America Foreign Relations
advertisement

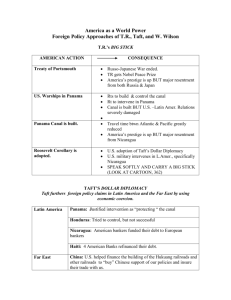
America as a global power Alfred Thayer Mahan The Influence of Sea Power Upon History, 1660-1783 •Mahan’s ideas become mandatory reading for politicians of the day •New generation of foreign policy makers [TR and Wilson] •Historic sense of Manifest Destiny - “White Man’s Burden” Asia Open Door Policy & China ~ In the 1890’s Russia, Japan, Great Britain, France and Germany had all established spheres of influence in China ~ Each country could dominate trade and investment within their sphere and shut out competitors ~ Sec. of State John Hay proposed the concept of an Open Door, by which all nations would have equal trading privileges in China. ~ No nation rejected his proposal and Hay declared all had accepted his Open Door Policy More Open Door ~ In 1900 the Boxers attacked foreign settlements and murdered dozens of Christian missionaries ~ U.S. troops participated in an international force that marched into Peking and quickly succeeded in crushing the Boxer Rebellion ~ Hay wrote a second note to imperialistic powers stating U.S. commitment to preserve China’s territorial integrity and safeguard “equal and impartial trade with all parts of the Chinese Empire”. New Diplomacy Teddy Roosevelt’s desire to establish the reputation of America as a World Power Monroe Doctrine and the Roosevelt Corollary Monroe Doctrine 1823 Latin America is off limits to Europe or anyone else. Stay out of our hemisphere! The Roosevelt Corollary1905 The U.S. will keep law & order in Latin America The US can intervene in our hemisphere whenever we feel it is in our interest. PANAMA CANAL 1904 The USA bought the rights to build the Panama Canal; the canal linked the Pacific & Atlantic Oceans Gave the US Gave the great influence in in in in Latin America TR as a Diplomat—AmericA’s extended role Treaty of Portsmouth (1905) --Imperialistic rivalry between Russia and Japan led to war which Japan was winning. --Japanese nationalists blamed the U.S. for not giving their country all that they wanted from Russia “Gentleman’s Agreement” (1908) --Japanese agree to limit emigration, CA changes school segregation laws Root-Takahira agreement (1908) --mutual respect for each nation’s Pacific possessions and support for the Open Door Policy Teddy’s “Big Stick” Policy ”Great White Fleet”—To demonstrate U.S. naval power Roosevelt sent a fleet of battleships around the world from 1907 – 1909, mostly to impress Japan Dollar Diplomacy—William Howard Taft Expansion depends on investors dollars rather than naval battleships Win-win—private business investment in China and Central America leads to stability in these areas while at the same time promote U.S. business interests Obstacle: Growing anti-imperialism here and abroad 1911—U.S. intervenes in Nicaragua’s financial affairs 1912—Civil War breaks out there and the Marines are sent to Nicaragua and stay until 1933 Lodge Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine, 1912 Henry Cabot Lodge’s resolution that said non-European powers, such as Japan, would be excluded from owning territory in the Western Hemisphere Offended Japan and angered Latin American countries Time to take a break for more bonus! Many people in 1941 said that “What did we do to the Japanese?? Why would they want to attack us?” What we are going to see is that there are many examples of where the Japanese feel disrespected by the U.S. Actually, they start during this time In this power point, you have seen some sources of tensions between the Japanese and the United States. Identify these sources. Moral Diplomacy—Woodrow Wilson REFORM in our international behavior U.S. would be the CONSCIENCE of the world Spread democracy, promote peace, condemn colonialism ANTI-IMPERIALISM---No Big Stick or Dollar Diplomacy Against self-interested imperialism The Philippines Congress passed Jones Act of 1916 1. Granted Full territorial status to Philippines 2. Guaranteed a bill of rights and universal male suffrage to Filipino citizens 3. Promised Philippine independence as soon as a stable government was established Puerto Rico Congress passed Jones-Shafroth Act in 1917 1. granted U.S. citizenship to all the inhabitants 2. Provided for limited self-government Conciliation treaties WJ Bryan negotiated treaties in which nations: 1. Submit disputes to international commissions 2. Observe a one-year cooling-off period before taking military action 3. Bryan arranged with Wilson's approval, 30 such conciliation treaties. Though Wilson did not live up to his principles when vital U.S. Interests were concerned: Latin America---kept Marines in Nicaragua, ordered troops into Haiti and the Dominican Republic in 1916 ---Rationale: necessary to maintain stability in the region and to protect the Panama Canal Mexico—Francisco Madero attempts democratic reforms but is overthrown, and assassinated, by General Victoriano Huerta ---Wilson refused to recognize Huerta and brought pressure against the new government