Relative_Age_Dating
advertisement

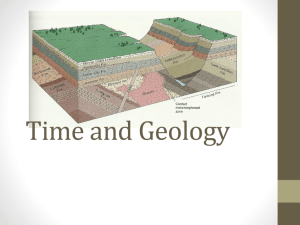
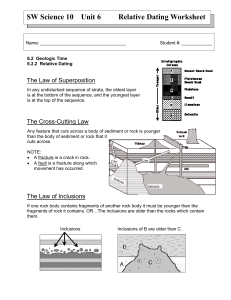
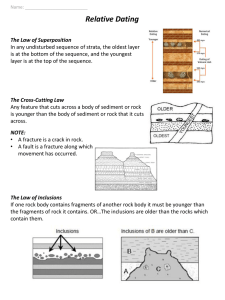
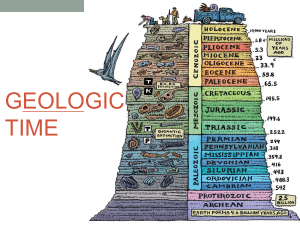
Relative-Age Dating • Scientists have not always thought Earth was as old as it is. • James Hutton in the late 1700’s was the first geologist to think Earth was very old. • Hutton explained Earth’s history in terms of geologic forces, such as erosion and sea level changes Uniformitarianism • States that geologic processes occurring today have been occurring since Earth formed. • Example the waves coming in on a beach today, occurred back during the Jurassic Period Principles for determining relative age • Because of uniformitarianism scientists can study the order in which geologic events occurred using a method called relative age dating. • CONS – Can not determine exactly how many years ago an event occured • PROS – Gives scientists a clear undertanding about geological events • Several ways to determine relative ages called relative dating. – Original Horizontality – Superposition – Cross-cutting relationships – Inclusions Original Horizontality • The principle that sedimentary rocks are deposited in horizontal or nearly horizontal layers. • Sediments are deposited in horizontal layers, because gravity combined with wind and water spreads them evenly • This can be seen in the walls of the Grand Canyon Superposition • The principle that in an undisturbed rock sequence, the oldest rocks are at he bottom and each consecutive layer is younger than the layer beneath it Cross-cutting relationship • The principle that an intrusion is younger than the rock it cuts across. • Intrusion rocks are rocks that form when magma solidifies in existing rock Inclusions • States that the fragments, called inclusions, in a rock layer must be older than the rock layer that contains them • Can occur after an exposed layer has eroded and the loose material on the surface has incorporated into the layer deposited on top of it • Compare and contrast the 3 types of unconformities on pg. 598