Culture & Diffusion
advertisement

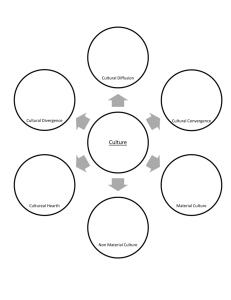
Part 2 Culture region: area within a particular system Culture trait : single attribute of a culture Culture Complex: all the cultural traits that exist with a cultural region Culture realm: multiple culture regions grouped together Cultural hearth: sources or birthplaces of a civilization The process of dissemination, the spread of an idea or innovation from its source area to other areas 2 Types of Diffusion Expansion diffusion Relocation diffusion In expansion diffusion, an innovation or idea develops in a hearth and remains strong there while spreading outward Types of Expansion Diffusion 1) Contagious diffusion- nearly all adjacent individuals are affected 2) Hierarchical diffusion- idea or innovation spreads by passing first among the most connected people or places 3) Stimulus diffusion- cultural adaptation is created as a result of the introduction of a cultural trait from another place Involves the actual movement of individuals who have already adopted the idea or innovation, and who carry it to a new, perhaps distant, locale, where it proceeds to remain strong Which one is Contagious? Relocation? Hierarchical? Environmental determinism- holds that human behavior, individually and collectively, is strongly affected by (even controlled or determined by) the physical environment….suggest that the climate is the critical factor in how humans behave Possibilism- argues that the environment merely serves to limit the range of choices available to a culture Sometimes called a uniform region A region that has striking similarities in terms of one or a few physical or cultural features Ex. Linguistic region- everyone speaks the same language Regional boundaries can be very simple or very complex Ex. Political boundaries are finite and well defined, cultural boundaries are fuzzy Also called nodal regions Areas that have a central place or a node that is a focus or point of origin that expresses some practical purpose Ex. Market areas The influence of this point is strongest in the areas close to the center, and the strength diminishes as distance increases from that point (distance decay) Tobler’s Law- states that all places are interrelated, but closer places are more related than further ones When the length of distance becomes a factor that inhibits the interaction of two places, its known as friction of distance Also called Vernacular region its based upon the perception or collective mental map of the region’s residents Ex. Dixie (America’s south) What is America’s south? -some define it as states of the Civil war, some as the number of country music bands, some as NASCAR races *No matter what is used to spatially define the regional concept, the reason tends to be a point of pride for residents ***Be careful with your vernacular definitions (there’s country music and NASCAR everywhere) Scale – the relationship of an object or place to the earth as a whole Scale can be thought of in 2 ways 1) map scale- describes the ratio of distance on a map and distance in the real world in absolute terms 2) relative scale- also known as scale of analysis; this describes the level of aggregation, which is the level at which you group things together for examination Large Scale Small Scale Local City County State Regional National Continental International