Compounds
advertisement

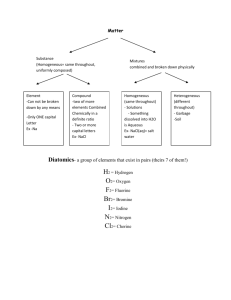
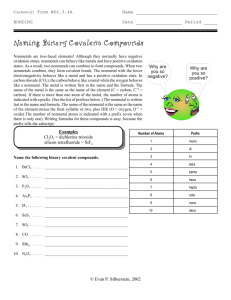
COMPOUNDS WHAT IS A COMPOUND? A pure substance made of 2 or more elements that are chemically combined, forming a molecule. If the proportion of elements is changed in a molecule, the compound changes. Water Hydrogen Peroxide. CO CO2 Properties of a compound are different than properties of the elements that make it up. Compounds do not look like or act like the elements that form them. Water H2O Sucrose C12H22O11 Carbon dioxide CO2 Sodium chloride NaCl Baking soda NaHCO3 3H2O 3 Molecules of water 6Atoms of Hydrogen 3 Atoms of Oxygen 3H2O The 3 is the COEFFICIENT The 2 is the SUBSCRIPT 3H2O The COEFFICIECT tells how many molecules The SUBSCRIPT tells how many atoms. Coefficient X subscript total number of atoms Coefficient X subscript total number of atoms 3H2O Three molecules of water 6 atoms of hydrogen 3 atoms of oxygen Coefficient X subscript total number of atoms CO2 One molecule of carbon dioxide 1 atom of carbon 2 atoms of oxygen Coefficient X subscript total number of atoms 8CO 8 molecules of carbon monoxide 8 atoms of carbon 8 atoms of oxygen Coefficient X subscript total number of atoms H2O2 \ 1 molecule of hydrogen peroxide 2 atoms of hydrogen 2 atoms of oxygen Coefficient X subscript = total number of atoms 6C6H12O6 6 molecules of sugar 36 atoms of carbon 72 atoms of hydrogen 36 atoms of oxygen 144 total atoms Writing CHEMICAL FORMULAS A group of element symbols that shows 2 things: the make-up of elements the ratio of the elements in a compound Examples NaCl (salt) made of 1 Sodium atom and 1 Chlorine atom ratio of elements=1:1 CO2 (carbon dioxide) made of 1 Carbon atom and 2 Oxygen atoms ratio of elements = 1:2 More examples: H2O (water) ratio of elements = 2:1 Ca(OH)2 (calcium hydroxide) ratio of elements= 1:2:2 H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) ratio of elements = 2:2 CO (carbon monoxide) Ratio of elements = 1:1 Assignment: Compound Practice Due Friday Women in Science Day? Do illiterate people get the full effect of Alphabet Soup? In chemistry, metal-nonmetal compounds are called SALTS. 2 RULES FOR NAMING COMPOUNDS Rule #1: METAL-NONMETAL COMPOUNDS Use “ide” ending Metal is always written first EXAMPLES: ZnCl2 Zinc chloride NiI2 Nickel iodide Fe2O3 Iron oxide (rust) MgS Magnesium sulfide Rule #2: NONMETAL COMPOUNDS - use prefixes - “Mono” = 1 “Di” = 2 “Tri” = 3 “Tetra” = 4 EXAMPLES: CO = Carbon monoxide CO2 = Carbon dioxide SO3 = Sulfur trioxide CCl4 = Carbon tetrachloride Some Common Compounds ACIDS HCl - hydrochloric acid (stomach acid) H2SO4 - sulfuric acid (battery acid) HNO3 - nitric acid HC2H3O2 - acetic acid (vinegar) H2CO3 - carbonic acid (in carbonated drinks) BASES NaOH - sodium hydroxide (lye) NH4OH - ammonium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 - calcium hydroxide Mg(OH)2 - magnesium hydroxide (Rolaids, Milk of Magnesia) OTHERS (SOME WE USE IN LABS) C6H12O6 - glucose MnO2 - manganese dioxide CO - carbon monoxide SO2 - sulfur dioxide CuSO4 - copper sulfate PbI2 - lead iodide KI - potassium iodide Fe2O3 - iron oxide (rust) BaCl2 - barium chloride NaNO3 - sodium nitrate ZnCl2 - zinc chloride N2O - nitrous oxide (laughing gas) Let's start with using your flash cards.............. HCl NaOH H2O2 C6H12O6 H2SO4 NaHCO3 HC2H3O2 NaNO3 Ca(OH)2 NH3 H2CO3 MnO2 CuSO4 Mg(OH)2 CaCO3 Fe2O3 CaO ZnCl2 NaOH SiO2 NH4OH N2O PbI2 C2H5OH Dot Diagrams Practice Beryllium Silicon Chlorine Neon Magnesium Argon Sulfur Calcium Lewis Dot Diagrams of the First Three Periods Lithium Sodium Potassium Let's start with using your flash cards.............. Write the compound in your notebook, write the name of the compound next to it. See how many you know! BaCl2 C6H12O6 CuSO4 HNO3 C2H5OH C12 H22 O11 SiO2 Fe2O3 Ca(OH)2 HCl NH3 CaO H2O2 Mg(OH)2 BaCl2 Barium Chloride C6H12O6 Glucose HNO3 Nitric Acid CuSO4 Copper Sulfate C12 H22 O11 Sucrose C2H5OH Ethanol Fe2O3 Iron Oxide NH3 Ammonia Gas SiO2 Silicon dioxide Ca(OH)2 Calcium Hydroxide CaO Calcium Oxide HCl Hydrochloric acid H2O2 Hydrogen peroxide Mg(OH)2 Magnesium hydroxide Molecules A molecule contains two or more atoms bonded together into one particle. Oxygen atom Hydrogen atom Oxygen molecule (O2 ) Water molecule (H2O) Does one atom make a difference in a molecule? CO CO2 Objective: The smallest part of a compound that still has the properties of that compound is called a molecule. Molecules are groups of atoms that are chemically bonded together due to the interactions of their electrons. Today, we are going to construct some basic molecules to strengthen our understanding of why certain atoms prefer to bond with each other. Procedure: Our task today is to construct 15 molecule models. Then, we are going to draw, label and color these models on the back of this sheet. Use the information in the table below when creating your models so that we have consistency throughout the classroom. Provide a key for your drawings. ELEMENT COLOR No. of BONDS Hydrogen Yellow 1 Sodium Purple 1 Chlorine Green 1 Oxygen Red 2 Nitrogen Blue 3 Carbon Black 4 CH4 2 CH4 C2H6 H2 4 H2 H2O 2H2O NaCl 2HCl NaOH 2 H2O2 NH3 CCl2H2 NaNH2 N2 + 2 H2 + 2 O2 Water Molecule H2O Two atoms of hydrogen One atom of oxygen Fire needs oxygen so in this demo, you can see the candle burning normally in air in the presence of oxygen. The combustion reaction is: wax + oxygen in the air ---> carbon dioxide + water C22H44 + 33 O2 ---> 22 CO2 + 22 H2O + heat energy When the baking soda and vinegar combine, they form carbon dioxide gas. Carbon dioxide is more dense than air, so therefore it fills the bottom of the beaker first. The carbon dioxide slowly rises to the top of the beaker, forcing the air with oxygen out of the beaker. Since there is a lack of oxygen, the flame is extinguished. vinegar + baking soda ---> sodium acetate + carbon dioxide gas +water acetic acid + sodium bicarbonate HC2H3O2 + NaHCO3---> NaC2H3O2 + CO2 + H2O