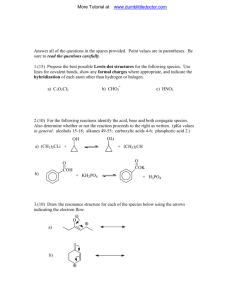
Modeling NMR Chemical Shifts
advertisement

Aromatic Nomenclature Naming substituted benzenes Monosubstituted Benzenes • Most monosubstituted aromatics are named using -benzene as the parent name preceded by the substituent name (as a prefix; all one word): fluoro nitro ethyl F NO2 CH2CH3 fluorobenzene nitrobenzene ethylbenzene Alkyl-substituted Benzenes • Alkyl substituted benzenes are named according to the length of the carbon chain of the alkyl group. • With six carbons or fewer in the alkyl chain, they are named as ‘alkylbenzene.’ • e.g., propylbenzene: CH2CH2CH3 Alkyl-substituted Benzenes • With more than six carbons in the alkyl chain, they are named as a ‘phenylalkane,’ where the benzene ring is named as a substituent (phenyl) on the alkane chain • e.g., 4-phenylnonane CH 3CH 2CH 2 CH2CH2CH3 CHCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 = CHCH 2CH 2CH 2CH 2CH 3 CH3CH2CH2CHCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 4-phenylnonane Common Names of Subs. Benzenes • There are a number of nonsystematic (common) names commonly used for certain monosubstituted benzenes (see next slide) • These ten common names should be memorized. • These common names are used as base names when naming more their more highly substituted derivatives. Examples of these will be given later. Common Names of Subs. Benzenes CH3 NH2 OH toluene OCH3 O C C O anisole C H benzaldehyde benzonitrile CH2 styrene O C OH benzoic acid C N aniline H phenol CH3 CHCH3 cumene CH3 acetophenone The Benzyl Group • The benzyl group is a common name for a methyl substituted benzene (toluene) having substitution for one of the hydrogens on the methyl group. CH2 the benzyl group CH 2Br CH2Br CH2OH benzyl bromide benzyl alcohol Disubstituted Benzenes • Disubstituted benzenes can be named in one of two ways. Each method describes the relative positions of the two groups on the benzene ring. • Systematic numbering of the aromatic ring. • Using the prefixes ortho-, meta-, or para-. • When numbering the ring carbons, carbon # 1 is always a substituted carbon. • The substituents are listed alphabetically. Disubstituted Benzenes ortho- (abbreviated o- ) = 1,2-disubstituted (two groups on adjacent carbons on the ring) F F CH2CH3 Br o-difluorobenzene or 1,2-difluorobenzene o-bromoethylbenzene or 1-bromo-2-ethylbenzene Disubstituted Benzenes meta- (abbreviated m- ) = 1,3-disubstituted (two groups having one unsubstituted carbon between them) Br Br m-dibromobenzene or 1,3-dibromobenzene Br NO2 m-bromonitrobenzene or 1-bromo-3-nitrobenzene Disubstituted Benzenes para- (abbreviated p- ) = 1,4-disubstituted (two groups on opposite sides of the ring) Br Cl Cl p-dichlorobenzene or 1,4-dichlorobenzene Cl p-bromochlorobenzene or 1-bromo-4-chlorobenzene Disubstituted Benzenes • When one of the substituents changes the base name, either o-, m-, and p- or numbers may be used to indicate the position of the other substituent. • Carbon # 1 is always the carbon bearing the substituent that changes the base name. Br 4 1 OH 3 1 2 Cl 2 NH2 p-bromoaniline or 4-bromoaniline o-chlorophenol or 2-chlorophenol Common Names of Disubs. Benzenes • There are a few nonsystematic (common) names for disubstituted benzenes that you should be familiar with: CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 m-xylene o-xylene CH3 p-xylene CH3 OH o-cresol CH3 CH3 OH m-cresol OH p-cresol Polysubstituted Benzenes • Polysubstituted benzenes must be named by numbering the position of each substituent on the ring (with more than two substituents, o-, m-, and pcan NOT be used.) • The numbering is carried out to give the substituents the lowest possible numbers. Carbon #1 always has a substituent. CH2CH3 • List the substitutents 2 F 1 3 alphabetically with 4 their appropriate #s. NO2 2-ethyl-1-fluoro-4-nitrobenzene Polysubstituted Aromatics having a Common base name • Common names of the monosubstituted benzenes are used as parent names for polysubstituted aromatics when one of the substituents changes the base name. • For such rings with common names, the carbon bearing the substituent responsible for the common name is always carbon #1. toluene CH3 • The substitutents are 1 Cl chloro listed in alphabetical 2 order. bromo Br 5 3 4 5-bromo-2-chlorotoluene Polysubstituted Benzenes Br OH 4 1 1 3 2 CH2CH3 NO2 4-bromo-2-ethyl-1-nitrobenzene Cl 2 Br 5 3 4 5-bromo-2-chlorophenol Polysubstituted Benzenes Br 2 3 O2N 4 Br 1 CH3 6 5 6 Cl 2-bromo-6-chloro-4-nitrotoluene O2N 5 1 2 CH2CH3 3 4 Cl 1-bromo-3-chloro-2-ethyl-5-nitrobenzene Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) anthracene naphthalene phenanthrene pyrene benzo [a] pyrene Metabolic byproducts of benzo [a] pyrene react with DNA to form adducts, leading to carcinogenesis (cancer).