Land Navigation

Map Reading
For use with the Tenino map
Basic Map Skills
Identify Map Colors
Identify Map Symbols
Identify Marginal Information
Identify Terrain Features
Map Colors
Black - Indicates cultural (man-made) features such as buildings and roads, surveyed spot elevations, and all labels.
Red - Classifies cultural features, such as populated areas, main roads, and boundaries, on older maps
Red-Brown - Combined to identify cultural features, all relief features, non-surveyed spot elevations, and elevation, such as contour lines on red-light readable maps.
Map Colors
Blue - Identifies hydrography or water features such as lakes, swamps, rivers, and drainage.
Green - Identifies vegetation with military significance, such as woods, orchards, and vineyards.
Brown - Identifies all relief features and elevation, such as contours on older edition maps, and cultivated land on red-light readable maps.
Other - Occasionally other colors may be used to show special information. These are indicated in the marginal information as a rule.
Identify Map
Symbols
Refer to Legend
Marginal Information
Name of map sheet: named after largest city or natural feature
Series name: name of major political subdivision ie: state
Scale: ratio of map distance to corresponding distance on Earth
Series number: sequence reference
Edition number: newest edition will have highest number
Sheet number: reference to link adjoining maps together
Legend: annotates what map symbols represent
Bar scale: rulers to convert map distance to ground distance
Declination diagram: angular relationships of true, grid and magnetic north; map/compass azimuth conversion
Grid reference box: Grid zone identification
Adjoining Sheets Diagram: relation of sheet to other sheets
3
Marginal Info Map Location
1
6 5 2
4
7
2 5 6 1
1. Sheet Name: Tenino
2. Sheet Number: 1477 IV
3. Series Name: Washington
4. Scale: 1:50,000
5. Series Number: V791
8
9
11
10
6. Edition Number: 7-DMATC
7. Legend
8. Grid Reference Box.
9. Bar Scales
10. Declination Diagram
11. Adjoining Sheets Diagram
Check On Learning
1. What are the six colors used on a military map and what do they represent?
2. What portion of a map explains the symbols and features used, and where can you find it?
3. What are the Map Series Name , Scale , and Series Number of your Tenino Map?
4. Where is the declination diagram and what does it tell you?
5. What is the adjoining sheet number directly south of the
Tenino Map Sheet?
Terrain Features
Terrain Features - Major
Hill
Valley
Ridge
Saddle
Depression
Need help remembering?
Hidden Valley Ranch Salad Dressing
HILL
A hill is an area of high ground. From a hilltop, the ground slopes down in all directions. A map depicts a hill by showing contour lines forming concentric circles (circles having a common center). The inside of the smallest closed circle is the hilltop
VALLEY
A valley is a stretched out groove in the land, usually formed by streams or major rivers. If standing in a valley, three directions offer high ground, while the fourth direction offers low ground. The contour lines forming a valley are either U-shaped or V-shaped.
The closed end of the contour line (U or V) always points upstream or toward higher ground.
RIDGE
A ridge is a sloping line of high ground. If you are standing on the centerline of a ridge, you will normally have low ground in three directions and high ground in one direction with varying degrees of slope. If you cross a ridge at right angles, you will climb steeply to the crest and then descend steeply to the base. Contour lines forming a ridge tend to be U-shaped or V-shaped. The closed end of the contour line points away from high ground.
SADDLE
A saddle is a dip or low point between two areas of higher ground. A saddle is not necessarily the lower ground between two hilltops; it may be simply a dip or break along a level ridge crest. If you are in a saddle, there is high ground in two opposite directions and lower ground in the other two opposite directions.
DEPRESSION
A depression is a low point in the ground or a sinkhole. It could be described as an area of low ground surrounded by higher ground in all directions, or simply a hole in the ground. Usually only depressions that are equal to or greater than the contour interval will be shown. On maps, depressions are represented by closed contour lines that have tick marks pointing toward low ground.
Terrain Features - Minor
Draw
Spur
Terrain Features - Supplementary
Cliff
Cut
Fill
DRAW
A draw is a stream course that is less developed than a valley. In a draw, there is essentially no level ground and, therefore, little or no maneuver room within its confines. If you are standing in a draw, the ground slopes upward in three directions and downward in the other direction. A draw could be considered as the initial formation of a valley.
SPUR
A spur is a short, continuous sloping line of higher ground, normally jutting out from the side of a ridge. A spur is often formed by two roughly parallel streams cutting draws down the side of a ridge. The ground will slope down in three directions and up in one. Contour lines on a map depict a spur with the U or
V pointing away from high ground.
CLIFF
A cliff is a vertical or near vertical feature; it is an abrupt change of the land. When a slope is so steep that the contour lines converge into one “carrying” contour of contours, this last contour line has tick marks pointing toward low ground. Cliffs are also shown by contour lines very close together and, in some instances, touching each other.
CUT
A cut is a man-made feature resulting from cutting through raised ground, usually to form a level bed for a road or railroad track.
Cuts are shown on a map when they are at least 10 feet high, and they are drawn with a contour line along the cut line. This contour line extends the length of the cut and has tick marks that extend from the cut line to the roadbed, if the map scale permits this level of detail.
FILL
A fill is a man-made feature resulting from filling a low area, usually to form a level bed for a road or railroad track. Fills are shown on a map when they are at least 10 feet high, and they are drawn with a contour line along the fill line. This contour line extends the length of the filled area and has tick marks that point toward lower ground. If the map scale permits, the length of the fill tick marks are drawn to scale.
PRACTICAL EXERCISE
1. Hill 2. Valley 3. Ridge 4. Saddle 5. Depression
ANSWERS:
6. Draw 7. Spur 8. Cliff 9. Cut 10. Fill
Basic Map Skills
Identify Grid
Determine Elevation
Determine Azimuth / Back Azimuth
Grid vs. Magnetic Azimuth
Determine Distance
Identify a Grid
Grid Zone Identification
•4-Digit Coordinate: within 1000 meters
•6-Digit Coordinate: within 100 meters
•8-Digit Coordinate: within 10 meters
*The more digits in a grid coordinate, the closer the location.
4-Digit Grid
•Read Right then Up
•Bottom left corner identifies first two digits
Right:11 Up: 81 ex. 11 81 e
•Add proper grid zone designator to front ex. AB1181
6-Digit Grid
•Read Right then Up
•Bottom left corner identifies first two digits 11 81 e
•Use coordinate scale to identify last digit ex. 115813
•Add proper grid zone designator to front ex: AB115813
50m tick marks
8-Digit Grid
•If point is between 2-100 meter tick marks use the
50 meter tick marks to help estimate
8-Digit Grid
82
6
5
4
3
2
9
8
7
AB 11578136
1
81
4 5 6 7 8 9
12
•Read Right then Up
•Bottom left corner identifies first two digits 11 81 e
•Use coordinate scale to identify last two digits ex: 11578136
•Add proper grid zone designator to front ex: AB 11578136
PRACTICAL EXERCISE
1. What is the name of the mountain in grid EG1486?
ANSWER: Northcraft Mountain
2. What’s the name of the lake in grid EH0103?
ANSWER: Black Lake
3. What number benchmark is in grid EG0589?
ANSWER: BM 86
4. What is the 6-digit coordinate of the TV relay tower found at EG1287?
ANSWER: EG 126877
5. What is the 6-digit coordinate of the lake found at EG0998?
ANSWER: EG 095984
6. What is the 8-digit coordinate of the Deschutes Fire Tower found at EG1795?
ANSWER: EG 17679514
7. What is the 8-digit coordinate of the coal mine found at EG1582?
ANSWER: EG 15848215
8. What is the 8-digit coordinate of the hilltop found at EH0302?
ANSWER: EH 03390235
Determine Elevation
Determine Elevation
Locate point on the map
Determine contour interval of map
Locate index contour line nearest point
Count number of contour lines up or down that must be crossed to get to point
Points at top of hill add half the contour interval
Points at bottom of depression subtract half the contour interval
Determine Azimuth
Determine Azimuth
Azimuth: a horizontal angle measured clockwise from a north base line. This north base line could be true north, magnetic north, or grid north. The azimuth is the most common military method to express direction.
Plot location of two points.
Use straight edge to draw line between both points (line must be long enough to cross scale on protractor)
Place the index of the protractor at the point where the drawn line crosses a vertical (north-south) grid line.
Keeping the index at this point, align the 0-to-180 degree line of the protractor on the vertical grid line.
Read the value of the angle from the scale; this is the grid azimuth from point A to point B.
A
104 °
B
When measuring azimuths on a map, remember that you are measuring from a starting point to an ending point. If a mistake is made and the reading is taken from the ending point, the grid azimuth will be opposite, thus causing the user to go in the wrong direction.
Back Azimuth
A back azimuth is the opposite direction of an azimuth. It is comparable to doing an "about face."
Back Azimuth - azimuth taken from a distant point toward your location
Used in Resection
Numbers less than 180
°
: add 180
°
Ex: azimuth = 145 ° , resection = 145 ° +180 ° = 325 °
Numbers greater than 180
°
: subtract 180
°
Ex: azimuth = 270 ° , resection = 270 ° -180 ° = 90 °
PRACTICAL EXERCISE
1. What is the grid azimuth from the TV relay tower in EG1287 to the water tower in EG0985? What is the back azimuth?
ANSWER: azimuth = 233 ° back azimuth = 53 °
2. What is the grid azimuth from the bridge in EG0292 to the mine pit in
EG0694? What is the back azimuth?
ANSWER: azimuth = 68
° back azimuth = 248
°
3. What is the grid azimuth from the Deschutes Fire Tower in EG1795 to
BM 88 in EG1798? What is the back azimuth?
ANSWER: azimuth = 6 ° back azimuth = 186 °
4. What is the grid azimuth from the BM 65 in EH0900 to the bridge in
EG1196? What is the back azimuth?
ANSWER: azimuth = 161
° back azimuth = 341
°
Grid vs. Magnetic
Azimuth
The Three Norths
•True North: A line from any point on the earth's surface to the north pole. All lines of longitude are true north lines.
•Magnetic North: The direction to the north magnetic pole, as indicated by the north-seeking needle of a magnetic instrument. ie: a compass
•Grid North: The north that is established by using the vertical grid lines on the map.
Grid-Magnetic Angle: The G-M angle value is the angular size that exists between grid north and magnetic north. Azimuths translated between map and ground will be in error by the size of the declination angle if not adjusted for it.
Converting Grid/Magnetic Azimuths
Since the location of magnetic north does not correspond exactly with the grid-north lines on the maps, a conversion from magnetic to grid or vice versa is needed.
Refer to the conversion notes with Declination Diagram.
21°
Grid to Magnetic azimuth:
– East G-M angle: subtract
– Ex: GM angle: 21°, grid azimuth: 360° magnetic azimuth: 360°-21°=339 °
Easterly Declination
Magnetic to Grid azimuth:
– East G-M angle: add
– Ex: GM angle: 21°, grid azimuth: 360° magnetic azimuth: 360°+21°=21 °
*There are no negative azimuths on the azimuth circle; will be between 0° and 360° ex: -30° = 330°, 380°= 220°
Converting Grid/Magnetic Azimuths
Since the location of magnetic north does not correspond exactly with the grid-north lines on the maps, a conversion from magnetic to grid or vice versa is needed.
Refer to the conversion notes with Declination Diagram.
30°
Grid to Magnetic azimuth:
– West G-M angle: add
– Ex: GM angle: 30°, grid azimuth: 140°
Westerly Declination magnetic azimuth: 140°+30°=170°
Magnetic to Grid azimuth:
–
–
West G-M angle: subtract
Ex: GM angle: 30°, grid azimuth: 140° magnetic azimuth: 140°-30°=110°
*There are no negative azimuths on the azimuth circle; will be between 0° and 360° ex: -30° = 330°, 380°= 220°
PRACTICAL EXERCISE
1. The G-M angle is 21° east. You plot an azimuth of 146 °. What is your magnetic azimuth? ANSWER: 146°-21° = 125°
2. The G-M angle is 45° west. You plot an azimuth of 30 °. What is your magnetic azimuth? ANSWER: 30°+45° = 75°
3. The G-M angle is 40° east. You plot an azimuth of 15 °. What is your magnetic azimuth? ANSWER: 15°-40° = 335°
4. The G-M angle is 21° east. You shoot an azimuth of 146 °. What is your grid azimuth? ANSWER: 146°+21° = 167°
5. The G-M angle is 45° west. You shoot an azimuth of 30°. What is your grid azimuth? ANSWER: 30°-45° = 345°
6. The G-M angle is 40° east. You shoot an azimuth of 15 °. What is your grid azimuth? ANSWER: 15°+40° = 55°
Grid to Magnetic azimuth:
East G-M angle: subtract
West G-M angle: add
Magnetic to Grid azimuth:
East G-M angle: add
West G-M angle: subtract
Determine Distance
Determine Distance
Straight-Line Distance
A straight-line distance is the shortest route between two points.
STEP 1 : Use edge of paper and mark distance between points.
Determine Distance
Straight-Line Distance
STEP 2 : Line paper up next to scale to determine distance.
PRACTICAL EXERCISE
1.
What is the straight-line distance in meters from BM 61 in EH1603 to the horizontal control station in EG1798?
ANSWER: 5850 meters
2. What is the straight-line distance in meters from the mine pit in
EG0694 to the bridge in EG0292?
ANSWER: 3575 meters
3. What is the straight-line distance in meters from the TV relay tower in
EG1287 to the water tower in EG0985?
ANSWER: 4090 meters
4. What is the straight-line distance in meters from the horizontal control point "Skook" in EG1682 and the water tower in EG1088?
ANSWER: 8,640 meters
–
–
Determine Distance
Curved or road distances are used when you need to measure the distance along a winding road, stream, or any other route following an irregular course.
Break curve into series of straight lines and measure from curve to curve
Line paper up next to scale to determine distance
STEP 1: Mark on your map starting point A and finishing point B.
STEP 2: Place a tick mark near one end of a straight edge piece of paper.
STEP 3 : Align the straight edge of the paper with the road on the map so that the tick mark is on the start point and the edge of the paper extends along the route to a point where the route changes direction.
Determine Distance
Curved/Road Distance
STEP 4: At the point where the road changes direction and does not follow the edge of the paper, place a tick mark at that point on your map and the piece of paper.
Determine Distance
Curved/Road Distance
STEP 5: Rotate the paper so that the tickmark you just made on the paper and map are aligned and the straight edge follows the road until the road changes direction again. As before, place a tickmark on the piece of paper and the map at the location where the road changes direction.
Continue this process until you reach Point B.
STEP 6: Now that you have a straight-line measurement, determine the distance on the bar scale the same way to you learned to measure straightline distances.
PRACTICAL EXERCISE
1. What is the road distance in meters from the horizontal control station "Skook" in grid square EG16108255 and the bridge in grid square EG13558355?
ANSWER: 3240 meters
10% margin of error: between 2916 m and 3564 m.
2.
What is the road distance in meters from the road intersection located at EG14008840 to the road intersection located at
EG16358835?
ANSWER: 2600 meters
10% margin of error: between 2340 m and 2860 m.
3. What is the road distance in meters from EG 10759700 to
EH08950100?
ANSWER: 5150 meters.
10% margin of error: between 4,635 m and 5,665 m.
Advanced Skills
Compass Familiarization
Intersection
Resection
Modified Resection
Compass
Familiarization
Compass-to-Cheek Method
Centerhold Method
Intersection
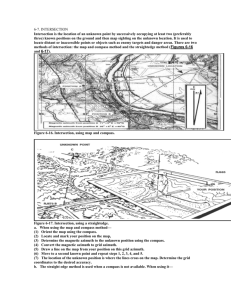
Intersection
Intersection is the location of an unknown point by successively occupying at least two (preferably three) known positions on the ground and then map sighting on the unknown location. It is used to locate distant or inaccessible points or objects such as enemy targets and danger areas.
SCENARIO:
We have two OPs located in front of our defensive position. Both OPs can see enemy activity. From OP1, the enemy activity is 32
° magnetic and from OP2, it is 322
° magnetic. The G-M angle is 18
° easterly.
What is the enemy’s location?
How to Solve
Step 1:
Identify / plot OPs or points of reference
Step 2:
Convert azimuth from magnetic to grid
G-M Angle: 18
° east
OP1: 32 ° magnetic
32
°
+18
°
= 50° grid
OP2: 322 ° magnetic
322
°
+18
°
= 140° grid
Step 3:
Using the protractor
Plot first azimuth
- 50
° grid
Step 3:
Using the protractor
Plot first azimuth
- 50
° grid
Step 4:
Plot second azimuth
- 240 ° grid
Step 3:
Using the protractor
Plot first azimuth
- 50
° grid
Step 4:
Plot second azimuth
- 240 ° grid
Bad Guys
Step 5:
Plot intersection
The enemy will be at the point where the lines intersect.
Step 3:
Using the protractor
Plot first azimuth
- 50
° grid
Step 4:
Plot second azimuth
- 240 ° grid
Bye Bye
Step 5:
Plot intersection
Step 6:
Kill Bad Guys
Practical Exercise - Intersection
You receive radio calls from both OP1 and OP2. Each report enemy activity to their south. Both report approx 5 dismounted troops and one vehicle. You believe they are looking at the same enemy unit. If you can determine their location, you can destroy them with artillery fires. OP1, located atop Hill 210 vic EG1290, reports the enemy to be at 100
° magnetic from his location.
OP2, located atop Hill 222 vic EG1690, reports the enemy to be at 168
° magnetic from his location. What is the 8-digit grid to the enemy?
ANSWER: EG16238850
Resection
Resection
Resection is the method of locating one's position on a map by determining the grid azimuth to at least two well-defined locations that can be pinpointed on the map. For greater accuracy, the desired method of resection would be to use three or more welldefined locations.
SCENARIO:
Looking out from our position we can see a bridge. Using our compass we determine the azimuth to its location to be 159° . We can also see a large road intersection. The azimuth to its location is 117° . We locate these positions on our map which has a westerly G-M angle of 1
°
. What is our location?
Step 1:
-Identify / plot OPs or points of reference
Step 2:
-Convert azimuth from magnetic to grid
G-M Angle: 1
° west
Bridge: 159
° magnetic
159
°
- 1
°
= 158° grid
Road Int: 117
° magnetic
117
°
- 1
°
= 116° grid
WHERE
AM I?
Step 3:
-Convert azimuth to back azimuth
Bridge: 158 ° grid from you
Back Az: 158 ° + 180 ° = 338 °
Road Int: 116 ° grid from you
Back Az: 116 ° + 180 ° = 296 °
WHERE
AM I?
Step 4:
- Plot 1st back azimuth from bridge 338
°
Step 4:
Plot 1st back azimuth from bridge 338
°
Step 5:
Plot 2nd back azimuth from road intersection 296
°
Step 4:
Plot 1st back azimuth from bridge 338
°
Step 5:
Plot 2nd back azimuth from road intersection 296
°
Step 6:
- Plot your position
X
Your position will be at the point where the lines intersect.
Step 4:
Plot 1st back azimuth from bridge 338
°
Step 5:
Plot 2nd back azimuth from road intersection 296
°
Step 6:
- Plot your position
Step 7:
- Call for a pizza!
X
Practical Exercise - Resection
You are patrolling vicinity of Rock Prairie/ Grid EG0986 and your CO wants to know your position. You look around and see a water tower to the north / EG1088 at
344 degrees magnetic. You turn to your left and see a church at the town of “Violet Prairie” at 256 degrees magnetic. What is the 8-digit grid of your location?
ANSWER: EG10058662
Modified Resection
Modified Resection
Modified resection is the method of locating one's position on the map when the person is located on a linear feature on the ground, such as a road, canal, or stream
SCENARIO:
Looking out from our position along Steam Mill Road, you can see the top of Hill 445 to our NW. Using your compass you determine the magnetic azimuth to its location to be 299 ° . You locate the road and Hill 445 on your map which has a G-M angle of 18
° easterly. Where are you?
Step 1:
-Identify / plot OPs or points of reference
Step 2:
- Convert azimuth from magnetic to grid
G-M Angle: 18
° east
Hill 445: 299
°
299
°
+18
°
= 317
° grid
Step 3:
- Convert azimuth to back azimuth
Hill 445: 317
° grid from you
Back Az: 317
°
- 180
°
= 137
°
Step 4:
- Plot back azimuth from Hill 445 - 137°
Step 4:
- Plot back azimuth from Hill 445 - 137°
Step 5:
- Plot your position where the line intersects the road you are on
X
Step 6:
- Drive on airborne,
START WALKING!!
Your position is where the line crosses the road.
Practical Exercise – Modified Resection
You are driving south on I-5 and run out of gas. You stop on the right side of the Freeway to check your location. From your position you can see a school located at grid EH0603 at a 117 degree magnetic azimuth.
What is your 8-digit grid coordinate? ANSWER :
EH06550444