Lecture 2 - Personal.kent.edu
advertisement

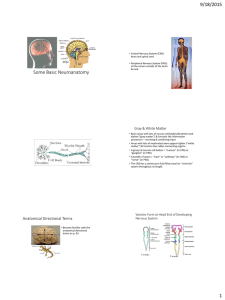
Physiological Psychology 41363 Outline 2 I. Review of last time II. Structure and function of the nervous system Nervous System 1. CNS - protected by: A. 3 protective membranes (meninges) 1. Dura mater 2. Arachnoid membrane 3. Pia mater B. CSF 1. Ventricles - lateral, 3rd, and 4th 2. Produced by choroid plexus 2. PNS - relay info to and from external receptors and CNS 3. Somatic NS - conscious movements 4. Autonomic NS - “self-governing” 5. Parasympathetic - saves energy 6. Sympathetic - uses energy Brain A.orientation lateral medial- rostralcaudaldorsalventralB. forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain, neural tube C. gray vs white matter D. convolutions 1. fissures 2. sulci (sulcus) 3. gyri (gyrus) E. 2 hemispheres I. Forebrain A. Cerebral cortex - thinking and mental processes: planning - left hemisphere deals with analysis of serial/sequential processes - right hemisphere is predominantly synthesis-oriented: perception of wholes -contralateral vs ipsilateral -corpus callosum: split brain patients 1. Lobes -frontal lobe - primary motor cortex -parietal - primary somatosensory cortex -temporal - primary auditory cortex -occipital - primary visual cortex -association cortex - integrates info from primary cortices 2. Broca’s area 3. Wernicke’s area B. Limbic system - emotion, motivation and learning/memory 1. Amygdala - anger, aggression, reproduction 2. Hippocampus - learning and memory formation 3. Septum - anger, fear C. Basal ganglia - control of movement D. Thalamus - conductor E. Hypothalamus - survival II. Midbrain A. Reticular formation - regulation of consciousness B. Superior and inferior colliculi - vision and hearing C. Substantia nigra - movement III. Hindbrain A. Cerebellum - coordinates and smooths movements B. Pons - relay station C. Medulla (oblongata) - heart rate, breathing, digestion, crossover Spinal cord - routes sensory and motor info to and from the brain I. Dorsal horn - sensory II. Ventral horn - motor III. Simple reflex Research Methodology I. Experimental ablation - lesion studies A. Producing brain lesions - surface lesions - subcortical regions - excitotoxic lesions - uses kainic acid - 6-hyroxydopamine - sham lesions -reversible lesions B. Stereotaxic surgery C. Determining pathways of communication 1. Anterograde labeling - PHA-L -immunocytochemical technology 2. Retrograde labeling - fluorogold D. How do we find out about the brain? 1. Electroencephalogram (EEG) 2. X-rays or angiograms 3. Computerized axial tomography (CAT) scan 4. Magnetic resonance imaging - (MRI) 5. Positron emission tomography (PET) 6. Functional MRI