Republicans - Waterford Union High School
advertisement

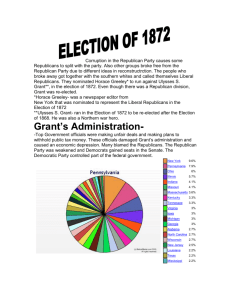
A.P. U.S. History “The Gilded Age” POLITICS: 1877-1894 • Problems of the underclass ignored • Instead, govt. had belief in laissez faire, and concentrated on only 3 issues: (1) tariff (2) money supply (3) civil service reform • House changes majority 5 times • Previous President Grant’s presidency plagued with corruption & scandal (“Grantism”) • Spoils system popular in the time period • 1873 stock market panic led to depression in 18731878 which had an impact on the period Major Parties Platforms and Bases of Support Republicans - New England, Upper Midwest, & Plains - small towns and rural areas - Protestants - Immigrants: British, Swedes, & Norwegians - African Americans - Grand Army of the Republic (veterans of the Civil War) - High tariffs - Temperance - English-only compulsory education Democrats - South & Lower Midwest - cities in the North - Catholics - Immigrants: Irish, Germans, & New Immigrants - Low tariffs - Anti-temperance - No English-only education Rutherford B. Hayes Republican 1877-1881 • Won Election of 1876 • Restores respectability to office of President • Attacked corrupt NYC customs house and fired Chester Arthur there • Sent in federal troops to end the B&O railroad strike • Munn v. Illinois (1877) ruling supported Granger laws • Greenback Party formed (1877) – supported expanded money supply, and benefits to farmers and industrial workers During the Hayes administration the Republican Party was split into two factions: Stalwarts - conservative faction - opposed to Hayes' efforts to reconcile with the South - opposed all forms of civil service reform, preferring spoils or patronage system Half-Breeds - moderate faction - backed Hayes' lenient treatment of the South - supported moderate civil James Garfield Republican 1881 • Won Election of 1880 • Half-Breed who won Republican nomination named Stalwart Chester Arthur as his running mate to keep party together • Garfield assassinated by an angry Stalwart who supported Garfield in hopes of gaining a govt. position in the spoils system • Arthur becomes President Chester Arthur Republican 1881-1885 • Became President when Garfield assassinated • Arthur has reputation for corruption from his days in NY political machine and the NYC custom house • Partly because Arthur was president the cause of civil service reform became a hot issue • Pendleton Civil Service Act (1883) – set up exams and standards for gaining federal govt. positions, and forbade workers from giving contributions to candidates Grover Cleveland Democrat 1885-1889 • Won Election of 1884 by gaining support of Mugwumps (republicans who switched sides as they felt that the Republican candidate Blaine was part of the corrupt spoils system) • Supporter of laissez faire • Wanted lower tariffs so federal budget surplus would drop, so Congress not tempted to add pork barrel projects to laws Grover Cleveland Democrat 1885-1889 • Wabash Railroad Strike (1885) • Haymarket Square Incident (1886) • vetoed a bill (1887) that gave pensions to all veterans even if their disability was unrelated to war • Wabash v. Illinois (1887) – ruling overturned Munn decision and prohibited states regulation of interstate RR trade • Interstate Commerce Act (1887) – overturned Wabash decision allowing federal govt. to regulate interstate transportation and trade Benjamin Harrison Republican 1889-1893 • gained $4 million “war chest” from industrialists upset with Cleveland’s low tariffs to win election in 1888 • Increased Civil War pensions by 43% • McKinley Tariff (1890) – pushed them to all-time high • Sherman Anti-Trust Act (1890) – first major attempt by federal govt. to regulate monopolies and trusts • Sherman Silver Purchase Act (1890) – U.S. to buy nation’s output of silver Benjamin Harrison Republican 1889-1893 • Southern and Northwestern Alliances merged in 1889 and ran candidates in 1890 midterm elections – wanted govt. action on behalf of farmers and workers, such as tariff reduction, graduated income tax, public ownership of RRs, & unlimited coinage of silver – Party split over whether it could operate within the Democratic Party (which Southerners wanted) Benjamin Harrison Republican 1889-1893 • Democrats won back control of Congress in the 1890 midterm elections as people were upset about Republican ties to big industry • People’s Party or Populist Party (1892) – took alliances platform and added political reforms like direct election of US Senators, initiative, recall, and referendum, and called for govt. warehouses for crops so they could be stored until prices rose • Homestead Strike (1892) Grover Cleveland Democrat 1893-1897 • Won Election of 1892 due to these factors: – Populists hurt by lack of Southern support as they kept traditional loyalties to Democratic Party and because the Populists ran a former Union general James Weaver – Republicans hurt by public reaction to labor violence (Homestead Strike) and McKinley Tariff – Cleveland grew more conservative and won back support of businessmen by opposing populism and by supporting the gold standard Grover Cleveland Democrat 1893-1897 • Panic of 1893 – caused by agricultural stagnation, slumping RR growth which led to crisis in the iron and steel industries, depletion of the gold supply, and depletion of govt. surplus due to veterans’ pensions and pork barrel projects – banks and RRs failed and stock prices dropped – led to the depression from 1893-1897 – Industrial unemployment 20-25% – Agricultural prices dropped 20% Grover Cleveland Democrat 1893-1897 • Sherman Silver Purchase Act repealed in (1893) to save the gold supply • Pullman Strike (1894) • In re Debs case (1895) • Bankers like J.P. Morgan loaned the govt. millions in exchange for discounted US bonds (which stopped the gold drain) Lower classes perceived a govt. and money class alliance that they couldn’t break: • Morgan loan for huge profits • Inability to pass lower tariff by Congress • Cleveland’s using force to end Pullman Strike • End of Sherman Silver Purchase Act angered farmers as it meant money supply would not grow Grover Cleveland Democrat 1893-1897 • Republicans gained seats in 1894 midterm elections winning both houses • Immigrants battered by depression throughout Cleveland’s presidency left the Democratic Party • Progressive movement within the Republican Party emerges and takes votes from the Populists • Democratic Party split over gold standard and silver advocates take control of the party’s platform William McKinley Republican 1897-1901 • Won Election of 1896 • William Jennings Bryan’s “Cross of Gold” Speech made adding silver to the money standard the major issue for the Democrats • Populists joined the Democrats giving up many of their platform goals to try to gain free silver • Republican McKinley’s victory meant end to the Populist Party William McKinley Republican 1897-1901 • By stressing one issue in the 1896 election the Democrats couldn’t appeal to factory workers and the urban middle class • Protestant revivalist preacher Bryan turned off immigrants who were Jews & Catholics and against his temperance stance • Defeat of Populism led to Republican reign of power (with exception of Wilson’s two terms) that lasted until FDR in 1932 William McKinley Republican 1897-1901 • Dingley Tariff (1897) – pushed rates to a new alltime high • Currency Act (1900) – officially committed the US to the gold standard • Populist movement ended, but a new reform movement called progressivism would emerge • Thorstein Veblen’s “Theory of the Leisure Class” – conspicuous consumption of the rich Progressive Reforms in the Gilded Age • Only three major pieces of progressive legislation were passed during the period – Pendleton Civil Service Act – Interstate Commerce Act – Sherman Anti-Trust Act