Chapter 6 Muscular Tissue
advertisement

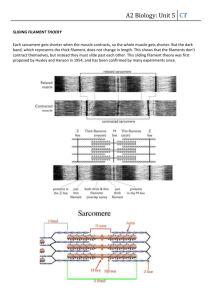
Chapter 6 Muscular Tissue 1. General description 1) components: ---cell: muscle fiber-myofiber elongated thread-liked Sarcolemma Sarcoplasm sarcoplasmic reticulum: SER ---extracellular G.S: CT with BV, LV and N 2) classification According to the structure and function skeletal muscle: striated, voluntary cardiac muscle: striated, involuntary smooth muscle: unstriated, involuntary 2. Skeletal muscle Muscle is an organ, consists of muscle fiber and CT, fixed on bone by tendons CT: epimysium: DCT Perimysium Endomysium muscle satellite cell: differentiate and proliferate function: supporting, connecting, nourishing and regulating 1) microstructure of skeletal muscle fiber ① long cylindrical 10-100um in diameter,1-40mm long ② multinucleate, nuclei are ovoid, distributed under sarcolemma ③ filled with longitudinal parallel-arranged myofibrils myofibril: 1-2um in diameter cross striation: light band -I(isotropic) band, dark band- A(anisotropic) band --A band: M-line, H-band --I band: Z-line * sacromere: a segment of myfibril extending from one Z line to next Z line, which is composed of 1/2 I band, A band and 1/2 I band ,is the smallest structural and functional unit of myofibril 2) Ultrastructure of myofiber ① myofibril: composed of ---thick myofilament: 1.5 um long, 15nm in diameter composed of myosin: -rob: in bundles -head: cross bridgebinding site(ATPase activity) ---thin myofilament: 1um long, 5nm in diameter composed of: A. actinspherical monomers of globularactin arranged in two row and twisted- filamentous actin, each monomer has binding site B.tropomyosin: filamentous protein of two polypeptide chains C. troponin: three subunits: -Tn T: bind to tropomyosin -Tn C: binds to calcium ions -Tn I: inhibite actinmyosin interaction ② Transverse tubule (T tubule): ---definition: sarcolemma and basement membrane invaginate into sarcoplasm to form a transverse distributed tubular system ---location: A-I junctional part ---function: transfer the information into cytoplasm ③ Sarcoplasmic reticulum: ---definition: A longitudinal distributed tubular system formed by smooth endoplasmic reticulum ---structure: H-A band: longitudinal enclose myofibril-longitudinal tubule A-I junction: enlarge to form flattened sac— terminal cisternae * triad: one T-tubule +two terminal cisternae ---function: there are calcium pump proteins (ATPase) on membrane, so it can store and release calcium ions ④ Mitochondria, glycogen, lipid droplet 3) Sliding filament hypothesis During the contraction, the A band remained constant in length, whilst the I band and H band both decreased in width, which suggest that the actin filament slide along the myosin toward the M –line. a. b. c. Myoneural junction transfer the impulse from NF to sarcolemme. The impulse spreads to interior part of cell by T- tubule, then through the triad, impulse is transferred to sarcoplasmic reticulum, the calcium ions are released by sarcoplasmic reticulum. Calcium bind to Tn C, troponin and tropomyosin change their position and structure, the binding site on actin and myosin is exposed d. Binding site on actin and myosin combine, ATP(adenosine triphosphate) are splitted into ADP(adenosine diphosphate) by ATPase on head of myosin, and energy are release. The energy is provided to band the head in the direction of M-line, and actin filament are pulled toward to M line. e. After contraction, calcium ions in sarcoplasm are withdrawed into sarcoplasmic reticulum. A new ATP molecules bind to the myosin, the actinmyosin separated, troponin-tropomyosin cover the binding site, the myofiber relax. 3.Cardiac muscle 1) Microstructure of cardiac muscle ① short column in shaped, 100um long,15um in diameter, with branches, the branches associated with each other to form a network ② 1-2 ovoid nuclei, centrally-located ③ striated, but no very clear ④ intercalated disc: junctional part LM: dark striation across the cardiac fibers 2) Ultrastructure of cardiac muscle similar to skeletal muscle, composed of thick, thin filament and have sarcomere ① myofibril have different diameter, the boundary of myofibril is not very clear ② thansverse tubule are thicker, located at Z-line level ③ sarcoplasmic reticulum is not well-developed, form less terminal cisternae * diad: one T-tubule + one terminal cisternae ④ intercalated discs step-liked structure transverse portion: -intermediate junction -desmosome -connection longitudinal portion: -gap junction -communication ⑤rich in mitochondria glycogen pigment 4. Smooth muscle 1) microstructure of smooth muscle ① elongated, spindle-shaped cells, 8um in diameter, 200( 20-500)um long ② rob-liked or ovoid nucleus ③ no striation, no myofibril 2) ultrastructure of smooth muscle ① caveola: sarcolemme invaginate into cytoplasm ② /dense patch: under sarcolemma /dense bodya: in sarcoplasm ③ intermediate filament: /composed of desmin /10nm in diameter /connect between dense body ④ /thick filament: myosin, 15 nm /thin filament: actin, 5 nm- fixed on dense patch or body percentage: thick/thin filament=1/12-30 contractile unit: several thick filament and thin filament aggregate