root word
advertisement

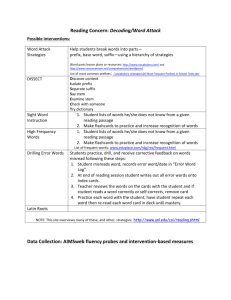
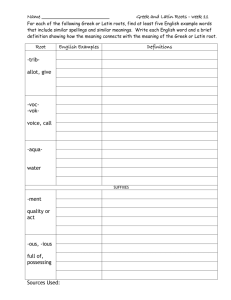
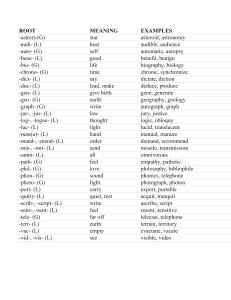
Affix- a word element, such as a prefix or a suffix, that occurs before or after a root or base word to modify its meaning. Root- the form of a word after all affixes are removed; meaning: base, root, stem, theme What are roots and root words? Many English words are formed by taking basic words and adding combinations of prefixes and suffixes to them. A basic word to which affixes (prefixes and suffixes) are added is called a root word because it forms the basis of a new word. The root word is also a word in its own right. For example, the word lovely consists of the word love and the suffix -ly. In contrast, a root is the basis of a new word, but it does not typically form a stand-alone word on its own. For example, the word reject is made up of the prefix re- and the Latin root -ject, which is not a stand-alone word. Understanding the meanings of the common word roots can help us deduce the meanings of new words that we encounter. Root Meaning Example -auto- (Greek) self Automatic, autopsy -bio- (Greek) life Biology, biography -audi- (Latin) hear Audible, audience -dict- (Latin) say Diction, dictate -duc- (Latin) lead,make Deduce, produce -geo- (Greek) earth Geography, geology -terr-(Latin) earth Territory, Terrain -graph- (Greek) write Autograph, graph -mand-, -mend- (Latin) order Recommend, demand -path- (Greek) feel Empathy, pathetic -sens-, -sent- (Latin) feel Resent, sensitive -vid-, -vis- (Latin) see Visible, video Parts of an Affix: Prefix- an element placed at the beginning of a word to adjust or qualify its meaning. Example: De-, non-, re-, un-. Can be used in words such as: decomposition, nonrefundable, restart, and unlikely. Suffix- an element placed at the end of a word to form a derivative, frequently one that converts the stem into another part of speech. Example: -ness, -less, -ian, -ology Can be words such as: viciousness, speechless, magician, biology A PREFIX is a letter or a group of letters attached to the beginning of a word that partly indicates its meaning. For example, the word prefix itself begins with a prefix--pre-, which generally means "before.“ Be careful: some prefixes (such as in-) have more than one meaning (in this example, "not" and "into"). Prefix Meaning Example Auto- self Autopilot, Autobiography Com-, Con- with Companion, Contact De- off, away from Devalue, denial Mis- wrong Misunderstand, Misprint Re- again, back Retake, retreat Un- not, opposite Unattractive, unusual Mono- one Monogamy, Monotonous Omni- all, every Omniscient, Omnify A SUFFIX is a letter or a group of letters attached to the end of a word to form a new word or to alter the grammatical function of the original word. For example, the verb read can be made into the noun reader by adding the suffix -er; read can be made into the adjective readable by adding the suffix -able. Suffix Meaning Example -ance, -ence state of quality of Defiance, eminence -able can be done Unable, readable -est most Oldest, greediest -ic, -ical pertaining to Musical, mythic -ive having the nature of Productive, creative -er more, one who Reader, slower -less without Useless, fearless -y characterized by Sleepy, needy -logy study, theory Psychology, biology To sum it all up Many of our words come to us from Greek or Latin. They don’t come to us complete; they come in parts. These parts are called Roots and Affixes. There are two different kind of affixes: Prefixes and Suffixes. The part at the beginning of a word is a prefix. The part in the middle is the root or root word. The part at the end is the suffix. Put it all together: Put the prefixes, roots, and suffixes together and you end up with words. Keep in mind that not all words have all three parts. Some simply have a prefix and a root. Others, just a root and suffix.