Year 9 Light Trial Test Answers
advertisement

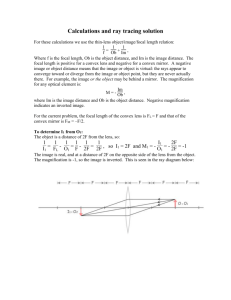
Year 9 General Science – Light Trial Test 2014 Name: _______________________ Class: __________ Instructions: Write answers in the right-hand column. Date: _______ Score: ____________ / 100 marks Section A—Multiple choice (20 marks) 1 mark Each 1 Which ray below is the one that is reflected from a plane mirror? B 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Perspex has a higher refractive index (density) than air. Light entering air from perspex will: A slow down slightly and be bent towards the normal B slow down slightly and be bent away from the normal C speed up slightly and be bent towards the normal D speed up slightly and be bent away from the normal Light travels with a speed at about A. 300,000 meters per second B. 3,000,000 meters per second C. 30,000 kilometres per second D. 300,000 kilometres per second Which of the Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) has the highest frequency? A infrared light B radio waves C X-rays D microwaves Which of the following waves does not belong to electromagnetic radiation? A infrared light B white light C X-rays D sound waves When a pencil is viewed through water, it appears bent because light: A slows down as it passes from water to air B is reflected at the surface of the water C is refracted away from the normal as it passes from water to air D is refracted towards the normal as it passes from water to air What is the meaning of the formation of a REAL image? A You can see the image of an object B The image has the same size as the object C The image can be focused on a screen D The image that is formed by a plain mirror D 1 D 1 C 1 D 1 C 1 C 1 Year 9 General Science – Light Trial Test 2014 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 The image produced by a convex lens when the object is inside the focal length: A enlarged and upright B diminished and inverted C diminished and upright D enlarged and inverted Which of the following(s) can form an image on a screen? A plane mirror B concave mirror C a transparent glass D convex mirror Which of the radiation is involved in scanning luggage at the airport? A X-rays B microwaves C gamma rays D blue light What colour will a green leaf placed in green light appear to be? A black B green C red D blue A 1 B 1 A 1 B The image produced on the back of our eyes (retina) is: A virtual, upright and enlarged B virtual, inverted and diminished C real, upright and enlarged D real, inverted and diminished D What colour is transmitted when cyan light is shone on a green filter? A cyan B blue C green D red C Which colours are absorbed by blue paint? A blue only B red, orange and yellow C green, blue, indigo and violet D red only B In the eye disorder known as long-sightedness, the image of an object forms behind the retina. Long-sightedness is corrected by bringing the image forward using: A convex lenses that bend the light less B convex lenses that bend the light more C concave lenses that bend the light less D concave lenses that bend the light more Which is the correct image formed by the plain mirror? 1 1 1 1 B 1 C 1 17 In a primary rainbow, what colour is at the top of the rainbow? A blue B green C orange D red D 1 Year 9 General Science – Light Trial Test 2014 18 19 20 Comparing microwaves and ultraviolet rays, A microwaves have lower frequencies B ultraviolet rays have longer wavelengths C microwaves have more energy than ultraviolet rays D ultraviolet rays are more visible than microwaves Which of the following colours of light is most strongly refracted? A red B yellow C green D violet A 1 D Three primary colours of light which mix to make white light, they are: A yellow, green, red B cyan, yellow, magenta C green, blue, red D red, green, orange 1 C 1 Section B—Written answers (60 marks) 1 2 3 60o 60o If a light ray strikes a mirror at an angle of 30o to the mirror, what is: a the angle of incidence? b the angle of reflection? a b What is meant by the refraction of light? The bending of a light ray as it passes from one substance into another substance (different media) 2 The diagram on the right shows a light ray travelling through air to the interface between the air and a glass block. 2 Incident ray i On the diagram, draw the normal, and a possible path for the ray in the glass. r Label on the diagram: normal, angle of incidence, angle of refraction, refracted ray, incident ray 4 Which type of lens (convex or concave): a is fatter in the middle than at the ends? b can produce a real image? Refracted ray 4 a convex b convex 3 Year 9 General Science – Light Trial Test 2014 5 Curved mirrors are usually shown in cross-sectional views to indicate their shapes. Three such shapes are shown below. a Diagram I = convex mirror Diagram II= parabolic mirror Diagram III = concave mirror b convex mirror – light diverges out parabolic mirror – light reflects in a parallel manner concave mirror – light converges a Which mirror is which? (parabolic, convex, concave ) b What happen when a spot light is placed in front of each of these mirrors? c Give one use of each of these mirrors. 6 You have two lenses. Lens A is fat and highly curved. Lens B is flatter, being only slightly curved. Which lens (A or B) can be expected to: a bend light the most? b have the longest focal length? c convex mirror – security mirror in shops parabolic mirror – torch, headlight in cars concave mirror – shaving mirror, dental mirror 9 a b Lens A Lens B 2 7 What is the name given to the: a splitting of light into component colours by a prism? b Why do light split up into rainbow colours? c List all the rainbow colours in the correct order. a Dispersion b White light consists of different colours and they travels at different speed and bend differently c Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet 4 Year 9 General Science – Light Trial Test 2014 8 Complete the following table on EMR. Radiation Special Feature Uses microwave wavelengths ranging from 1 mm to 1 m cooking ultraviolet just beyond the visible spectrum sun tanning radiowaves longest wavelength and lowest frequency telecommunication gamma ray shortest wavelength and the most powerful energy cancer treatment visible only spectrum visible to human eye photosynthesis 10 9 This question concerns colours of light. a Name the primary colours of light. b Why are they called primary colours? c Name the secondary colours of light. d Why are they called secondary colours? e Is White a colour? a Red, green and blue. b They can be combined in various proportions to form all the other colours. c Cyan, magenta and yellow. d They are produced when just two primary colours overlap. e Yes, white is a combination of rainbow colours.. 5 10 The diagram below shows combinations of light colours. State the name of the colours seen in a to d. a b c d cyan magenta white yellow 4 Year 9 General Science – Light Trial Test 2014 11 12 What colour (if any) is transmitted when: a white light is shone on a blue filter? b red light is shone on a green filter? c magenta light is shone on a red filter? a b c What colour or colours of light are: a absorbed by a blue shirt? b reflected by a red shirt? c combined to produce yellow light? a b c blue no light red 3 all colours other than blue red red and green 3 13 a What are the three ‘primary colours of pigments’? b Give an example of secondary colour created by 2 primary colours. a b cyan, magenta and yellow e.g blue+yellow = green blue+red = purple red+yellow = orange 2 14 a b c People having short-sightedness is due to the fact that the eyeball is longer than the normal. The image of the far object is formed in front of the retina. Complete the diagrams to illustrate the problem. d What lens can be used to correct this problem? Convex lens – it diverges the light further and reaches the retina – giving sharp focus of image. 8 Year 9 General Science – Light Trial Test 2014