Integumentary System Study Guide
advertisement

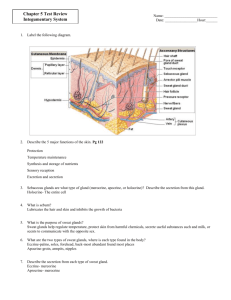
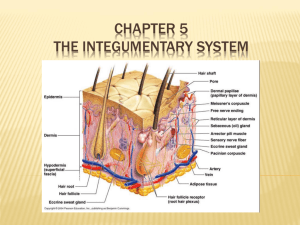
Integument Study Guide 1. List three locations where epithelial membranes are typically found within the human body. a. b. c. 2. Why are epithelial membranes considered a simple organ, while connective tissue membranes are only considered a tissue (and not an organ)? a. 3. List and briefly describe each of the three types of epithelial membranes. a. b. c. 4. List and briefly describe each of the three types of serous membranes. a. b. c. 5. What type of tissue would be found within synovial joints? a. 6. What are the 5 components of the integumentary system? a. b. c. d. e. 7. How much does the average human skin weigh? a. 8. Describe how your skin functions in the following situations: a. Mechanical Damage – b. Chemical Damage – c. Bacterial Damage – d. UV Radiation – e. Thermal Damage – f. Dessication – g. Thermal Regulation (Body temp homeostasis) – h. Excretion of Urea and Uric Acid – i. Sythesizing Vitamin D – 9. Define the following terms: a. Vascular – b. Avascular – c. Stratified Squamous Epithelia – d. Dense irregular connective tissue – 10. List and briefly describe each of the three layers associated with the skin. a. b. c. 11. Which of the above listed layers associated with the skin is considered subcutaneous? Why? a. 12. List and briefly describe each of the 5 layers of cells found within the epidermis. Begin with the deepest layer! a. b. c. d. e. 13. How long does it take the epidermis to completely replace itself? a. 14. When we look at another person, do we see living or dead cells (is the skin we see alive or dead)? a. 15. Where is thick skin found on the human body? How much thinker is it than thin skin? a. b. 16. Where is thin skin found on the human body? a. 17. How is a callus created? a. 18. What is keratin? Where is it produced? What does it do? a. 19. What is melanin? Where is it produced? What does it do? a. 20. A person of dark skin has more melanocytes or more active melanocytes than a person of light skin. 21. List three things that can happen to the skin due to excessive exposure to UV radiation. a. b. c. 22. What do each of the following cells of the epidermis assist with? a. Langerhans Cells – b. Merkel Cells – 23. List and briefly describe each of the 2 regions of the dermis. a. b. 24. In which layer do hair fibers, sweat glands, and oil glands begin? a. 25. Why do we have fingerprints? a. 26. Compare and contrast Meissner’s Corpuscles and Pacinian Corpusles. Consult your textbook or an online source for more thorough information. a. Meissner’s Corpuscles – b. Pacinian Corpuslces – 27. The hypodermis is highly vascular and highly composed of adipose (fat). Why does fat tissue need a large blood supply? a. 28. Compare and contrast Subcutaneous Injections and Intramuscular Injections. Consult your textbook or an online source for more thorough information. a. Subcutaneous Injections – b. Intramuscular Injections – 29. Describe how each the following the three pigments contribute to skin color. a. Melanin – b. Carotene – c. Hemoglobin – 30. Which locations of the body do not contain sebaceous glands? a. 31. List the characteristics of sebum? a. b. c. d. 32. Using the terms polar and non-polar, describe how secreting sebum onto the skin can prevent water loss through the skin. a. 33. How are pimples caused? a. 34. How many sudoriferous glands are found on the skin of each person? a. 35. List and describe the two main types of sudoriferous glands. Include the common locations of each. a. b. 36. Which branch of the central nervous system is responsible for a “cold sweat” – sympathetic or parasympathetic? 37. Why is sweating an ineffective way to cool your body on a very humid day? a. 38. Which areas of the body do not contain hair? a. 39. List the functions of hair. a. b. c. d. 40. How are “goose bumps” caused? a. 41. Why do people (and especially other animals) get goose bumps during a fight or flight response? a. 42. Why do people (and especially other animals) get goose bumps when they are cold? a. 43. Label the skin diagram using the following terms: Hair shaft, melanocytes, sebaceous gland, sweat gland, blood vessels, hair follicle, erector pili muscle, pacinian corpuscle, hypodermis, dermis, and epidermis. 44. How is the hair growth cycle affected in Male Pattern Baldness? a. 45. What pigment is responsible for hair color? a. 46. Explain how people have white or grey hair as they age. a. 47. How are stretch marks formed? (What happens anatomically?) a. 48. How are blisters formed? (What happens anatomically?) a. 49. List and describe each of the three types of burns? a. b. c. 50. List and describe the three types of skin cancers a. b. c.