Topic 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells
advertisement
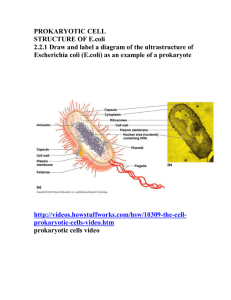
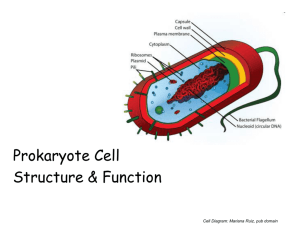
Topic 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells Assessment Statements: 2.2.1 Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of Escherichia coli (E. coli) as an example of a prokaryote 2.2.2 Annotate the diagram from 2.2.1 with the functions of each named structure. 2.2.3 Identify structures from 2.2.1 in electron micrographs of E. coli 2.2.4 State that prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission Introduction to Prokaryotes Prokaryotic Cell Structure Annotate the diagram Cell Membrane Controls passage of materials into and out of the cell All cells have a cell membrane Cytoplasm Fluid portion of all cells Location of cellular metabolism Ribosomes Float freely in the cytoplasm of all cells Smaller in prokaryotes (70s) The site of protein synthesis. Nucleoid The glob of DNA in all prokaryotic cells Still a double helix Ends come together to form a circle Not wrapped around proteins as in eukaryotic cells (termed “naked DNA”). Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Chromosome Prokaryote DNA double helix Eukaryote Plasmid A small circle of DNA found in some prokaryotes that exists and replicates independently of the main DNA in the nucleoid. Often contain genetic instructions for resistance to antibiotics (antibiotics are chemicals that kill bacteria) Some Prokaryotes have a cell wall Gives shape, support and protection to the plasma membrane and cytoplasm of the cell. Eubacteria wall made of peptidoglycan* (protein-sugar molecules). Flagellum (flagella) Some bacteria have one or more Used for motility. Pili Short fibers projecting from the cell wall found on some bacteria. They may help the bacteria cling to surfaces. Capsule (or slime layer) A special mucus-like protective coating found on some disease-producing bacteria. Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane bound organelles Reproduction in Prokaryotes Binary Fission Reproduction in Prokaryotes Prokaryotes reproduce by binary fission “division in half” Type of asexual reproduction The cell replicates its genetic material The cytoplasm divides by cytokinesis Two identical daughter cells are produced (unless mutation occurs) Review Something interesting to finish...