proven guilty To be tried in court within a reasonable amount of time To not be forced to testify at your own trial The right to trial by jury for serious charges Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 7-13: LEGAL RIGHTS 12 – Cruel and Unusual Treatment or Punishment Governments cannot treat or punish individuals in an unnecessarily harsh manner In deciding what is “cruel” the court considers: The gravity of the offence The personal characteristics of the offender The particular circumstances of the case Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 7-13: LEGAL RIGHTS 13 – Rights of Witnesses in Court Witnesses giving evidence in court cannot have testimony used against them Anyone who is hearing impaired or cannot understand or speak the language used in court has the right to an interpreter Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms SECTION 15: EQUALITY RIGHTS Every citizen is equal before and under the law Every citizen has the right to equal protection and benefit of the law These rights are to be applied equally and without discrimination Assisted Suicide Issue in Canada