Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
advertisement

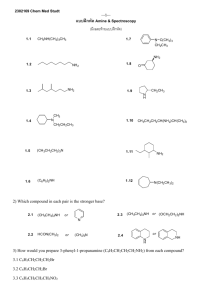
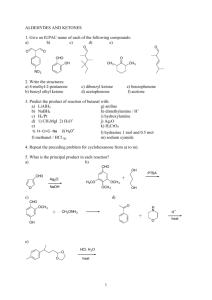
15.6 Reactions of Alcohols: A Review and a Preview Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Table 15.2 Review of Reactions of Alcohols Reaction with hydrogen halides Reaction with thionyl chloride Reaction with phosphorous trihalides Acid-catalyzed dehydration Conversion to p-toluenesulfonate esters New Reactions of Alcohols in This Chapter Conversion to ethers Esterification Oxidation Cleavage of vicinal diols 15.7 Conversion of Alcohols to Ethers Conversion of Alcohols to Ethers RCH2O CH2R H OH H+ RCH2O CH2R + H OH Acid-catalyzed Referred to as a "condensation" Equilibrium; most favorable for primary alcohols Example 2CH3CH2CH2CH2OH H2SO4, 130°C CH3CH2CH2CH2OCH2CH2CH2CH3 (60%) Mechanism of Formation of Diethyl Ether Step 1: •• CH3CH2O •• H OSO2OH H + CH3CH2O •• H + H – OSO2OH Mechanism of Formation of Diethyl Ether Step 2: H CH3CH2 +O •• H •• CH3CH2 + CH3CH2O •• H + • O •• • H H CH3CH2O •• H Mechanism of Formation of Diethyl Ether Step 3: CH3CH2 CH3CH2 + CH3CH2O •• CH3CH2O •• + •• H H •• •• OCH CH 2 3 H •• OCH CH 2 3 H + Intramolecular Analogue HOCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH via: H2SO4 130° •• •• O O (76%) H Reaction normally works well only for 5- and 6-membered rings. H O •• + H 15.8 Esterification Esterification O ROH + O H+ R'COR + R'COH condensation Fischer esterification acid catalyzed reversible H2O Example of Fischer Esterification O COH + CH3OH 0.1 mol 0.6 mol H2SO4 O COCH3 + H2O 70% yield based on benzoic acid Reaction of Alcohols with Acyl Chlorides O ROH + R'CCl O R'COR + High yields Not reversible when carried out in presence of pyridine. HCl Example CH3CH2 O OH + O2N CCl CH3 pyridine CH3CH2 O NO2 OC CH3 (63%) Reaction of Alcohols with Acid Anhydrides O O ROH + R'COCR' O R'COR + O R'COH analogous to reaction with acyl chlorides Example O O C6H5CH2CH2OH + F3CCOCCF3 pyridine O C6H5CH2CH2OCCF3 (83%) 15.9 Oxidation of Alcohols Oxidation of Alcohols Primary alcohols O O RCH2OH RCH RCOH Secondary alcohols OH O RCHR' RCR' from H2O Typical Oxidizing Agents Aqueous solution Mn(VII) Cr(VI) KMnO4 H2CrO4 H2Cr2O7 Aqueous Cr(VI) H FCH2CH2CH2CH2OH OH K2Cr2O7 H2SO4 H2O Na2Cr2O7 H2SO4 H2O O O FCH2CH2CH2COH (74%) (85%) H Mechanism •• O H •• H C O HOCrOH OH O H O C O CrOH O Involves formation and elimination of a chromate ester. C O Nonaqueous Sources of Cr(VI) All are used in CH2Cl2 Pyridinium dichromate (PDC) (C5H5NH+)2 Cr2O72– Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) C5H5NH+ ClCrO3– Example: Oxidation of a Primary Alcohol with PCC ClCrO3– +N H PCC CH3(CH2)5CH2OH O CH3(CH2)5CH CH2Cl2 (78%) Example: Oxidation of a Primary Alcohol with PDC (CH3)3C CH2OH PDC CH2Cl2 O (CH3)3C CH (94%) 15.10 Biological Oxidation of Alcohols Enzyme-catalyzed CH3CH2OH + NAD + alcohol dehydrogenase CH3CH O + NAD H + H+ Figure 15.2 Structure of NAD+ nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (oxidized form) Enzyme-catalyzed H O CNH2 CH3CH2OH + + N R + H+ Enzyme-catalyzed H H O CH3CH O CNH2 •• N R 15.11 Oxidative Cleavage of Vicinal Diols Cleavage of Vicinal Diols by Periodic Acid C HO HIO4 C OH C O + O C Cleavage of Vicinal Diols by Periodic Acid CH3 CH HO CCH3 OH HIO4 O CH (83%) O + CH3CCH3 Cyclic Diols are Cleaved OH HIO4 O O HCCH2CH2CH2CH OH