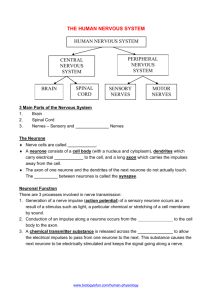
Integumentary and Nervous
advertisement

Homeroom Read or complete any missing assignments! Complete the “Body’s Communication” worksheet in your notebook. Write the Stimuli in your notebook, then write how you would respond to each one. Warm-up • What does the skin of an apple do for the apple? • What does it prevent? Think about an apple. • • • • Consists of 3 things: Skin Hair Nails Integumentary System • Flat sheets of cells • Protects your body from outside materials skin • • • • Repels water Guards against infection Helps maintain homeostasis Senses the environment vital functions of skin The Skin • Sweat glands help control body temperature • Present almost everywhere • Oil glands give moisture to skin and hair • Keep liquids from entering Sweat and oil glands • Skin grows at the base of the epidermis • Skin cells grow and divide • Dead cells are brushed off Healing and Growth • Gives the brown color in the skin • Made by melanocytes in the epidermis Melanin • Your skin contains sensory receptors • Tell you when something is hot or cold • Part of your nervous system • • • • • • 5 types Heat Cold Pain Touch Pressure Sensory Receptors • Stimulus: Change to your environment that you react to. • Could be any of your 5 senses Nervous System • Consists of the brain and spinal cord • Communicates with the rest of the nervous system through electrical signals sent through nerve cells. Central Nervous System • Nerve cells • Brain contains at least 10 billion Neuron • Main pathway for information • Connects the brain and nerves throughout the body. • 31 pairs of nerves extend from the spinal cord. • It weighs a little over a pound • 17 inches long Spinal Cord • Nerves found throughout the body • Sensory Nerves: receive information from the environment (hot or cold) • Motor Nerves: send signals to your muscles that allow you to move • Voluntary and involuntary! Peripheral Nervous System • Autonomic: controls the movement of the heart, the smooth muscles in the stomach, the intestines, and the glands. • Voluntary: Monitors movement that can be controlled consciously. Autonomic vs. Voluntary • Read over all directions on the Lab. • With your piece of candy, fill out the table using your senses. • Complete the 2 questions on the bottom of the page. Candy Lab