Tables - Mrs. Buchanan's Classroom Blog
advertisement

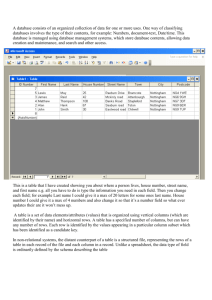
Creating Tables LESSON 6 - #1.06 ESSENTIAL STANDARD #1 - UNDERSTAND WORD PROCESSING INDICATOR #6 – CREATING TABLES Table 2 Arrangement of data made up of horizontal rows and vertical columns. Tables are useful to organize, increase readability, summarize and emphasize information of a document. Heading 1 Heading 2 3 Parts of a Table Cell: Intersection of a row and column Column: Runs vertical Row: Runs horizontal Budget Column Cell Actual Variance Salaries and wages $20,000 $19,345 $655 Stationery $3,000 $3,125 ($125) Rent and cleaning $5,200 $5,250 ($50) Other expenses $1,800 $750 $1,050 Total expenses $30,000 $28,470 $1,530 Row 4 Ways to Insert/Create a Table Insert by Dragging thru the squares (cells) under Insert Table Open the Insert Table command to open the Dialog Box Drawing a Table – Create a table with varying sizes of rows and columns Quick Table – Preformatted Table (for example calendars) Move Insertion Point and Select a Table Use the Tab key to move from left to right one cell at a time in your Table. Use the Shift+Tab to move back to the left You can also use the arrow keys to move around in a Table Select the entire Table with the Table Move Handle located in the upper left section. Also referred to as the Table Select Handle. 5 Table Tools Ribbons 6 When Tables are inserted into Word, two new Tabs Appear: Table Tools Design: Allows you to format the table (Styles, Borders, Shading, etc.) Table Tools Layout: Allows you to edit the layout of the table (Add/Delete columns/rows, change Height and Width, Sort, etc.) Table Quick Styles Located on the Table Tools Design Ribbon Preformatted Styles that adds formatting for a professional appearance to a Table Header Row: Formats top row of the table that contains information that helps identify the content of a particular column. It is usually formatted differently. Total Row: Formats the last row Banded Rows: Formats the even and odd rows differently First Column: Formats the first column differently Last Column: Formats the last column differently Banded Columns: Format even and odd columns differently 7 Table Quick Styles There are 3 categories available: Plain Tables Grid Tables List Tables As you point to a style Word displays a Live Preview, showing you what your Table will look like if you choose that style. 8 9 Table Style Options Table Style Options enable you to change the appearance of the preformatted styles you apply to your tables. They are linked to the Table Style you have selected and will be applied globally throughout the table. Styles can be changed in the Modify Styles’ Dialog box. 10 Managing Tables After you create a table, you can: Resize and Move its columns AutoFit command enables you to adjust column widths to fit the size of contents or to fit in a fixed width Use Drag and Drop for moving columns and rows Insert/add additional columns and rows Change the Alignment of the table or direction of its text Set a Header row to repeat on several pages View Gridlines 11 Borders can be removed from a Table, when this is done you may need to view the Gridlines to see the outline of the cells. On the Table Tools Layout tab, in the Table group, click the View Gridlines button to view the gridlines. This enables more precise editing. Click the View Gridlines button again to remove the gridlines. The gridlines are no longer displayed. Gridlines do not print. Resize Rows and Columns You can resize using the mouse or the commands on the Ribbon. Use the Table Tools ribbon – Layout Tab to adjust the Row – Height and the Column – Width Select Distribute Rows and Columns to make all rows or columns equal in height or width. 12 Sorting Tables 13 Located on the Table Tools – Layout Tab in the Data Group Allows you to reorder or rearrange the way in which the table is organized Alphabetically, numerically, or chronologically Ascending: Alphabetical Order/Numerical Order Descending: Reverse Alphabetical Order (Z to A) Merging/Splitting Cells 14 Located on the Table Tools Layout Ribbon in the Merge Group Merge Cells: Allows you to combine multiple cells into one. Often done in the header row, to center align headings over the entire Table Split Cells: Allows you to divide one cell into two or more cells Change the Position and Direction of Text 15 Word provides you with nine options for Aligning text in a cell. These options enable you to control the horizontal and vertical alignment of cell text, such as Top Left, Top Center, and Top Right. Rotating text in a cell provides additional options for creating interesting and effective tables. To change the direction of text in a cell, click the button three times to cycle through the three available directions. Cell Margins customize cell margins and the spacing between cells. Convert Text to Table Create a Table from already typed text – on the Insert Tab under Table Selected text separated by paragraph marks, commas, tabs, or some other character can be converted to a Table. The Table Tools ribbons automatically open and the Table can be formatted. 16 Convert a Table to Text On the Table Tools – Layout Ribbon in the Data Group is the command to Convert a Table back to Text The Table can be Converted and separated by Paragraph Marks, Tabs, Commas, etc. The text will appear in the document, but not in a Table format 17 Use Formulas in a Table Word provides options to use Formulas to calculate a total, calculate an average, determine the highest/lowest number, and count values. On the Table Tools Layout tab, in the Data group, the Formula button will open the Formula dialog box. By default, the =SUM formula displays. This function totals the values listed in the column. Word automatically detects values in a Table when using the Formula button. 18 Use Object Zoom 19 Object Zoom is new in Read Mode and allows you to zoom in on objects such as tables, charts, and images. Click the View Tab and select Read Mode to change the page layout of the document. Double-click the Table to zoom in on the Table. The table appears with a magnifier beside it and a shadow background of the document appears behind the Table. Click the magnifier button to zoom in to the Table. The Table fills up the screen, which makes it easier for reading. Click the magnifier button again to zoom out. Click anywhere outside of the Table to exit the object zoom feature and return to the document in Read mode.