SEHS
advertisement
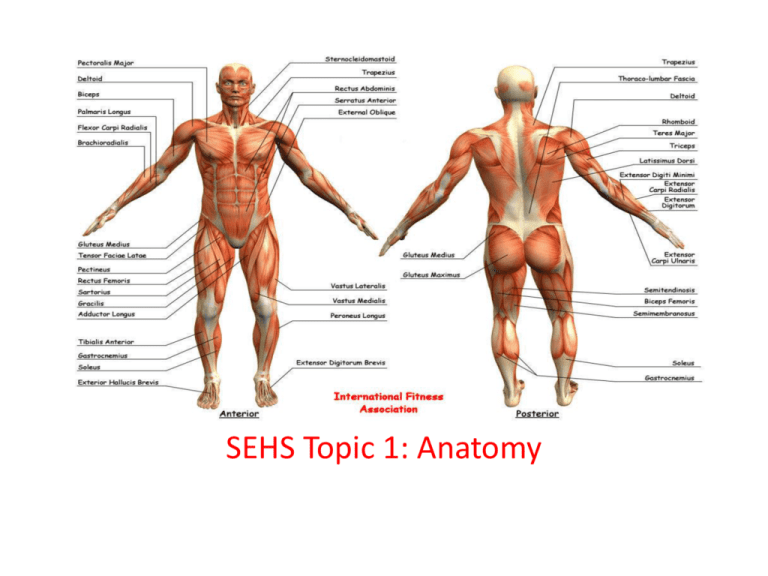
SEHS Topic 1: Anatomy Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton • Axial skeleton: • skull, ribs, sternum, and vertebral column: cervical -7; thoracic – 12; lumbar – 5; sacral – 5 (fused as 1); coccyx – 4 (fused as 1) • Appendicular skeleton: • Pectoral girdle (scapulae and clavicles); humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges • Pelvic girdle (ilium, ischium and pubis); femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals and phalanges Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton in terms of function • The axial skeleton consists of the 80 bones along the central axis of the human body. Primary function is protection. Of what? _________ • The appendicular skeleton is composed of 126 bones of the lower limbs and upper limbs. Primary function is locomotion. State four types of bones • Long • Short • Flat • Irregular • Long: Typical bone type (ex. like a dog bone), long, straight + sometimes rounded ends. -----Ex. Humerus, Femur, Radius, Ulna, Tibia, Fibula, etc.. Cont’d • Short; Very small bones in the hands and feet. -----Ex. Carpal and Tarsal bones. • Irregular: Strange shape, doesn't really fit into another category. -----Ex. temporal bone, skull bones with facial features, etc... • Flat: Protective bones that are smooth and flat -----Ex. Top of cranium, ribs, sternum, etc... Draw and annotate the structure of a long bone • Must include the: • Epiphysis, spongy bone, articular cartilage, diaphysis, compact bone, bone marrow, marrow cavity, blood vessel, periosteum Cont’d Your turn – Draw one Anatomical Terminology • **assume anatomical position: Terminology • A. Superior: toward the head or upper part of a structure • Example: The head is superior to the shoulders. • • B. Inferior: away from the head or toward the lower part of a structure • Example: The intestines are inferior to the lungs • • C. Anterior (also known as ventral): toward the front of the body • Example: The trachea is anterior to the esophagus. • D. Posterior (also known as dorsal): toward the back of the body • Example: The esophagus is posterior to the trachea. Terminology continued • E. Medial: locating a structure nearer to the midline of the body, which divides the body into equal right and left halves. • Example: The ulna is medial to the radius. • F. Lateral: locating a structure further from the midline of the body • Example: The lungs are lateral to the heart. • • H. Proximal: nearer to the point of attachment of an appendage to the trunk of the body • Example: The knee is proximal to the shin. • • I. Distal: farther from the point of attachment of an appendage to the trunk of the body • Example: The elbow is distal the shoulder. • Terminology cont’d • J. Superficial: toward or on the surface of the body • Example: The skin is superficial to the muscles. • • K. Deep: away from the surface of the body. Example: The ribs are deep to the skin Using the skeleton below and the one in the classroom, properly use each of the following only: • Inferior, superior, proximal, distal, medial, lateral, posterior, anterior Anatomical Planes • FRONTAL (or coronal) separates the body into Anterior and Posterior parts • MEDIAN (or midsagittal) separates body into Right and Left parts • HORIZONTAL separates the body into Superior and Inferior parts • SAGITTAL any plane parallel to the median plane • After Anatomical Planes continued Outline the function of connective tissue • What is connective tissue? Connective tissue (CT) is a kind of biological tissue that supports, connects, or separates different types tissues and organs of the body All CT has three main components: cells, fibers, and extracellular matrices of Examples of connective tissue • Special connective - reticular connective tissue, adipose tissue, cartilage, bone, and blood. • IB will limit CT to understanding the function of : – Ligaments – attach bone to bone - Cartilage – articular cartilage/is a type of cartilage found on many joint surfaces (aka hyaline cartilage) - Tendons – attach muscle to bone Define the term Joint • A joint occurs where two or more bones articulate • Types of joints: Outline the features of a synovial joint • Must include articular cartilage, synovial membrane, synovial fluid, bursae, meniscus, and articular capsule Hmwk • • • • • • Function of: Synovial Fluid – Bursae – Meniscus – Ligaments – Joint (articular) capsule – LIST the different types of synovial joints