Chapter 4 Powerpoint (Tissues)
advertisement

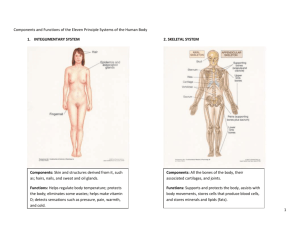
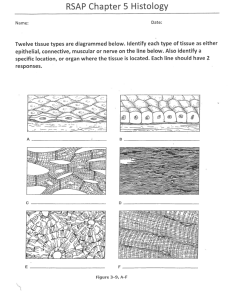
Chapter 4 Tissues 4 Types of Tissue Histology- study of tissues • 1. Epithelial- covers exposed surfaces, lines internal passageways and chambers, & forms glands • 2. Connective- fills internal spaces, provides structural support, transports materials within the body, & stores E reserves • 3. Muscle- contraction of (body, heart, hollow organs) • 4. Neural- carries information in the form of electrical impulses 1. Epithelial Tissue • Cells bound closely together • Polarity- has an exposed (apical) surface & attached (basal) surface • Has a basement membrane • nonliving layer because it is avascular lacks blood vessels • Gets nutrients from diffusion or absorption • Readily regenerates using stem cell divisions • injury heals fast Epithelial Tissue F(x): • Used for protection, secretion (glands), absorption, excretion • Extremely sensitive- large sensory nerve supply • Specialized: • Movement of fluids over layer- lubrication & protection • Movement through layer- control permeability • Produce secretions • Microvilli- on epithelium that line internally • Cilia- escalator to move something (mucus), respiratory tract Integrity • Intercellular connections- attached to one another • Cell Adhesion Molecules (CAMs)transmembrane proteins that connect large areas of opposing plasma membranes • Tight Junction- proteins lock plasma membrane tightly together • Adhesion belt- binds to neighbors • Keep things in a lumen/prevent diffusiondigestive enzymes don’t reach basal layer • Gap Junction- held together by transmembrane proteins called connexons • Allow small molecules & ions to pass (muscle cells) • Communication b/w cells • Desmosome- CAMS & proteoglycans • Resist stretching & twisting • Found in layers- why you peel instead of powder • 1. Spot- small discs connected to bands of intermediate filaments • 2. Hemidesmosomes- ½ spot, anchor to underlying tissue Arrangement & Shape of Cells • A. Simple- single layer • B. Pseudostratified- appears to have multiple layers but doesn’t • C. Stratified- 2 or more layers • A. Squamous- thin floor tiles • B. Cuboidal- cubes • C. Columnar- columns • D. Transitional- changes, flat>cuboidal Types of Simple Epithelium Glandular Epithelium • Gland- cell or group of cells that secrete • Endocrine- directly to blood (hormones) • Exocrine- onto surface of a covering or lining, into ducts • Ex: mucus, sweat, oil, saliva, earwax • Types of Exocrine: • Modes of secretion: • 1. Merocrine- release fluids by exocytosis • *most are this • Ex: salivary & sweat • 2. Apocrine- lose small portions by secretion • Ex: mammary glands • 3. Holocrine- cell bursts & is destroyed • Ex: sebaceous- oil gland of skin (why your hair is greasy) • Types of Secretions: • Serous glands- watery with enzymes • Ex: Parotid salivary glands • Mucous glands > mucus (mucin & H2O) < Note: spellings • Ex: sublingual salivary, submucosal of small intestine • Work to lubricate, protect, and trap foreign particles • Mixed > both • Ex: submandibular salivary Exocrine Gland Structure • Unicellular Multicellular • Only are: • Simple: 1 duct that does not divide • Compound: duct divides Mucous (Goblet) cells > mucins 2. Connective Tissue • 3 basic components: • Specialized cells • Extracellular protein fibers • Ground substance-fluid Last 2- Matrix 2. Connective Tissue F(x): • Structural framework • Transports fluids • Protect organs • Supporting, surrounding, & interconnecting other types of tissue • Storing E- triglycerides • Defends body from invaders Extra info: • Most abundant tissue in the body • Not found on the surface of the body • Very well vascularized (blood vessels) except tendons, ligaments, & cartilage = harder to heal • Has a nerve supply except cartilage • Has extracellular matrix-nonliving substance Cell types • A. Fibroblast-most common, secrete proteins to make fibers • B. Mast- produce histamine, react to injury or infection • C. Macrophages- can move around in order to clear foreign particles • D. Plasma-secretes antibodies • E. Adipocytes-fat • F. White blood cells- immune system • Matrix- between cells, supports cells, binds cells together Fibers • A. Collagen- strong, resists pulling • Ex: bone, cartilage, tendons, ligaments • B. Elastic- can stretch & return • Ex: skin, blood vessels, lungs • C. Reticular- support & strength • Ex: soft organs • Mesenchyme- embryonic connective tissue • Stem cells give rise to all other connective tissue • Mucous connective tissue (Wharton’s Jelly)- found in many parts of embryo Types of connective tissue • 1. Areolar/Loose- strength, elasticity • Ex: makes up basement membrane, blood vessels, packages organs • 2. Adipose-(fat) • insulation, energy reserve • Deep to skin & around heart & organs • 3. Reticular • Supporting framework of spleen & lymph nodes, filters & removes old blood cells • Liver, spleen, red bone marrow • 4. Dense Regular • Strong attachment • Tendons, ligaments • 5. Dense Irregular • Strength • Dermis of skin, fibrous capsules in joints Cartilage-3 types Chondrocytes-cartilage cells • 6. Hyaline • Smooth surface for movement at joints, flexibility • ends of long bones, ribs, trachea, nose • 7. Elastic • Support & shape • External ear, larynx • 8. Fibrocartilage • Support (very tough) • Intervertebral discs, knee, pubic • 9. Bone/Osseous- protection of other organs, structure, stores minerals & fat, makes new blood in red marrow • Bone cells sit in cavities called lacunae and are surrounded by layers of matrix made of calcium • Haversian System • Canal-blood vessels & nerves • Lacuna-space with a bone cell (osteocyte) • Lamellae- layers • Canaliculi- canals for nutrients & wastes • 10. Blood • Transports gases, nutrients, & wastes • Red & white cells in plasma 3. Muscular tissue • Contracts & shortens to produce movements • 1. Skeletal • Motion, posture, heat • Attached to bones by tendons • Voluntary, striated (bands), multinucleate, fibers don’t branch • 2. Smooth • Motion (constriction & contraction) • Blood vessels, airways, stomach, intestines, bladder, uterus • involuntary, single nucleus, spindle-shaped cells • 3. Cardiac • Pumps blood in heart • Involuntary, striated (bands), single nucleus, cylinder shaped cells • Intercalated discs- junctions that allow ions to pass from cell to cell= electrical impulse 4. Nervous Tissue • Regulates & controls body functions Membranes • 1. Mucous (mucosae)- lines a cavity that opens to the outside • Kept moist to reduce friction- releases mucus or uses urine/semen • 2. Serous- lines a cavity that doesn’t open to the outside • Parietal- inner surface of cavity • Visceral/Serosa- outer surfaces of organs • A. pleura-lungs • B. pericardium- heart • C. peritoneum- abdominal organs • 3. Synovial- where bones come together (Articulations) • Synovial fluid-lubricant in joints 4. Cutaneous- skin (ch5) Inflammation• impact, abrasion, distortion, chemicals, infection, extreme temps kills cells, damages tissue > Lysosomal enzymes > Necrosis- tissue destruction • Pus- accumulation of debris, fluid, dead cells • Abscess- accumulation of pus in an enclosed space • Causes redness, swelling, warmth, pain • If bacteria = infection Tissue repair: • Mast cells > release chemicals (histamine, heparin, prostaglandins) to stimulate inflammation (stimulate nerves=pain) • Blood vessels dilate to increase blood flow (warmth & redness), capillaries infuse plasma (swelling) > increases O2 & carries away waste • Phagocytes > eat debris & pathogens • Regeneration- repair by fibroblasts make scar tissue until tissue is returned to normal • Epithelia, connective (except cartilage), & smooth muscle heal well • Inflammatory Response Video #1 , Inflammatory Response Video #2, Inflammatory Response Video #3