Epe and Newton_s 2nd law
advertisement

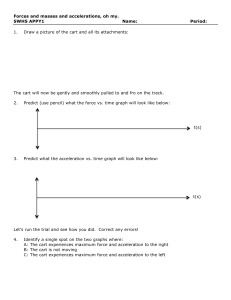
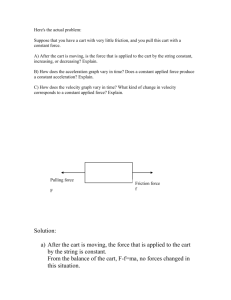
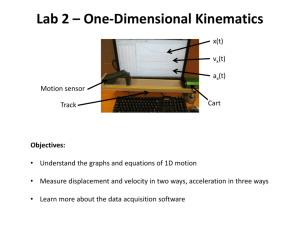
Warm-up • The extent of my disappointment in you is beyond words…. Do Not TALK!! • You are to write a letter of apology to Mrs. Gleason for having to clean up the MESS you guys left in the library on Friday. • Unfortunately, to those who were on point on Friday the rest of the class ruined it for you…. Warm up • If I told you that within a closed system a system only has 3 forms of energy KE, GPE, and HE and this system had the following: – 1542 J of total energy – 134 J of Kinetic Energy – 1045 J of GPE How much HE would the system have? What law would help explain this? Elastic Potential Energy • When an elastic material is stretched or compressed, a force is applied to transfer energy to that material. • The elastic force and the distance that the elastic is stretched or compressed are related to the properties of the material and are known as the elastic constant. • The elastic constant is different for every elastic material. • All elastic material have an elastic limit, which is the point the material will no longer return to it’s original shape and no longer behave like an elastic material Newton’s Second Law • Net Force = Mass x Acceleration (F = MA) • As force increases, acceleration increases • As mass increases, acceleration decreases Let’s Investigate • You will need the following: – One track – 2 blocks – 1 cars – weights – Meter stick Trial 1 Setting Mass Distance Force 1 .1 kg 1N 2 .1 kg 3N 3 .1kg 6N Work Acceleration Trial 1 Observe the motions of the carts with no Weight after you release the plunger by tapping on it with a pencil on setting 1. Measure the distance your car goes up the ramp Repeat for setting 2 and 3 Assume that the force from the plunger is : 1 Newton at setting 1 3 newtons at setting 2 6 newtons at setting 3. Each cart has a mass of 0.1 kg. • What is the work done by cart 1 at each setting • What is the acceleration on cart 1? Trial 2 Add the 20g mass to the cart. Record the distance the cart traveled up the ramp at all settings the mass you added to the red cart is 0.020 kg, so the new mass of cart is __________. • What is the work done by cart 1 at each setting • What is the acceleration on the cart? • How did the acceleration change when the mass increased? Trial 3 • Add the 200 g mass. Record the distance the cart traveled up the ramp at all settings • What is the work done by cart 1 at each setting • What is the acceleration on cart? • How did the acceleration change when the force increased? Lab Report • Introduction- restate our purpose and hypothesis and add some more details of what we are testing- using EPE we are testing newton’s second law. • Procedure- Repeat what we did • Data- Put all data in table like this: Setting Mass Distance Force 1 .1 kg .3 m 1N 2 .1 kg .63 m 3N 3 ,1kg 1.11 m 6N Work Acceleration Lab Report • Analysis- graph the distance for each trial! • Conclusion: How does Mass affect acceleration? Did you prove or disprove your hypothesis? What is EPE? How did we use it? Draw conclusion based on your data!