File
advertisement

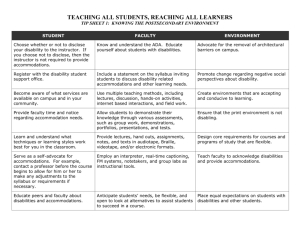
Exceptionalities Instructional Helps 10 Common Exceptionalities Josie Orton EDUCATION GUIDE Table of Contents Learning Disabilities Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Emotional/Behavioral Disorder Communication Disorder Traumatic Brain Injury Autism Spectrum Disorder Hearing Loss Vision Loss Intellectual Disability Gifted, Creative and Talented Works Cited Page Learning Disabilities A Learning disability is defined as a condition in which one or more of the basic psychological processes involved in understanding or using language are deficient. According to the Human Exceptionalities textbook written by Hardman, Drew, and Egan, “Learning disabilities have likely always been a struggle for the human condition, but it is only since the latter half of the 20 th century that we have focuses on this particular area of disorder.” Learning disabilities are often referred as the indivisible disabilities because they affect people of all ages and cannot be determined by appearance, dress, or behavior. Strategies: Provide a well-defined instructional environment Use manipulative objects and use repetition Cover, copy, and compare approach Use laptops, tablets, and interactive whiteboards Use downloadable web applications Accommodations/Mortifications: Extended time for completion of assignments or tests Small groups Concrete, positive reinforcement Study sheets, Summary Sheets, outlines of most important facts Visual demonstrations Presentation of material in small steps Large Print Material Seating to reduce distractions Frequent breaks Technology Resources: Overhead projector CD player and disc to replay information Voice Recorder Online Websites Calendar that remind the student of important dates and times PowerPoint presentations made for the student to review material Environment Resources: Classroom Aide that assists the student throughout the day Field Trips Tutor Special Education classes Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder Attention deficit hyperactive disorder, more commonly known as “ADHD” is a disorder characterized by impulsive actions, hyperactivity, and difficulties in maintaining attention. ADHD usually begins in early childhood but may continue into adult years. It is the most commonly diagnosed behavioral disorder in children, and is more common in boys than girls. It is not clear what causes ADHD. According to A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia, “A combination of genes and environmental factors likely plays a role in the development of the condition”. “Imaging studies suggest that the brains of children with ADHD are different from those of children without ADHD.” Seeing how attention deficit hyperactive disorder effects a students learning ability in a negative way, it is important to be aware and discover the disorder early in the child’s lifetime. Strategies: School assignments must be broken down into smaller, less complex units. Encouragement on completion of projects and assignments Re-enforcements and rewards Keep the student busy and engaged Immediate consequence for inappropriate behavior such as time out station to calm down Plan ahead Accommodations/Modifications: An IEP plan Give extra time on tests and assignments Extra classroom structure Shorter work periods Frequent eye contact with student Technology Resources: Short videos Pictures Short Slideshows Laser pointers Music and sounds Environmental Resources: Create positive learning environment Promote interaction and learning Set the student in the front of the classroom Keep them engaged by assigning them important tasks daily Lessons outside of the classroom Emotional/Behavioral Disorder According to the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, Emotional disturbances are defined as the following: an inability to learn; an inability to build or maintain satisfactory relationships with peers and teachers; inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances; a general unhappiness or depression; and a tendency to develop physical systems or fears associated with personal or school problems. Unluckily for the students that suffer from emotional or a behavior disorder and have not been diagnosed yet, do not receive appropriate care and treatment, merely because their academic achievement in school appears normal or above average. Strategies: Create a silent signal with students so you don’t have to signally call them out Use journaling so your students can be in touch with their emotions Reward frequently and promote positive behaviors Focus on fairness Limit the number of rules Accommodations/Modifications: Set up goals aimed to social interactions Use role-playing situations Stay consistent in expectations Use behavior contracts Set limits and boundaries Technology Resources: Use of headphones or ear plugs Word processing program with voice recognition Functional evaluation for assistive technology can be conducted to determine what types of assistive technology might benefit the student Voice recorder they can use to record lessons and replay them when needed Environmental Resources: Set a “cool down” zone Use seating arrangements to encourage social interaction Create a friendly environment with your students on a personal level Keep your classroom a safe environment where your students feel safe and like they will not be emotionally or physically harmed Make a board that recognized students achievement and goals Communication Disorder A communication disorder is a speech and language disorder which refers to problems in communications and in related areas such as oral motor function. The delays and disorders can range from simple sound substitution to inability to understand or use one’s native language. Strategies: Create open lines of communication between students’ parents and teachers by having frequent phone calls or face to face conferences Identify strengths of children which can be rewarded or reinforced in the classroom and at home Develop a self- esteem enhancing model of managing the behavioral concerns related to Communication Disorders Accept personal limitations Involve the students in steps to address their target behaviors in the classroom Involve other students in assisting students with communications and learning disorders to alter the targeted behaviors in the classroom Accommodations/Modifications: Keep the noise level in the classroom as low as possible With the help of the speech teacher altering traditional classroom games students play to reinforce concepts for review. Incorporating group reading into lessons Repeat questions with proper diction, articulation and tone. Incorporate one on one tutorials Technology Resources: Picture exchange communicate system Hand-held (portable) or computer electronic speech devices Communication board Sign language Head set that student can listen to that pronounces and repeats the correct way to pronounce words. Environment Resources: Provide child with more learning opportunities Encouraging the child at every step and not criticizing the child for the slow response or failure to answer your question Trying and using simple vocabulary that the students can keep up with Help the child to feel confident Do NOT single out the student or embarrass the student in front of his/her peers Traumatic Brain Injury Traumatic Brain Injury is also known as intracranial injury, and occurs when an exterior force traumatically injures the brain. TBI can be classified based on severity, mechanism, or other features. TBI is a major cause of death and disability worldwide, especially in children and young adults. Males sustain traumatic brain injuries more frequently than do females. Causes include falls, vehicle accidents, and violence. Strategies: Reduce distractions in the student’s work area Frequently repeat information and summarize it Teach the students to categorize information to aid retention Written checklist of steps for complex tasks with instructions for checking off each completed step in an assignment or task Outline based on class lectures Provide oral and written instructions Accommodations/Modifications Have student sit near teacher in the classroom Keep distractions to a minimum Use peer note takers Provide assignments in writing Teach in small groups Allow student to have frequent breaks Technology Resources: Tape recorder Iphone/Ipad applications Handheld microcomputer Message recorders Checklist Talking clock and talking calendar to remind student of evens and homework Environment Resources: Schedule modifications (shorter days, rest periods, etc.) A student “buddy” Keep the student in a safe environment and protect him/her from causing more harm by providing helmets, lessons on importance of seatbelts etc. Teachers, health providers, and parents work as a team Create an environment that encourages the student to develop appropriate social behaviors Autism Spectrum Disorder Autism is a pervasive developmental disorder. Its symptoms include differences and disabilities in many areas including social communication skills, fine and gross motor skills, and sometimes intellectual skills. Strategies: Provide Support Implement IEPs Meet with parents Evaluate various teaching styles Provide warnings for changes in routines Ensure consistency Accommodations/ Modifications: Portable picture schedule Extra time to take tests Seating in front of classroom Changes in curriculum to meet child’s needs Visual or written daily schedule Provide instructions orally as well as visually Allow extra time for students to respond to directions Classroom aides Incorporate visual components Let students use a stress ball Often alternate activities Minimize distractions Technology Resource: Word processing Computer based learning Use visual physical guidance Use peer modeling Calculator Environment Resources: Create an environment that is not over stimulating Create a structured environment with predictable routines Give fewer choices Select repetitive motions when working on projects Keep voices low and clear when teaching Hearing Loss Hearing loss is an impairment in hearing, whether permanent or fluctuating, that adversely affects a child’s educational performance but that is not included under the definition of deafness. Deafness means a hearing impairment that is so severe that the child is impaired in processing linguistic information through hearing with or without amplification that adversely affects a child’s educational performance. Strategies: Face the student at all times Don’t cover your mouth with your hands Speak in a normal rate Provide a listing of all key concepts Implement testing accommodations identified in the students IEP Accommodations/ Modifications American Sign Language Fingerspelling Be sure to signal topic changes Provide a note taker Reword, rephrase, or paraphrase what you have said when the student appears lost Make sure the student learns reading comprehension strategies Alternate tasks to give the student a break from having to focus so intently Hearing aid Technology Resources: Interpretation Translator that translates words into a visual sign language Projector Slideshows Open caption Closed captioning Environment Resources: Make sure that there is not a light source behind you shining in the student’s eyes Have the student sit at the front of the classroom Make sure that the screen isn’t blurry When writing on the board make sure that it is big and legible Over exaggerate lip movement when you’re speaking Vision Loss Vision loss is the absence of vision where it existed before, which can happen either abruptly or over a long period of time. People with vision that is worse than 20/200 with glasses or contact lenses are considered legally blind. Vision loss refers to partial or complete loss of vision. Some types of vision loss never lead to complete blindness. Strategies: Speak to the class upon entering and leaving the room Use descriptive words like “forward, left, straight,” ect. Don’t distract guide dogs Have another student read written info for them Use bold, large print on papers and on the computer screen Accommodations/ Modification: Braille Alphabet Math counter Ruler with indents Reading machine Number lines with indents Technology Resources: Early Braille Template and tool Braille computer keyboard adaptor Braille computer “note taker” Visual amplifier Overhead Opaque projector Tactile 3D models Environmental Resources: Have student sit in the front of the classroom Handouts available in large print, audiotapes, computer disk, or braille use a voice amplifier keep sun out of students eyes use handouts often Intellectual Disability Intellectual Disability is the current preferred term over what has historically been called mental retardation. Mental retardation is a disability characterized by significant limitations both in intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior as expressed in conceptual, social, and practical adaptive skills. This disability originates before the age of 18. Someone that is intellectually disabled also has an approximate IQ of 70 and below. This gives them a limited ability to reason, plan, solve problems, think abstractly, comprehend complex ideas, learn quickly, and learn from experience. Intellectual disability is common in as many as 3 out of every 100 people. Strategies: Work together with the parents and other school personnel to tailor their IEP Demonstrate while you tell Break new tasks into small steps Use repetition Give immediate feedback (positive) Accommodations/ Modifications: Use concrete items and examples to explain new concepts Identify what behaviors you expect in the classroom Plan ahead with your class activities Use appropriate communication method Do not overwhelm a student with multiple or complex instructions Use strategies such as chunking, backward shaping and role modeling Technology Resources: Computer games and tasks are used as a reward and motivation Taped stories Headset Audio book PowerPoint Use Pictures Environmental Resources: Have the student set goals and guidelines to focus on Create positive learning environment Promote interaction and learning Set the student in the front of the classroom Keep them engaged by assigning them important tasks daily Gifted, Creative, and Talented Someone who shows, or has the potential for showing, an exceptional level of performance in one or more areas of expression is someone who is gifted and talented. About 5% of the student’s population is gifted. Gifted, creative and talented are terms that apply to individuals with extraordinary abilities or the capacity for developing them. Strategies: Create alternative activities Work with student to design an independent project that they would be interested in completing for credit Involve students in academic competitions in your area Create tiered assignments, which have different expectations for different levels of learning Promote independence Accommodations/ Modifications: Enrichment through a broader range of texts and tasks Extension through more detail and complexity Accelerate the pace of learning and tackle objectives earlier Support reflection and self- evaluation Allow student to work at own pace and have more complex assignments prepared for them Technology Resources: Computer Calculator Online testing headset lecture recordings Environmental Resources: provide encouragement and support open place to study and work challenge the student fast paced learning system keep the student focused and engaged Works Cited "Accommodations." Accommodations for Students with Disabilities. NCLD, 2013. Web. 17 Sept. 2013. "Assistive Technology for Individuals with Traumatic Brain Injury." Assistive Technology for Individuals with Traumatic Brain Injury. WETA, 2013. Web. 22 Oct. 2013. "Down Syndrome: MedlinePlus." U.S National Library of Medicine. U.S. National Library of Medicine, 13 May 2013. Web. 22 Sept. 2013. Hardman, Michael L., Clifford J. Drew, and M. Wilson Egan. Human Exceptionaality School, Community, and Family. 11th ed. N.p.: Wadsworth Cengage Learning, 2013. Print. "Instructional Strategies for Educators." LD OnLine: The World's Leading Website on Learning Disabilities and ADHD. WETA, 2010. Web. 17 Sept. 2013. Lash, Marilyn. Teaching Strategies for Students with Brain Injuries. Vol. 4. N.p.: n.p., n.d. Blausa.org. 2 Nov. 2000. Web. 23 Oct. 2013. Plumley, Karen. "A Better Way to Learn from Each Other." Suite101.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 17 Oct. 2013. "Specialties." Medscape Reference - Specialties. N.p., n.d. Web. 17 Oct. 2013. "Web Site Design by Flyte New MediaContact Web Developer." Classroom Modifications and Accommodations For Students With Learning Disabilities. Idat, n.d. Web. 17 Sept. 2013.