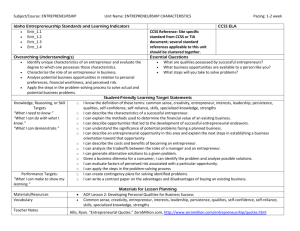
ACCOUNTING Idaho Entrepreneurship Standards and Learning
advertisement
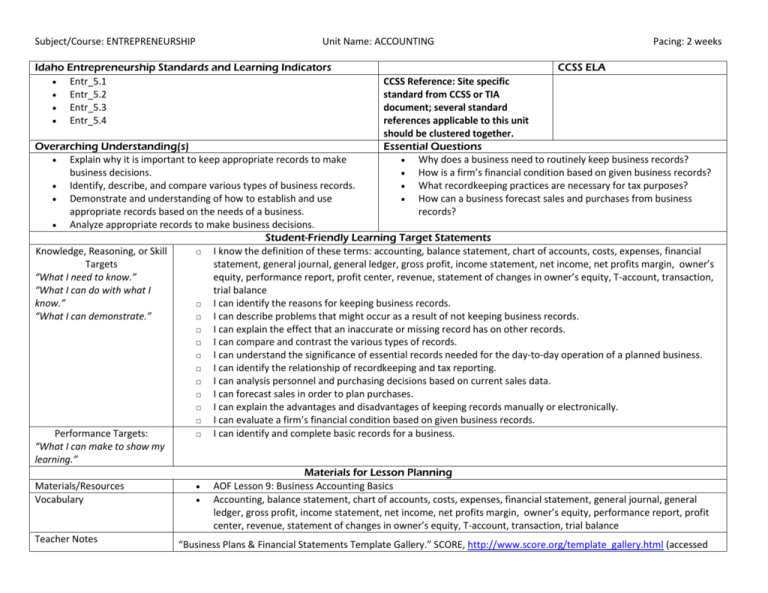
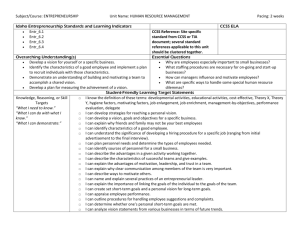
Subject/Course: ENTREPRENEURSHIP Unit Name: ACCOUNTING Idaho Entrepreneurship Standards and Learning Indicators Entr_5.1 Entr_5.2 Entr_5.3 Entr_5.4 Pacing: 2 weeks CCSS ELA CCSS Reference: Site specific standard from CCSS or TIA document; several standard references applicable to this unit should be clustered together. Essential Questions Why does a business need to routinely keep business records? How is a firm’s financial condition based on given business records? What recordkeeping practices are necessary for tax purposes? How can a business forecast sales and purchases from business records? Overarching Understanding(s) Explain why it is important to keep appropriate records to make business decisions. Identify, describe, and compare various types of business records. Demonstrate and understanding of how to establish and use appropriate records based on the needs of a business. Analyze appropriate records to make business decisions. Student-Friendly Learning Target Statements Knowledge, Reasoning, or Skill □ I know the definition of these terms: accounting, balance statement, chart of accounts, costs, expenses, financial Targets statement, general journal, general ledger, gross profit, income statement, net income, net profits margin, owner’s “What I need to know.” equity, performance report, profit center, revenue, statement of changes in owner’s equity, T-account, transaction, “What I can do with what I trial balance know.” □ I can identify the reasons for keeping business records. “What I can demonstrate.” □ I can describe problems that might occur as a result of not keeping business records. □ I can explain the effect that an inaccurate or missing record has on other records. □ I can compare and contrast the various types of records. □ I can understand the significance of essential records needed for the day-to-day operation of a planned business. □ I can identify the relationship of recordkeeping and tax reporting. □ I can analysis personnel and purchasing decisions based on current sales data. □ I can forecast sales in order to plan purchases. □ I can explain the advantages and disadvantages of keeping records manually or electronically. □ I can evaluate a firm’s financial condition based on given business records. Performance Targets: □ I can identify and complete basic records for a business. “What I can make to show my learning.” Materials for Lesson Planning Materials/Resources AOF Lesson 9: Business Accounting Basics Vocabulary Accounting, balance statement, chart of accounts, costs, expenses, financial statement, general journal, general ledger, gross profit, income statement, net income, net profits margin, owner’s equity, performance report, profit center, revenue, statement of changes in owner’s equity, T-account, transaction, trial balance Teacher Notes “Business Plans & Financial Statements Template Gallery.” SCORE, http://www.score.org/template_gallery.html (accessed Subject/Course: ENTREPRENEURSHIP Unit Name: ACCOUNTING Pacing: 2 weeks February 25, 2013). “Cash vs. Accrual Accounting.” Nolo, http://www.nolo.com/legal-encyclopedia/cash-vs-accrual-accounting-29513.html (accessed February 25, 2013). “Preparing Financial Statements.” SBA.gov, http://www.sba.gov/content/financial-statements (accessed February 25, 2013). Richardson, Mary Ann. “Create a General Ledger in Excel from General Journal data.” TechRepublic, http://articles.techrepublic.com.com/5100-10878_11-6164402.html (accessed February 25, 2013). “SBA Forms.” SBA.gov, http://www.sba.gov/tools/Forms/smallbusinessforms/fsforms/index.html (accessed February 25, 2013).