More on Strategies for Scaffolding Comprehension

Remember…
Comprehension is the main purpose of reading.
Reading is the process of constructing meaning from print.
Comprehension is a constructive, interactive process involving:
The reader
The text
The context in which the text is read
Don’t forget…
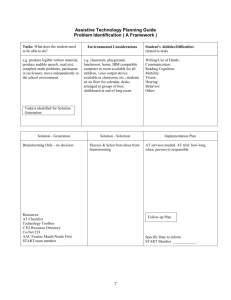
Build background,
Give students material on the appropriate level, and
Teach strategies, such as generating questions as they read, to help your students make connections
Strategy Instruction Works
Best When…
Students evidence a need for a strategy.
The strategy is taught and applied to a selection.
The teacher repeatedly models and explains the strategy.
When assessment is based on comprehension of the text and use of the strategy.
Louisiana Literacy Strategies
Brainstorming RAFT writing
DR-TA Reciprocal Teaching
GISTing SPAWN writing
Graphic Organizers Split-Page Notetaking
Learning Logs SQPL-Student Questions for Purposeful Learning Opinionnaires/
Anticipation Guides Story Chains
Professor Know-It-All Vocabulary Cards (AKA
Frayer Model) Process Guide
Vocabulary Self-Awareness Questioning the Author
(QtA) Word Grid (AKA Semantic
Feature Analysis)
Good Resource--Vermilion Parish Literacy Strategies-http://www.vrml.k12.la.us/cc/18str/18str.htm
More Strategies…
ABC Brainstorming
Quick Write/List
Quick Talk
Foldables
Flying High with
Academics
GISTing
Opinionnaires/
Anticipation Guide
i-Chart
Vocabulary Cards AKA
Frayer Model
RAFT
List-Group-Label
Professor-Know-It-All
ABC Brainstorming
Activate students’ background knowledge before talking about a topic by using ABC Brainstorming.
Students are asked to think of a word or phrase related to the topic by matching it to each letter of the alphabet.
http://www.readingquest.org/strat/abc.html
Quick Write or Quick Talk
Ask students to talk about or write down as many ideas they can think of about a given topic.
The ideas can be single words or phrases.
Give students 60 seconds to write.
ReadWriteThink overview of quick write/quick talk.
Also… http://www.litandlearn.lpb.org/strategies/strat_quick.
Foldables
http://foldables.wikispaces.com/
http://www.catawba.k12.nc.us/C_i_resources/Foldable s.htm
Flying High with Academics
From Dr. Cummins…
Strategy to get students moving
Requires students to think critically as develop clues for “teaching”
Legal to make paper airplanes
Do it…
Read passage
Make an airplane
Write a question about the passage
Fly your plane
Pick up a plane and answer the question
GISTing
A technique to help students to read text for main ideas.
Students are asked to summarize selected sections into a designated number of clear, concise words.
http://www2.etown.edu/bap/Resources/gisting.pdf
Opinionnaires/ Anticipation Guide
A series of statements where students note whether they agree or disagree with each one.
Students then read a selection then compare what they said with what was in the text.
http://www.greece.k12.ny.us/instruction/ela/6-
12/reading/Reading%20Strategies/anticipation%20gui de.htm
I-Chart
A planned framework for answering questions about a topic.
http://forpd.ucf.edu/strategies/stratIChart.html
Frayer Model/ Vocabulary Cards
Definition
To join or fasten together
Connect
Characteristics
Link
Interlocking
Associate
Relate
Examples
Bridge
Paper clips linked together
Nonexamples
Unlatched Gate
Illustrations
RAFT
Students respond in writing by thinking about a topic from various perspectives.
Role of the Writer: Who are you as the writer? A pilgrim? A soldier? The President?
Audience: To whom are you writing? A political rally? A potential employer?
Format: In what format are you writing? A letter? An advertisement? A speech?
Topic: What are you writing about?
From http://www.adlit.org/strategies/19783 .
List-Group-Label
A brainstorming activity that helps students see how words can belong in a variety of groups while activating and building background knowledge prior to beginning a unit of study.
Zebra
Deer
Pig
Cat
Horse
Dog
Tiger
Initial List of Animals
Cow
Mule
Antelope
Lion
Sheep
Goat
Raccoon
Possum
Parrot
Blue Jay
Goldfish
Elephant
Coyote
Giraffe
Jungle
Zebra
Tiger
Lion
Giraffe
Elephant
Antelope
Labeled Groups
Forest/Woods House
Deer
Possum
Raccoon
Coyote
Blue Jay
Cat
Dog
Goldfish
Parrot
Pig
Horse
Cow
Mule
Sheep
Goat
Farm
Professor Know-It-All
Provides students with opportunities to be the “expert” on a topic studied in class.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Establish groups of three or four students.
Students review the content just covered and generate three to four content related questions they anticipate being asked. The group discusses these topics in detail in preparation for later class discussion.
Come to the front of the room, one at a time, face the class and respond to questions posed by their classmates. Students should ask their proposed questions first and then others if more information is desired. The teacher should remind students to challenge and/or correct the professor-know-it-alls if needed.
Process continues until all groups have served as “professors” and/or until all content has been thoroughly and critically discussed. Ties, graduation caps, lab coats, clipboards, and other accessories can be used by the “professors” to add a touch of novelty.
Process Guides
Process Guides scaffold students’ comprehension from literal level processing to more critical and applied content knowledge.
Leveled formats designed by the teacher to match the content being studied helps guide students’ thinking.
Guides can be designed in a variety of ways to accompany the content being studied and/or the purpose and level of active learning to be implemented.
Process Guide Example
From LA Literacy Strategies…