AP Statistics CH. 4 Displaying Quantitative Data
advertisement

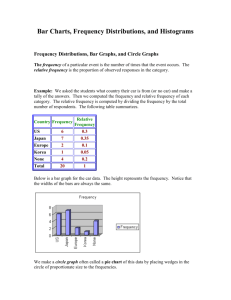
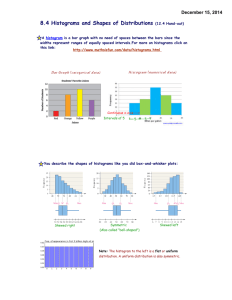
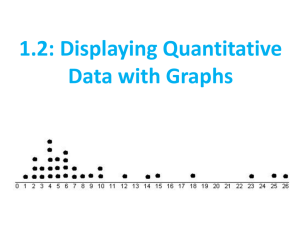
AP Statistics CH. 4 Displaying Quantitative Data By. Jamie Morreale and Thulasi Thiviyanathan What is a Histogram? ● Histograms plot the bin counts as the height of bars ● The bins and the counts in each bin give the distribution of the quantitative variable ● Relative Frequency Histogram- displays the percentage of cases in each bin instead of the count How to make a Histogram •Used with numerical data •The Bars touch •There are two types –Discrete-bars which are centered over discrete values –Continuous-bars cover a class (interval) of values What is a Stem-and-Leaf Display? Stem-and-leaf displays- contain all the information found in a histogram and, when carefully drawn, satisfy the area principle and show the distribution. In addition, stem-and-leaf displays preserve the individual data values. What are Dotplots? ● Dotplot is a simple display. It just places a dot along an axis for each case in the data ● They may be displayed vertically or horizontally CUSS Center Unusual Points Shape Spread Use CUSS when describing a distribution. Humps and Bumps Identify if the Histogram has a single, central, or several humps. Modes are humps Unimodal- a histogram with one main peak Bimodal- histograms with two peaks Multimodal- histograms with three or more peaks Uniform- a histogram distribution that is roughly flat Symmetry Identify if the Histogram is Symmetric Tails- are the parts that typically trail off on either side. They can be identified as having long tails or short tails. Skewed- a distribution is skewed if it’s not symmetric and one tail stretches out farther than the other. Skewed Left- when the longer tail stretches to the left Skewed Right- when the longer tail stretches to the right Unusual Outliers- extreme values that don’t appear to belong with the rest of the data. They may be unusual values that deserve further investigation. or just mistakes. Compare the graphs Compare the two graphs on the number of male and female patients What is a timeplot? Timeplot- displays data that change over time. Often, successive values are connected with lines to show trends more clearly. What can go Wrong? - Don’t make a histogram of a categorical variable - Don’t look for shape, center, and spread of a bar chart - Don’t use bars in every display- save them for histograms and bar charts - Choose a bin width appropriate to the data - Avoid inconsistent scales - Label Clearly HW Problem #35 7 3 45 3 222 10 3 01 98 3 8 777 2 7 2 2 222 11 2 0 999888 1 77776 1 U.S. Cars 44 67 According to the data U.S. car milage have a lower center and is skewed to the right. The mode is near 19 mpg. Others have more cars in their category with a mode at 32 mpg and another mode at 22 mpg. Others 3 1 l 6 means 16 mpg HW Problem #37 8 0148 7 9 6 02 3 5 6 4 3 25 2 8 2 l 8 means $28 thousand/mW b. The graph is skewed to the left and also has some gaps. d. According to the timeplot, the cost is generally increasing overtime.