Membrane Structure and Function (PowerPoint) Northwest 2012
advertisement

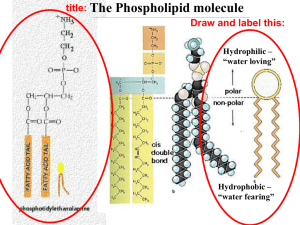
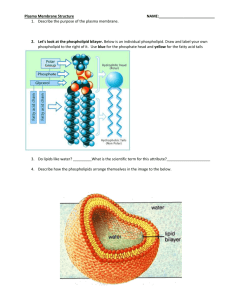
Team “Insane in the Membrane” Team members: Heather Addy, Anna Davis, Cindy Graham, Joan Marshall, Vesal Mahanian Membrane Structure and Function 26 July 2012 Learning Goals Understand why phospholipids spontaneously arrange into micelles and vesicles when mixed in water Identify the properties/structure of phospholipid bilayers make them selectively permeable. Collaborate with others to solve a problem Learn to communicate and defend a scientific argument based on experimental evidence After this session you will be able to… (1) (2) (3) Predict (and draw) the arrangements of phospholipids in an aqueous solution, based on their chemical properties Deduce the properties that govern membrane permeability of molecules from experimental data Evaluate whether different compounds can diffuse across a simple lipid bilayer based on polarity, size and charge. Foundations Previously we learned about the… Importance of intermolecular forces Relationship between polarity and hydrophobicity How functional groups influence the chemical properties of molecules Properties of water Oil and water don’t mix Oleic Acid (Lipid) Water Phospholipids are amphipathic Properties of Phospholipids If we mix phospholipids in water, how will they organize? In a group of 3, draw at least 2 arrangements of phospholipid molecules in water... 2 minutes Phospholipids spontaneously form micelles and bilayers in water Fatty acid chains aggregate together Phosphate-containing head groups associate with water Is this arrangement possible? What properties determine whether a molecule crosses a phospholipid bilayer? Small Group Activity In a recent experiment, the permeability coefficient of various molecules was determined Organize the molecules in order of permeability and consider what structural/chemical features contribute to their permeability 5 minutes Summative Assessment: #1 Which can pass through a membrane more readily? Why? #2 Summative Assessment: Answer #1 Vitamin B2: Water soluble, cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer because it’s large and polar Which can pass through a membrane more readily? Why? #2 #2 Vitamin E: Fat soluble, is able to pass through the phospholipid bilayer because it’s non-polar (looks like a fat) #1 Thank you! Supplemental Material Progesterone P=3.5x10E-4 cm/s O=O Oxygen P=42 cm/s Small Group Activity Cards Acetate P=1x10E-12 cm/s Acetic acid P=2x10E-2 cm/s Glycerol P=5x10E-5 cm/s Na + Glucose P=2x10E-7 cm/s Sodium ion P=1x10E-12 cm/s Water P=5x10E-2 cm/s