Slide 1
advertisement

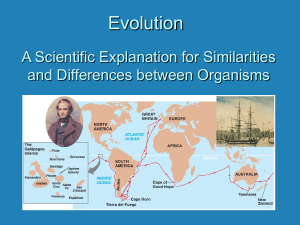
Chapter 15 Review Sheet How do fossils form? Buried in sediment Buried on ocean floor, swamp, mud etc… Tissue replaced by minerals Trapped in tree sap Where did Darwin collect much of his information? Galapagos Islands Darwin hypothesized that his finches probably evolved from: A common ancestor Process by which a population becomes better suited to its environment adaptation Evolution occurs because of Natural selection Organisms that are well suited for their environment that reproduce and pass on their traits do so by Natural selection What can happen to populations of the SAME species living in different places? Change as they become adapted to the new environment SAME structures are called homologous Example of a homologous structure from class Arm bones Human tailbone is an example of ________structure Vestigial ( a structure we no longer use) Wing of a bird and the wing of and insect are _________ structures. Analogous (evolve independently but have the same function) Accumulated differences in a population Divergent evolution When two or more species become more adapted over time to each other’s presence is coevolution When to species develop some of the same features even though they are NOT closely related Convergent evolution Any preserved trace of ancient life form fossil A species that has disappeared permanently extinct Short Answer You discover 4 new species of birds, each on a different island. Beaks are different. How can you explain the differences and similarities? (2 points) Why is competition among individuals of the same species so intense? (2 points)