Unit 5: Quadratic Functions Vocabulary Monomial
advertisement

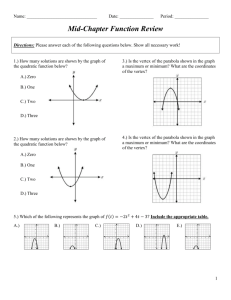
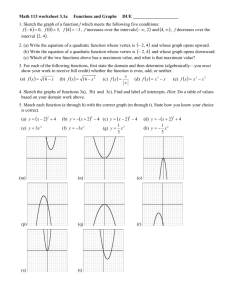
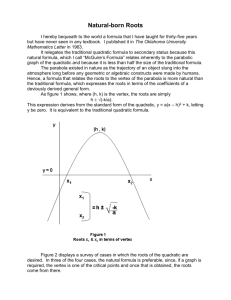
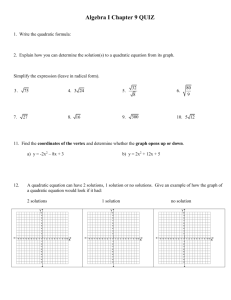
Unit 5: Quadratic Functions Vocabulary Monomial- is a number, a variable, or a product of numbers with whole-number exponents. Polynomial- is a monomial or sum of monomials Binomial- is a polynomial with two terms. Trinomial- is a polynomial that has three terms. Difference of Two Squares: a squared (multiplied by itself) number subtracted from another squared number. It refers to the identity a2 – b2 = (a + b) ( a – b) Perfect Square Trinomial: A trinomial that factors into two identical binomial factors. Quadratic Equation: An equation of degree 2, which has at most two solutions. Quadratic Function: A function of degree 2 which has a graph that “turns around” once, resembling an umbrella-like curve that faces either rightside up or upside down. This graph is called a parabola. Parabola- a U shaped curve vertex form of a quadratic function- is f(x) = a(x – h)2 + k, where a, h, and k are constants. The vertex is (h,k) Standard Form of a Quadratic Function: ax2+bx +c Vertex: The maximum or minimum value of a parabola, either in terms of y if the parabola is opening up or down, or in terms of x if the parabola is opening left or right. Axis of symmetry- is the line through the vertex of the parabola that divides the parabola into two congruent halves. Minimum value- When a parabola opens up, the y value of the vertex is the minimum Maximum value- When the parabola opens down, the y value of the vertex is the maximum. Quadratic model- a quadratic function that represents a real data set. Quadratic Regression- A statistical method to make a quadratic model for a given data set. Root/ zero of a function: The x-values where the function has a value of zero. Completing the Square: Completing the Square is the process of converting a quadratic equation into a perfect square trinomial by adding or subtracting terms on both sides. Perfect square- an expression that has two identical factors Discriminant of a quadratic equation: The discriminant of a quadratic equation of the form o ax + 2 2 bx+ c = 0, a ≠ 0, is the number b – 4ac. Nonlinear system of equations- a system in which at least one of the equations is non linear.