Barron v Baltimore
advertisement

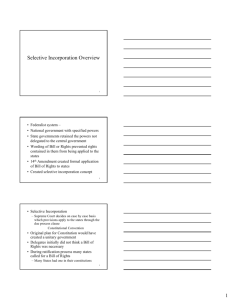
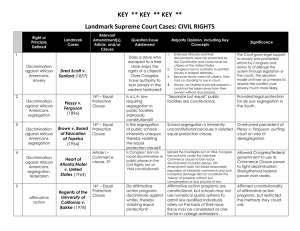
Bill of Rights First order of business for new government Compromise between Federalists and AntiFederalists James Madison author Received hundreds of suggestions Submitted 19 to Congress Congress proposed 12 to states States ratified 10 in 1791 • Ratio state pop to # rep in House (6000) • Congressional pay • Greater concerns than Bill of Rights • Madison feared legislative power of the states • Two suggestions to Congress – Unlimited veto power over all state laws – Joint executive-judicial council of revision • Access merit of state laws under review • Limited veto over national legislation • Benefits outweighed damage to separation of powers • Better safeguard of liberty than a Bill of Rights • When proposing amendments to Congress, Madison asked “would the people not be equally grateful if these ‘essential rights’ were secured against the state as well as the national government?” – House agreed, Senate disagreed • Barron v Baltimore 1833 – Supreme Court ruled Bill of Rights limited only the actions of the US Government and not those of the states “Congress shall make no law . . .” Selective Incorporation - p.163 • Supreme Court decided on a case-by-case basis, which provisions of the Bill of Rights to apply to the states through the due process clause Key case: Palko v. CT (1937) • Court rejected total incorporation • Established standard for selective incorporation – Rights rooted in tradition, implicit in the concept of ordered liberty Equal Protection Clause of the 14th Amendment Barron v Baltimore not challenged until the 14th amendment was ratified. . . . No state shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any state deprive any person of life, liberty, or property without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the law. Due Process Clause of the 5th & 14th Amendments • Guarantee to individuals a variety of rights ranging from economic liberty to criminal procedural rights to protection from arbitrary government action. • 1897 government began to hold states to a substantive due process standard whereby states had the legal burden to prove that their laws were a valid exercise of their power to regulate the health, welfare, or public morals of their citizens. 14th Amendment • Ensures that no individual state may deprive a person of his/her constitutional rights and freedoms: Privileges & Immunities Clause • Or deprive him/her of life, liberty or property without notice and hearing: Due Process Clause • Or treat one person differently from another simply because he/she is a member of a certain class: Equal Protection Clause.