CONVECTIONGOWITHTHEFLOW
advertisement
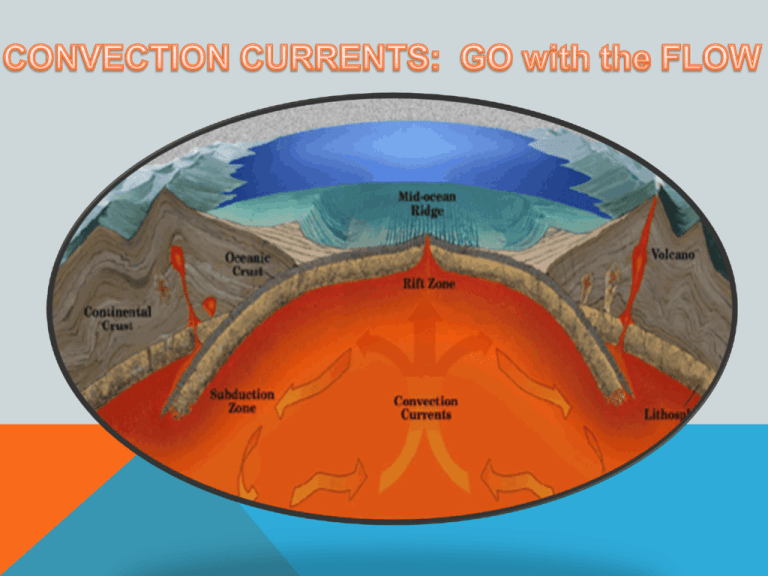
• A temperature increase produces a decrease in the density of a substance • Density is defined as mass divided by volume (D=M/V) • Less dense substances float on more dense substances • Convection is defined as the circulation of a fluid at a non-uniform temperature due to the variation of its density and the action of gravity COLD, HIGHER DENSITY Cool descending current Hot rising current HOT, LOWER DENSITY Cool descending current Circular Paths of Food Coloring Gel Created by Convection Currents in Heated Water • Water at the bottom is warmer and less dense; food coloring gel rises • Water at the top is cooler and denser; food coloring gel sinks A radiator in your home or classroom uses the principle of convection currents as a heat source. • A bulb at the bottom of the lamp heats up the two liquids in the lamp • One liquid expands more than the other, becomes less dense and rises • The liquid cools at the top; becomes denser; and sinks • As long as the lamp is on, this cycle continues • Lava lamp serves a model for internal processes occurring in the Earth’s mantle producing convection currents causing tectonic plate movement HOW DO TECTONIC PLATES MOVE? • Heat for convection comes from deep within the earth • Two main sources: radioactive decay and residual heat • Primary mechanism for mantle convection is seafloor spreading • “Ridge Push” caused by magma intrusion also provides additional force • “Slab Pull” caused by subduction now considered to be major driving force Convection Current crust mantle Hot material rises, cooler material sinks, creating a Convection Current or Cell RIDGE “RIDGE PUSH” and “SLAB PULL” LET’S REVIEW Continents are continuously slowly moving on the Earth’s crust --- only a few cm a year. Convection currents are what move the Earth’s continents. THE END