Notable Geographers
advertisement
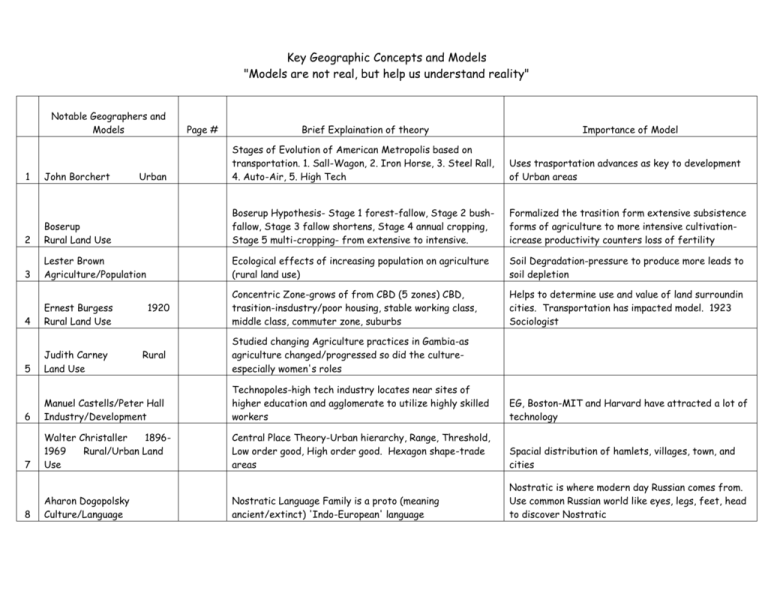
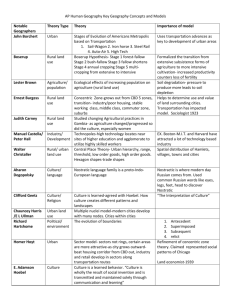
Key Geographic Concepts and Models "Models are not real, but help us understand reality" Notable Geographers and Models 1 John Borchert Urban Page # Brief Explaination of theory Importance of Model Stages of Evolution of American Metropolis based on transportation. 1. Sall-Wagon, 2. Iron Horse, 3. Steel Rall, 4. Auto-Air, 5. High Tech Uses trasportation advances as key to development of Urban areas Formalized the trasition form extensive subsistence forms of agriculture to more intensive cultivationicrease productivity counters loss of fertility 2 Boserup Rural Land Use Boserup Hypothesis- Stage 1 forest-fallow, Stage 2 bushfallow, Stage 3 fallow shortens, Stage 4 annual cropping, Stage 5 multi-cropping- from extensive to intensive. 3 Lester Brown Agriculture/Population Ecological effects of increasing population on agriculture (rural land use) Soil Degradation-pressure to produce more leads to soil depletion 4 Ernest Burgess Rural Land Use Concentric Zone-grows of from CBD (5 zones) CBD, trasition-insdustry/poor housing, stable working class, middle class, commuter zone, suburbs Helps to determine use and value of land surroundin cities. Transportation has impacted model. 1923 Sociologist 5 Judith Carney Land Use 6 Manuel Castells/Peter Hall Industry/Development Technopoles-high tech industry locates near sites of higher education and agglomerate to utilize highly skilled workers EG, Boston-MIT and Harvard have attracted a lot of technology 7 Walter Christaller 18961969 Rural/Urban Land Use Central Place Theory-Urban hierarchy, Range, Threshold, Low order good, High order good. Hexagon shape-trade areas Spacial distribution of hamlets, villages, town, and cities Nostratic Language Family is a proto (meaning ancient/extinct) 'Indo-European' language Nostratic is where modern day Russian comes from. Use common Russian world like eyes, legs, feet, head to discover Nostratic 8 Aharon Dogopolsky Culture/Language 1920 Rural Studied changing Agriculture practices in Gambia-as agriculture changed/progressed so did the cultureespecially women's roles 9 Clifford Geetz Culture/Religion Culture is Learned-atreed with Hoebel. How culture creates different patterns and landscapes 10 Peter Hall/Manuel Castells Technopoles-see Castells above 11 Chauncey Harris/E.L. Ullman 1945 Urban Land Use Multiple Nuclei Model-Modern cities develop with many nodes. Cities within cities Richard Hartshorne Rhte Evolution of Boundaries- Types of boundaries-1. Antecedent, 2. Superimposed, 3. Subsequent, 4. Relict Homer Hoyt Urban Sector Model-sectors, not rings, certain areas more attractive-as city grows, expands outward-best housing corridor from CBD out, Indstury and retail develop in sectors along trasportation routes 12 13 1939 "The Interpretation of Culture" Illustration is important! Illustration is important! Refinement of concentric zone theory. Claimed represented social patterns of Chicago. 1939-Land Economist 14 E. Adamson Hoebel Culture Culture is learned behavior. "Culture is whooly the result of social invention and is trasmitted and maintained soley through communications and learning" 15 Ellsworth Huntington Political/Development Environmental Determinism-climate and terrain were a major determinant of civilization Temperate climate of Europe lead to greater human efficiency and better standards of living. Mark Jefferson Every country has a "Primate City" (a city that dominates in economics, social factors, and poltics) Rank Size Rule2nd largest city is 1/2 the size of the Primate city, 3rd largest city is 1/3 the size of the Primate city and so on. "The law of the Primate city" The Heartland Theory-Geo-Political thought-explains why NATO and the WARSAW pact existed-control of Eastern Europe 1. Who rules Eastern Europe commands the Heartland, 2. Who rules the Heart land commands the World Island, 3. Who rules the world island commands the world 16 17 Urban Halford Mackinder 18611947 Poltical Thomas Malthus 1766-1834 Population Malthusian theory-Population growth relating to Food Supply. 1. food grows Arithmetically (1,2,3,4..), 2. Population grows Exponentially (1,2,4,8,16…), 3. Population peaks Neo-Malthusians-R. Kaplan, T.F. Homer-Dixon-look at Africa. Critics-E. Boserup, S. Kuznets, J.Simon, F. Engels-More people more growth, science will find a way, distribution of wealth, etc. 19 T.G. McGee Urban/Development Land Use in Southeast Asian cities. Old colonial port cities surrounded by a new commercial district with no formal CBD EG, Manila, Jakarta, Kuala Lumpur 20 Friedrich Ratzel 1844-1904 18 21 E.G. Ravenstein 22 W.W. Rostow Development 23 Carl Sauer 1975 24 25 26 1967 Political Organic Theory of Nations-nations act like living organisms-must grow and will eventually decline Migration Laws of Migration (11) 1. Most people migrate for economic reasons, 2. most long distance migrants are male, 3. long distance migrants head for major cities in other countries 1960 Cultural Landscape-Human activity superimposes itself on the physical landscape-each cultural group leaves imprints "The Morphology of Landscape" Ruth Leger Sivard Women/Men Gap widens with economic progress. Men are first to try unhealthy habits of progress-smoke, drink, etc. Women will catch up and lower their Life Expectancy Gideon Sjoberg Cities are products of their societies (4), 1. Folkpreliterate, 2. Feudal, 3. Pre-industrial, 4. Urban/industrial "The Pre-industrial city: Past and Present" Epidemiologist (medical geog.) control of epidemics. Link between water dupply and cholera-mapped cholera deaths and location of water wells/pumps Outbreak-a spread of disease in a short time in a limited area-school, hospital. Epidemic-spread of disease over a lareer region like a city, province or country Pandemicspread rapidly around the entire world John Snow Development 1889- Mondernization Model-5 stages of Economic Development1. Traditional society, 2. Pre-conditions to Take-off, 3. Take off, 4. Maturity, 5. Mass Consumption, etc. Culture Urban 27 Nicholas Spykman Political Rimland Theory-Eurasian Rim not the Heartland is/was the key to Global Power. Who Controls the Rimland rules Eurasia. Who rules Eurasia controls the destinies of the world 28 E.L. Ullman/Chaucey Harris Urban Multiple Nuclei Model-Modern cities develop with many nodes. Cities within cities 29 Vidal De La Blache 1845-1918 Culture Possibillism-Human/Environmental Interaction-Humans have a wide range of potential actions within an environment-they respond ased on their value systems, attitudes, and culture attributes "Principles of Human Geography" Culture determines a people respons to the Environment 30 Johann Hinrich vonThunen 1783-1850 Rural Agricultural Theory (concentric circles) 1. city center, 2. market gardening, 3. forest, 4. grains, 5. ranching, livestock. Pre-central place Distribution of Agricultureal activites around a city depends on Bulk and Perishablity of products. 31 Immanuel Wallerstein 1970 Development Core-Periphery Model. Core-MDC's-high soci-economic level. Periphery-LDC's-dependent on the core, suppplier of raw materials and labor EG. Auto Industry-clustered near Detroit-auto makers, labor, suppliers or car parts, transportation. Location depends on raw materials, markets and labor 32 Alfred Weber 1868-1956 Indsutry/Development Location of Industy-Least Cost Theory Agglomeration-People and activites concentrate in a location where they can share facilities and services. "Geography of the Place" Western Europe and Russia Europe, Middle East and Asia HeartlandRimland-Western




![Model_and_Theory_Chart[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008565077_1-f7a3d3b1b3bb86c6e31ff39e95c26da5-300x300.png)
