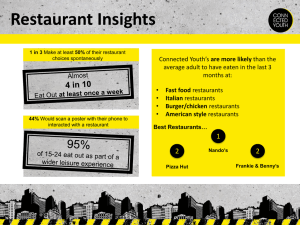
Food and Beverage
advertisement

Hospitality and Tourism 110 Food and Beverage Food and Beverage Largest of the 5 sectors Brings in about $24 billion annually in Canada according to the Canadian Tourism Human Resource Council Approximately 775,000 in 2006 Training ground for many people beginning their careers History Restaurants have existed since the 1500s Fork first introduced in 1533 First restaurant in the US opened in 1827 Antoine’s opened in New Orleans in 1840 and is still in operation today Two Divisions Commercial food services – 78% of market share - primary business is the service of food and drink E.g. Restaurants, fast food outlets, clubs, bars, pubs, etc. Non-commercial food services – 22% of the market share - found where the primary business is not the service of food and drink E.g. airports, museums, hospitals, schools, retirement homes, the military, recreational camps, etc. TRENDS Casual Dining Luxury of fine dining is being replaced by casual dining More casual atmosphere – plants, natural wood, earth tones Smaller and more intimate restaurant Fewer menu items to choose from Takeout Represents 50% of industry’s total growth Busier lives, more two income families mean more takeout Grocery stores offering more readyto-eat foods to compete with take-out Dining Out with Children Children often influence where the family eats Restaurants cater to children with a children’s menu (hamburgers, hot dogs, fries, etc) Crayons and menu that doubles as a game or colouring page Child friendly play area Service Tops the list of reasons a consumer returns to a restaurant Important for management to know what customer satisfaction is Restaurant surveys can indicate customer satisfaction Nutrition More choice for side dishes – salads instead of fries A lot of people are watching what they eat now, but most “treat themselves” when eating out Restaurants recognize diet trends Research shows that most people eat what they want and “get back on track” the next day Allergy Awareness More people are developing food allergies Ingredients should be available upon request Allergens include: MSG, peanuts, nut oils, preservatives Responsibility of the restaurant staff to identify all ingredients in a dish Legal Issues New alcohol laws Drinking-and-driving legislation New smoking laws Designated smoking room (DSR) No Smoking Ownership Independents Owned by one or two individuals Flexible business Owners can easily change menus or décor Can be risky – huge personal investment 80% bankrupt in 5 years Multi-Unit Corporate Corporate headquarters provide leadership, control and planning Managers trained by corporation Operate independently – but must follow company policy and meet quotas Examples: Lone Star, Boston Pizza Franchise Advantage of a brand name product, national advertising, training Disadvantage of high franchise fees, pay % of monthly revenue to company, no flexibility Examples: McDonalds, Tim Hortons Commercial Food Service Commercial Food Service Haute Cuisine Elegant and expensive Highly trained staff, exemplary service, exclusive clientele Restaurant has beautiful silverware, crystal goblets, fresh linen tablecloths and napkins, exotic flowers Food is cooked daily by chef and souschef Commercial Food Service Fine Dining Unique and exciting food Highly trained wait staff Costly table settings Not as exclusive as Haute Cuisine Commercial Food Services Dining Bistros – casual dining, simple decor Family style – found in suburbs or tourist attractions Specialty – serves one kind of food Ethnic – specialize in national dishes Theme – theme more important than the food Buffet – customers help themselves to the food Commercial Food Services Limited Service Restaurants Coffee houses – Tim Hortons, Starbucks Cafeterias – similar to buffet, but portions are preset Fast Food – customer does some of the work: locating napkins, condiments, straws, place to sit, and clean up Commercial Food Services Drinking Establishments Pubs – typical of an English bar Bars Lounges Clubs Non-commercial Food Service Social and contract caterers Major suppliers to the airlines, bus and rail systems, recreational camps, museums, historic sites, sports arenas, special events E.g. Cara Operations, Compass Group Tourism and the Food Service Industry Tourism Sales Dependent Restaurants – earn more than 50% of their sales revenues from tourists Example: McDonald’s across from train depot in Banff Tourism Profit Dependent Restaurants – earn 20-50% of their sales revenues from tourists Location is key, must be close enough to a major highway, attraction, high traffic shopping, accommodations Tourism and the Food Service Industry Resident Sales Dependent Restaurants – earn <20% of their sales revenues from tourists May profit from tourism dollars but survive without them