Competing for Advantage
advertisement
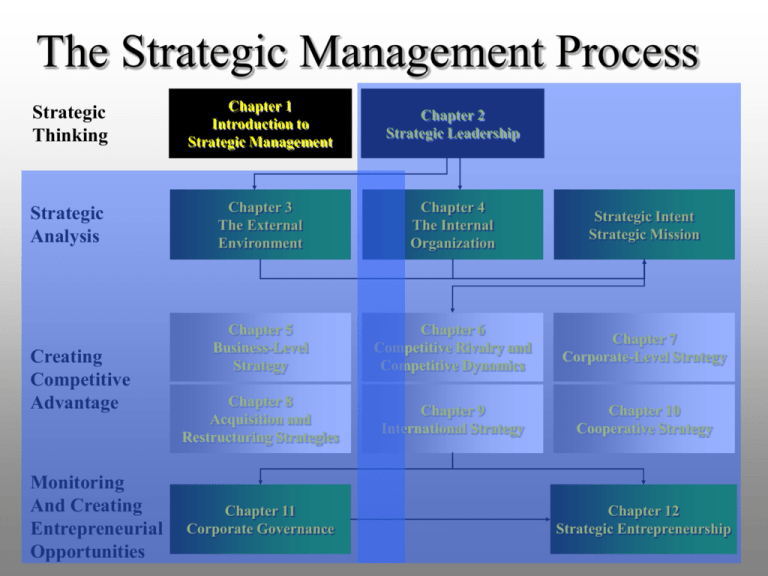
The Strategic Management Process Strategic Thinking Chapter 1 Introduction to Strategic Management Chapter 2 Strategic Leadership Strategic Analysis Chapter 3 The External Environment Chapter 4 The Internal Organization Strategic Intent Strategic Mission Chapter 5 Business-Level Strategy Chapter 6 Competitive Rivalry and Competitive Dynamics Chapter 7 Corporate-Level Strategy Chapter 8 Acquisition and Restructuring Strategies Chapter 9 International Strategy Chapter 10 Cooperative Strategy Creating Competitive Advantage Monitoring And Creating Entrepreneurial Opportunities Chapter 11 Corporate Governance Chapter 12 Strategic Entrepreneurship 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Strategic Management Robert E. Hoskisson Michael A. Hitt R. Duane Ireland ©2004 by South-Western/Thomson Learning 2 Determinants of Firm Respectability 1. Strong and well-thought-out strategy 2. Maximize customer satisfaction and loyalty 3. Business leadership 4. Quality products and services 5. Strong and consistent profits 3 Definitions Strategic Management Process The full set of commitments, decisions, and actions required for a firm to create value and earn above-average returns Value Creation What is achieved when a firm successfully formulates and implements a strategy that other companies are unable to duplicate or find too costly to imitate. 4 The Firm and Its Stakeholders Stakeholders Groups The firmwho must aremaintain affected by a firm’s performance performance at an adequate and who have level claims in orderontoits retain wealth the participation of key stakeholders 5 The Firm and Its Stakeholders Stakeholders Capital Market Stakeholders Shareholders Major suppliers of capital •Banks •Private lenders •Venture capitalists 6 The Firm and Its Stakeholders Stakeholders Capital Market Stakeholders Product Market Stakeholders Primary customers Suppliers Host communities Unions 7 The Firm and Its Stakeholders Stakeholders Capital Market Stakeholders Product Market Stakeholders Organizational Stakeholders Employees Managers Nonmanagers 8 Stakeholder Involvement Two issues affect the extent of stakeholder involvement in the firm Organizational Capital Market 1 How do you divide the returns to keep stakeholders involved? Product Market 9 Stakeholder Involvement Two issues affect the extent of stakeholder involvement in the firm Organizational Capital Market 2 How do you increase the returns so everyone has more to share? Product Market 10 Competitive Landscape Emergence of global economy Goods, services, people, skills, and ideas move freely across geographic borders Spread of economic innovations around the world Hypercompetitive environments Fundamental nature of competition is changing Political and cultural adjustments are required 11 Competitive Landscape Emergence of global economy Rapid technological change Increasing rate of technological change and diffusion The information age Increasing knowledge intensity Hypercompetitive environments Fundamental nature of competition is changing 12 Strategic Flexibility A set of capabilities used to respond to various demands and opportunities existing in a dynamic and uncertain competitive environment Andrew Grove, Intel’s former CEO: “Only paranoid companies survive and succeed.” 13 I/O Model of Above-Average Returns 1. External Environments General Global Industry Environment Competitor Environment Technological Environment 1. Strategy dictated by the external environment of the firm (what opportunities exist in these environments?) 2. Firm develops internal skills required by external environment (what can the firm do about the opportunities?) 14 Four Assumptions of the I/O Model 1. The external environment is assumed to possess pressures and constraints that determine the strategies that would result in above-average returns 2. Most firms competing within a particular industry or within a certain segment of it are assumed to control similar strategically relevant resources and to pursue similar strategies in light of those resources 15 Four Assumptions of the I/O Model 3. Resources used to implement strategies are highly mobile across firms 4. Organizational decision makers are assumed to be rational and committed to acting in the firm’s best interests, as shown by their profit-maximizing behaviors 16 I/O Model of Above-Average Returns Industrial Organization Model The External Environment 1. Study the external environment, especially the industry environment • economies of scale • barriers to market entry • degree of concentration of firms in the industry • etc. 17 I/O Model of Above-Average Returns Industrial Organization Model The External Environment An Attractive Industry 2. Locate an attractive industry with a high potential for above-average returns Attractive industry: one whose structural characteristics suggest above-average returns 18 I/O Model of Above-Average Returns Industrial Organization Model The External Environment 3. Identify the strategy called for by the attractive industry to earn above-average returns An Attractive Industry Strategy Formulation Strategy formulation: selection of a strategy linked with above-average returns in a particular industry 19 I/O Model of Above-Average Returns Industrial Organization Model The External Environment 4. Develop or acquire assets and skills needed to implement the strategy An Attractive Industry Strategy Formulation Assets and Skills Assets and skills: those assets and skills required to implement a chosen strategy 20 I/O Model of Above-Average Returns Industrial Organization Model The External Environment 5. Use the firm’s strengths (its developed or acquired assets and skills) to implement the strategy An Attractive Industry Strategy Formulation Assets and Skills Strategy Implementation Strategy implementation: select strategic actions linked with effective implementation of the 21 chosen strategy I/O Model of Above-Average Returns Industrial Organization Model The External Environment An Attractive Industry Strategy Formulation Assets and Skills Strategy Implementation Superior returns: earning of above-average returns Superior Returns 22 Resource-based Model of Above Average Returns 1. Firm’s Resources 1. Strategy dictated by the firm’s unique resources and capabilities 2. Find an environment in which to exploit these assets (where are the best opportunities?) 23 Resource-based Model of Above Average Returns Resource-based Model Resources 1. Identify the firm’s resources-strengths and weaknesses compared with competitors Resources: inputs into a firm’s production process 24 Resource-based Model of Above Average Returns Resource-based Model Resources Capability 2. Determine the firm’s capabilities--what it can do better than its competitors Capability: capacity of an integrated set of resources to integratively perform a task or activity 25 Four Attributes of Resources and Capabilities (Competitive Advantage) Rare Costly to imitate Nonsubstitutable Resources and Capabilities Valuable allow the firm to exploit opportunities or neutralize threats in its external environment possessed by few, if any, current and potential competitors when other firms cannot obtain them or must obtain them at a much higher cost when there are no structural equivalents, i.e., no strategically equivalent resources 26 Resources and capabilities that meet these four criteria become: Rare Costly to imitate Nonsubstitutable Resources and Capabilities Valuable Core Competencies 27 Core Competencies are the basis for a firm’s Competitive advantage Value Creation Core Competencies Ability to earn above-average returns 28 Resource-based Model of Above Average Returns Resource-based Model Resources 3. Determine the potential of the firm’s resources and capabilities in terms of a competitive advantage Capability Competitive Advantage Competitive advantage: ability of a firm to outperform its rivals 29 Resource-based Model of Above Average Returns Resource-based Model 4. Locate an attractive industry Resources Capability Competitive Advantage An Attractive Industry An attractive industry: an industry with opportunities that can be exploited by the firm’s resources and capabilities 30 Resource-based Model of Above Average Returns Resource-based Model Resources Capability 5. Select a strategy that best allows the firm to utilize its resources and capabilities relative to opportunities in the external environment Competitive Advantage An Attractive Industry Strategy Form/Impl Strategy formulation and implementation: strategic actions taken to earn above average returns 31 Resource-based Model of Above Average Returns Resource-based Model Resources Capability Competitive Advantage An Attractive Industry Strategy Form/Impl Superior returns: earning of above-average returns Superior Returns 32 Four Assumptions of the ResourceBased Model 1. Differences in firms’ performances are primarily due to unique core competences rather than industry characteristics 2. Across time, firms acquire different resources and develop unique capabilities 3. Resources are not highly mobile across firms 4. Each firm is a unique collection of resources and capabilities 33 Strategic Intent & Mission Strategic Intent Winning competitive battles by leveraging the firm’s resources, capabilities, and core competencies Strategic Mission An application of strategic intent in terms of products to be offered and markets to be served 34