Weeks 1 and 2 Checklist LO's Blood on the road
advertisement
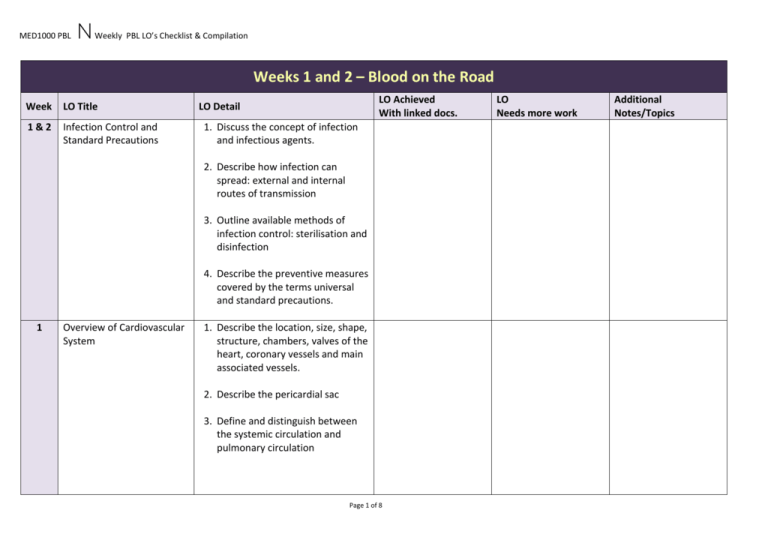
MED1000 PBL N Weekly PBL LO’s Checklist & Compilation Weeks 1 and 2 – Blood on the Road Week LO Title 1&2 Infection Control and Standard Precautions LO Achieved With linked docs. LO Detail 1. Discuss the concept of infection and infectious agents. 2. Describe how infection can spread: external and internal routes of transmission 3. Outline available methods of infection control: sterilisation and disinfection 4. Describe the preventive measures covered by the terms universal and standard precautions. 1 Overview of Cardiovascular System 1. Describe the location, size, shape, structure, chambers, valves of the heart, coronary vessels and main associated vessels. 2. Describe the pericardial sac 3. Define and distinguish between the systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation Page 1 of 8 LO Needs more work Additional Notes/Topics MED1000 PBL 1&2 N Weekly PBL LO’s Checklist & Compilation Anatomy of the Arterial and venous system Basic Anatomical Structures 1. Describe the structure of a blood vessel 2. Describe the different types of arteries, capillaries and veins 3. Trace the general route usually taken by the blood from the heart, to the systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation and then returning to the heart. 4. Describe the structure and special function of the portal system of circulation. Surface & Functional Anatomy; be able to 1. Locate and palpate (using surface landmarks) the major arterial pulses in the upper and lower limbs and the common carotid artery. 2. Locate the external and internal jugular veins. 4. Locate common sites used for venepuncture. Page 2 of 8 MED1000 PBL 1&2 N Weekly PBL LO’s Checklist & Compilation Homeostasis in the Cardiovascular System 1. Discuss the principle of homeostasis in the maintenance of physiological parameters such as body temperature, blood pressure, acid-base balance, etc 2. Explain the concepts of blood pressure [BP], blood flow and their importance in homeostasis. 3. Define Total Peripheral Resistance, and the relationship between TPR, mean BP and cardiac output [CO] 4. List and describe the determinants of blood flow in a tissue (autoregulation including functional hyperaemia, sympathetic nervous innervation of resistance vessels, hormonal influences on resistance vessels) 5. List and briefly describe the physiological mechanisms which defend against changes in arterial blood pressure 6. Describe how a reduction in blood volume, peripheral resistance or the efficiency of the heart as a pump, may lead to Page 3 of 8 MED1000 PBL N Weekly PBL LO’s Checklist & Compilation reduced cardiac output and tissue perfusion. 1&2 Cardiac Cycle & Cardiac Output 1. Identify systole and diastole in traces of blood pressure, ventricular pressures or heart sounds 2. Sketch the pressure changes in the aorta, left ventricle and central veins during the cardiac cycle 3. Indicate the time of valve events on graphs of the cardiac cycle 4. Define cardiac output and the relationship to stroke volume and heart rate 5. Sketch a graph of, and explain, the relationship between cardiac filling and cardiac output (FrankStarling Principle) 6. List and explain the 4 determinants of cardiac output 7. Describe the effect of altered inotropic state on the FrankStarling graph. Page 4 of 8 MED1000 PBL 1&2 N Weekly PBL LO’s Checklist & Compilation Shock 1. Classify the causes of shock into broad functional groups 2. Identify the signs and symptoms of shock List the sequence of clinical signs that appear as a patient continues to bleed 3. Describe the time-line of the changes, in particular defining the compensatory mechanisms appearing in progressive hypovolaemia and the change in signs as compensation fails 7. Be aware of the positive feedback of progressive damage in irreversible shock. Describe the role of the autonomic nervous system in the body's response to shock. 1&2 First Aid 1. Review senior first aid skills, including cardiopulmonary resuscitation and be able to demonstrate basic life support. 2. Understand the principles of first aid as applied in burns, head injuries, spinal injury and bleeding lacerations. Page 5 of 8 MED1000 PBL 1&2 N Weekly PBL LO’s Checklist & Compilation Public Health Perspective on Injury 1. Apply a population and public health framework to the issue of injury. 2. Outline the principles of effective injury prevention. 3. Identify effective interventions to reduce the number and severity of motor vehicle crashes and the severity of injury. 4. Outline the impact of injury on the health care system and society in terms of acute care and rehabilitation. 1&2 Community and Health Impact of Alcohol 1. Describe the social, health and economic impact of alcohol on the community. 2. Describe the relationship between the epidemiology of alcohol consumption and the incidence of motor vehicle crashes and injury. 1&2 Medical Law 1. Understand broad principles of the Australian legal system as it pertains to medical practice (Include key state differences). Page 6 of 8 MED1000 PBL N Weekly PBL LO’s Checklist & Compilation 2. Describe the categories of Australian law relevant to medical practice. 3. Be able to explain the ethical basis for medical law. 8. Explain how the inter-related fields of ethics and law provide a context for medical practice. 1&2 Duty of Care 1. Understand the concept of duty of care (as per Medical Board of Australia), considering physical, emotional and psychological aspects. 2. Demonstrate an understanding of how basic ethical and legal concepts inform the medical duty of care: 1. sympathy, compassion, care, need, harm 2. autonomy, beneficence consent, medical necessity 3. duty of care (definition: as per Medical Practice Act of relevant state). 4. standards of care, negligence. 5. duty of care in emergencies. Page 7 of 8 MED1000 PBL 2 N Weekly PBL LO’s Checklist & Compilation Standard precautions 1. Introduce and practice universal safety precautions in the clinical environment 2. Practice Hand-washing and Aseptic technique 2 Principles of Fluid Replacement 1. Outline the general principles of fluid balance management in hypovolaemic shock due to blood loss. 2. State the physiological objectives of fluid replacement with particular regard to blood pressure, heart rate and tissue perfusion. 3. Describe and compare the types of intravenous fluid available and their mechanism of action. Page 8 of 8