jeopardy first aid
advertisement

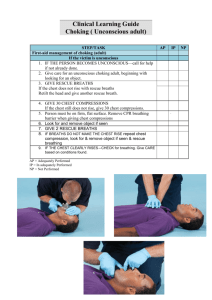
First Aid Taking Action Life Threatening Emergencies AED/ Sudden Illness Topic 5 10 10 10 10 10 20 20 20 20 20 30 30 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 40 50 50 50 50 50 Question 1 - 10 • What should you do if the person does not give consent to care for them? • • • • A.) Do not give care, but instead call 911 B.) Give care and call 911 C.) Give care but do not call 911 D.) None of the above Answer 1 – 10 • A.) Do not give care, but instead call 911 Question 1 - 20 • By following standard precautions to protect yourself and the injured, you can: • A.) Increase the risk od disease transmission • B.) Minimize the risk of disease transmission • C.) Reduce the number of times you need to wear gloves • D.) None of the above Answer 1 – 20 • B.) Minimize the risk of disease transmission Question 1 - 30 • You determine that a person may be in shock. Do each of the following except: • A.) Give the person water • B.) Have the person lie down • C.) Keep the person from getting chilled or overheated • D.) Monitor the person’s condition Answer 1 – 30 • A.) Give the person water Question 1 - 40 • What is the purpose of good samaritan laws? • A.) To help protect people who voluntarily give care without accepting anything in return • B.) To discourage people from helping other in an emergency • C.) To protect people who give care beyond their level of training • D.) None of the above Answer 1 – 40 • A.) To help protect people who voluntarily give care without accepting anything in return Question 1 - 50 • You see a woman collapse in front of you while entering the lobby of your office. You check the scene and then check the person for consciousness, but she does not respond. What should you do next? • A.) Call or have someone call 911 • B.) Check for breathing • C.) Drive the person to the hospital • D.) Give 2 rescue breaths Answer 1 – 50 • A.) Call or have someone call 911 Question 2 - 10 • The steps to follow in an emergency are: • • • • • A.) Call, Check, Secure B.) Care, Call, Check C.) Check, Call, Care D.) Check, Care, Defibrillate Answer 2 – 10 • C.) Check, Call, Care Question 2 - 20 • If a person is suffering from pain or discomfort in the chest that lasts more then 3-5 minutes or that goes away and comes back, this person is most likely having: • • • • A.) A cold emergency B.) A heart attack C.) Diabetic emergency D.) A seizure Answer 2 – 20 • B.) A heart attack Question 2 - 30 • About how many seconds should you check for breathing? • • • • A.) No more than 5 B.) No more than 10 C.) No more than 15 D.) No more than 20 Answer 2 – 30 • B.) No more than 10 Question 2 - 40 • How should you care for a conscious infant who is choking and cannot cough, cry, or breath? • A.) Give abdominal thrusts • B.) Give 5 back blows and 5 chest thrusts to clear airway • C.) Open the infants mouth to clear airway • D.) Give back blows until the infant starts to breath normal Answer 2 – 40 • B.) Give 5 back blows and 5 chest thrusts to clear airway Question 2 - 50 • Care for a person who in unconscious and has a blocked airway includes: • A.) Giving chest compressions • B.) Looking for an object between compressions and breaths • C.) Pressing on the person’s abdomen 5 inches deep • D.) Both A and B Answer 2 – 50 • D.) Both A and B Question 3 - 10 • When giving a rescue breath, you should: • A.) Blow hard and fast • B.) Blow harder if the chest does not rise • C.) Blow in for about 1 full second to make the chest clearly rise • D.) Give a breath that lasts for several seconds Answer 3 – 10 • C.) Blow in for about 1 full second to make the chest clearly rise Question 3 - 20 • What care should you give to a conscious adult or child who is choking and cannot cough, speak, or breathe? • • • • A.) Do a foreign object check/removal B.) Give 2 slow rescue breaths C.) Give back blows and abdominal thrusts D.) Lower the person to the floor and open airway Answer 3 – 20 • C.) Give back blows and abdominal thrusts Question 3 - 30 • When giving chest compressions: • A.) Allow the chest to return to its normal position • B.) Are delivered fast, about 100 per minute • C.) Are smooth, regular, and given straight up and down • D.) All of the above Answer 3 – 30 • B.) Are delivered fast, about 100 per minute Question 3 - 40 • A cycle of chest compressions and rescue breaths in CPR is: • A.) 15 chest compressions for every 1 rescue breath • B.) 15 chest compressions for every 3 rescue breaths • C.) 30 chest compressions for every 1 rescue breath • D.) 30 chest compressions for every 2 rescue breaths Answer 3 – 40 • D.) 30 chest compressions for every 2 rescue breaths Question 3 - 50 • If the AED pads risk touching each other such as with a small child, you should: • A.) Place them as usual, it does not matter if they touch • B.) Place one pad on the stomach and one on the chest • C.) Reverse the pads’ position on the chest • D.) Place one pad in middle of the chest and other on the back Answer 3 – 50 • D.) Place one pad in middle of the chest and other on the back Question 4 - 10 • Why is it important to stand clear and not touch the person while the AED is analyzing or defibrillating? • A.)The AED will turn itself off • B.) You could be injured by shock • C.) You might prevent AED from analyzing heart rhythm properly • D.) Both B and C Answer 4 – 10 • D.) Both B and C Question 4 - 20 • What should you do before the AED analyzes the heart rhythm? • A.) Ensure that no one is touching the person (including yourself) • B.) Ensure that head-tilt/jaw-thrust is maintained • C.) Ensure that the person is breathing • D.) None of the above. Answer 4 – 20 • A.) Ensure that no one is touching the person (including yourself) Question 4 - 30 • How do you care for a person with a possible head, neck, or spinal injury? • A.) move the injured area so that it rests above the person’s heart • B.) Move the person into a comfortable position • C.) Support the head in the position that you find it. Do not move it. • D.) None of the above Answer 4 – 30 • C.) Support the head in the position that you find it. Do not move it. Question 4 - 40 • In stroke recognition, FAST means: • • • • A.) Face, Arm, Speech, Time B.) Feet, Airway, Speech, Temperature C.) Fever, Anxiety, Stress, Taste D.) Flexibility, Asthma, Sudden Tightness in chest Answer 4 – 40 • A.) Face, Arm, Speech, Time Question 4 - 50 • What sudden illness is caused by a blockage of blood flow to the brain? • • • • A.) Diabetic Emergency B.) Heart-Related C.) Heart Attack D.) Stroke Answer 4 – 50 • D.) Stroke Question 5 - 10 • When caring for a person who is having a seizure, you should: • A.) Place a spoon or wallet between the person’s teeth. • B.) Remove nearby objects that might cause injury • C.) Try to hold the person down • D.) All of the above. Answer 5 – 10 • B.) Remove nearby objects that might cause injury Question 5 - 20 • The general care for a muscle, bone, or joint injury includes the following: • • • • A.) Reduce, Insulate, Compress, Evaluate B.) Rest, Ibuprofen, Cool, Evacuate C.) Rest, Immobilize, Cold, and Elevate D.) None of the above Answer 5 – 20 • C.) Rest, Immobilize, Cold, and Elevate Question 5 - 30 • A scrape is an example of: • • • • A.) An avulsion B.) An abrasion C.) A puncture D.) A laceration Answer 5 – 30 • B.) An abrasion Question 5 - 40 • When splinting: • A.) Lower the injured body part below the heart • B.) Keep the injured part as straight as possible • C.) Support the injured part in the position it was found • D.) Use only rigid splints Answer 5 – 40 • C.) Support the injured part in the position it was found Question 5 - 50 • A victim loses a finger while slicing an apple. What do you do with the finger when you arrive on the scene? • • • • A.) Put it in the refrigerator B.) Take it with you to the hospital C.) Put it in a bag of ice D.) Both B and C Answer 5 – 50 • D.) Both B and C