Session 3 Sheet
advertisement

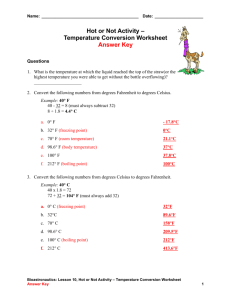
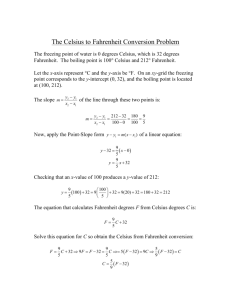
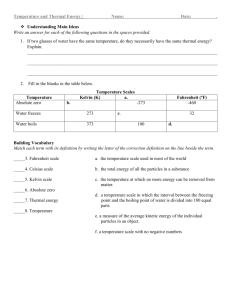
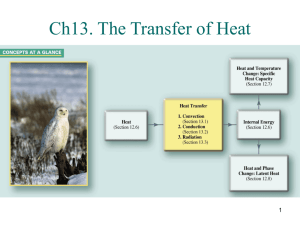
Physical Science Session 3 Sheet To receive full credit on a session sheet you must define all vocabulary terms in their entirety, record all essential questions in your science journal and provide an answer for each. Vocabulary: Look up each vocabulary term on discoveryeducation.com. Watch the video and animation, if one is present. Following this please record the definition from discoveryeducation.com within your science journal Celsius, conduction, conductor, convection, energy, Fahrenheit, heat, infrared, insulation, kinetic energy, radiation, temperature, thermal energy, thermometer, convection, thermal energy, current, radiant energy, infrared, spectrum, conduction, conductor, heat, thermal energy ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Please go to the following sections and write down the essential questions and provide a thoughtful answer for each. Please record all these questions within your science journal: Heat and Temperature: • What is the difference between heat and temperature? • What happens to the molecules of a substance when heat is added to it? • Which types of measurements are used to describe quantities of heat and temperature? • How can heat be transferred from one object to another? Convection: • How are liquids and gases affected by heat? • How is thermal energy transferred through liquids and gases? Conduction: • How does heat travel by conduction? • What is thermal equilibrium? Radiation • What is radiant energy? • How does heat travel as radiant energy? NEED TO KNOW HOW TO CALCULATE: Fahrenheit Fahrenheit is a thermodynamic temperature scale, where the freezing point of water is 32 degrees Fahrenheit (°F) and the boiling point 212°F (at standard atmospheric pressure). This puts the boiling and freezing points of water exactly 180 degrees apart. Therefore, a degree on the Fahrenheit scale is 1/180 of the interval between the freezing point and the boiling point of water. Absolute zero is defined as -459.67°F. A temperature difference of 1°F is the equivalent of a temperature difference 0.556°C. ºC =ºF – 32/1.8000 Celsius The Celsius scale is an interval system but not a ratio system, meaning it follows a relative scale but not an absolute scale. This can be seen because the temperature interval between 20 °C and 30 °C is the same as between 30 °C and 40 °C, but 40 °C does not have twice the air heat energy of 20 °C. A temperature difference of 1 deg C is the equivalent of a temperature difference 1.8°F. Kelvin Based upon the definitions of the Centigrade scale and the experimental evidence that absolute zero is -273.15ºC ºF =(ºK - 273.15)* 1.8000+ 32.00 GREAT WEBSITES TO VISIT TO EXPAND YOUR KNOWLEDGE: https://www2.chemistry.msu.edu/faculty/reusch/virttxtjml/Spectrpy/InfraRed/infrared.htm http://www.chem.ucla.edu/~webspectra/irintro.html http://infrared.als.lbl.gov/BLManual/IR_Interpretation.pdf http://www.jagerpro.com/faq.aspx